My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

How to Write an Outline for a Persuasive Speech, with Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Persuasive speeches are one of the three most used speeches in our daily lives. Persuasive speech is used when presenters decide to convince their presentation or ideas to their listeners. A compelling speech aims to persuade the listener to believe in a particular point of view. One of the most iconic examples is Martin Luther King’s ‘I had a dream’ speech on the 28th of August 1963.
In this article:
What is Persuasive Speech?
Here are some steps to follow:, persuasive speech outline, final thoughts.

Persuasive speech is a written and delivered essay to convince people of the speaker’s viewpoint or ideas. Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking people engage in the most. This type of speech has a broad spectrum, from arguing about politics to talking about what to have for dinner. Persuasive speaking is highly connected to the audience, as in a sense, the speaker has to meet the audience halfway.
Persuasive Speech Preparation
Persuasive speech preparation doesn’t have to be difficult, as long as you select your topic wisely and prepare thoroughly.
1. Select a Topic and Angle
Come up with a controversial topic that will spark a heated debate, regardless of your position. This could be about anything. Choose a topic that you are passionate about. Select a particular angle to focus on to ensure that your topic isn’t too broad. Research the topic thoroughly, focussing on key facts, arguments for and against your angle, and background.
2. Define Your Persuasive Goal
Once you have chosen your topic, it’s time to decide what your goal is to persuade the audience. Are you trying to persuade them in favor of a certain position or issue? Are you hoping that they change their behavior or an opinion due to your speech? Do you want them to decide to purchase something or donate money to a cause? Knowing your goal will help you make wise decisions about approaching writing and presenting your speech.
3. Analyze the Audience
Understanding your audience’s perspective is critical anytime that you are writing a speech. This is even more important when it comes to a persuasive speech because not only are you wanting to get the audience to listen to you, but you are also hoping for them to take a particular action in response to your speech. First, consider who is in the audience. Consider how the audience members are likely to perceive the topic you are speaking on to better relate to them on the subject. Grasp the obstacles audience members face or have regarding the topic so you can build appropriate persuasive arguments to overcome these obstacles.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
4. Build an Effective Persuasive Argument
Once you have a clear goal, you are knowledgeable about the topic and, have insights regarding your audience, you will be ready to build an effective persuasive argument to deliver in the form of a persuasive speech.
Start by deciding what persuasive techniques are likely to help you persuade your audience. Would an emotional and psychological appeal to your audience help persuade them? Is there a good way to sway the audience with logic and reason? Is it possible that a bandwagon appeal might be effective?
5. Outline Your Speech
Once you know which persuasive strategies are most likely to be effective, your next step is to create a keyword outline to organize your main points and structure your persuasive speech for maximum impact on the audience.
Start strong, letting your audience know what your topic is, why it matters and, what you hope to achieve at the end of your speech. List your main points, thoroughly covering each point, being sure to build the argument for your position and overcome opposing perspectives. Conclude your speech by appealing to your audience to act in a way that will prove that you persuaded them successfully. Motivation is a big part of persuasion.
6. Deliver a Winning Speech
Select appropriate visual aids to share with your audiences, such as graphs, photos, or illustrations. Practice until you can deliver your speech confidently. Maintain eye contact, project your voice and, avoid using filler words or any form of vocal interference. Let your passion for the subject shine through. Your enthusiasm may be what sways the audience.

Topic: What topic are you trying to persuade your audience on?
Specific Purpose:
Central idea:
- Attention grabber – This is potentially the most crucial line. If the audience doesn’t like the opening line, they might be less inclined to listen to the rest of your speech.
- Thesis – This statement is used to inform the audience of the speaker’s mindset and try to get the audience to see the issue their way.
- Qualifications – Tell the audience why you are qualified to speak about the topic to persuade them.
After the introductory portion of the speech is over, the speaker starts presenting reasons to the audience to provide support for the statement. After each reason, the speaker will list examples to provide a factual argument to sway listeners’ opinions.
- Example 1 – Support for the reason given above.
- Example 2 – Support for the reason given above.
The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement. This is where the speaker must sum up and tie all of their arguments into an organized and solid point.
- Summary: Briefly remind the listeners why they should agree with your position.
- Memorable ending/ Audience challenge: End your speech with a powerful closing thought or recommend a course of action.
- Thank the audience for listening.
Persuasive Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Walking frequently can improve both your mental and physical health.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to start walking to improve their health.
Central idea: Regular walking can improve your mental and physical health.
Life has become all about convenience and ease lately. We have dishwashers, so we don’t have to wash dishes by hand with electric scooters, so we don’t have to paddle while riding. I mean, isn’t it ridiculous?
Today’s luxuries have been welcomed by the masses. They have also been accused of turning us into passive, lethargic sloths. As a reformed sloth, I know how easy it can be to slip into the convenience of things and not want to move off the couch. I want to persuade you to start walking.
Americans lead a passive lifestyle at the expense of their own health.
- This means that we spend approximately 40% of our leisure time in front of the TV.
- Ironically, it is also reported that Americans don’t like many of the shows that they watch.
- Today’s studies indicate that people were experiencing higher bouts of depression than in the 18th and 19th centuries, when work and life were considered problematic.
- The article reports that 12.6% of Americans suffer from anxiety, and 9.5% suffer from severe depression.
- Present the opposition’s claim and refute an argument.
- Nutritionist Phyllis Hall stated that we tend to eat foods high in fat, which produces high levels of cholesterol in our blood, which leads to plaque build-up in our arteries.
- While modifying our diet can help us decrease our risk for heart disease, studies have indicated that people who don’t exercise are at an even greater risk.
In closing, I urge you to start walking more. Walking is a simple, easy activity. Park further away from stores and walk. Walk instead of driving to your nearest convenience store. Take 20 minutes and enjoy a walk around your neighborhood. Hide the TV remote, move off the couch and, walk. Do it for your heart.
Thank you for listening!
Topic: Less screen time can improve your sleep.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to stop using their screens two hours before bed.
Central idea: Ceasing electronics before bed will help you achieve better sleep.
Who doesn’t love to sleep? I don’t think I have ever met anyone who doesn’t like getting a good night’s sleep. Sleep is essential for our bodies to rest and repair themselves.
I love sleeping and, there is no way that I would be able to miss out on a good night’s sleep.
As someone who has had trouble sleeping due to taking my phone into bed with me and laying in bed while entertaining myself on my phone till I fall asleep, I can say that it’s not the healthiest habit, and we should do whatever we can to change it.
- Our natural blue light source is the sun.
- Bluelight is designed to keep us awake.
- Bluelight makes our brain waves more active.
- We find it harder to sleep when our brain waves are more active.
- Having a good night’s rest will improve your mood.
- Being fully rested will increase your productivity.
Using electronics before bed will stimulate your brainwaves and make it more difficult for you to sleep. Bluelight tricks our brains into a false sense of daytime and, in turn, makes it more difficult for us to sleep. So, put down those screens if you love your sleep!
Thank the audience for listening
A persuasive speech is used to convince the audience of the speaker standing on a certain subject. To have a successful persuasive speech, doing the proper planning and executing your speech with confidence will help persuade the audience of your standing on the topic you chose. Persuasive speeches are used every day in the world around us, from planning what’s for dinner to arguing about politics. It is one of the most widely used forms of speech and, with proper planning and execution, you can sway any audience.
How to Write the Most Informative Essay
How to Craft a Masterful Outline of Speech
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
- How to Order
Persuasive Speech
Persuasive Speech Outline
Persuasive Speech Outline - Samples, Format, and Writing Tips
12 min read
People also read
Making Persuasive Speech Writing Easy: Steps and Tips
Good Persuasive Speech Topics & Ideas for Debaters
200+ Motivational Speech Topics and Ideas To Inspire You (2024)
16 Best Persuasive Speech Examples for Students
3 Basic Types of Persuasive Speeches
Have you ever been captivated by a persuasive speech that left a lasting impact? Persuasive speeches have the remarkable power to sway opinions, inspire action, and ignite change.
Students are often tasked with assignments to develop their persuasive communication skills. Creating an outline ensures you cover all necessary points and avoid repetition or confusion.
In this blog, we will not only provide you with a persuasive speech outline template but also offer valuable writing tips.
So, without further ado, let’s get right into it!
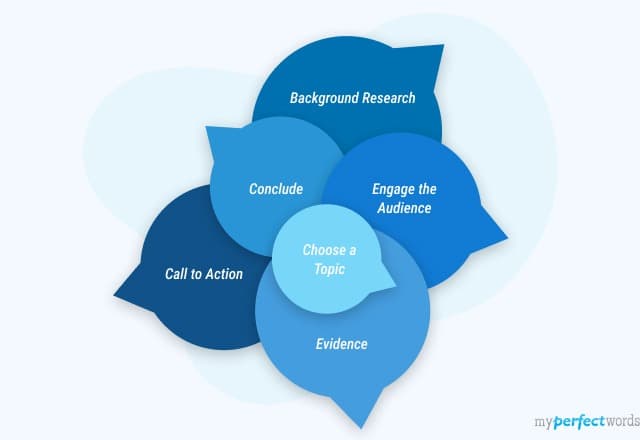
- 1. Components of a Persuasive Speech Outline
- 2. Persuasive Speech Outline Examples
- 3. Writing Tips for Creating Persuasive Speech Outlines
- 4. Mistakes to Avoid in Persuasive Speech Outlines
Components of a Persuasive Speech Outline
A persuasive speech aims to convince the audience of a specific point of view. Creating an outline helps in organizing thoughts and arguments.
It ensures that every point, supporting evidence, and counterarguments are considered and presented systematically.
Let's look into the components of a persuasive speech outline, specifically, the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Persuasive Speech Introduction Outline
The introduction of your persuasive speech is your opportunity to make a strong first impression and capture your audience's attention.
Its primary purpose is to set the stage for the speech and introduce the topic in an engaging way.
Here's how to craft an effective introduction:
- Hook Your Audience: Start with a hook that captures your audience's attention, like a quote, a shocking fact, a thought-provoking question, or a captivating story related to your topic.
- Thesis Statement: After the hook, clearly state your thesis statement , a concise, one-sentence declaration of your main argument or the central message of your speech.
- Overview of Main Points: End the introduction by briefly outlining the main points you'll cover in the body of your speech, giving your audience a roadmap of what to expect.
Let’s take a look at the example of this section in a speech:
Did you know that more than 80% of American adults don't get enough exercise? Picture this: A few years ago, I struggled with low energy and frequent illness until I discovered the power of regular exercise.
Regular exercise offers a multitude of physical, mental, and emotional benefits that can significantly improve our overall quality of life.
In today's fast-paced world, where many of us lead sedentary lives, understanding the advantages of regular exercise is essential for our well-being.
In the following minutes, I will discuss the physical health benefits, the positive effects on mental well-being, and the emotional advantages of incorporating regular exercise into your daily routine. |
Persuasive Speech Body Outline
The body of your persuasive speech outline is where you present your main points and supporting evidence to make a compelling case for your argument.
Here's how to effectively organize and structure this section:
- Main Points: List your main arguments, with each one contributing to your overall message. Each point should be distinct and significant.
- Supporting Evidence: For each main point, provide supporting evidence, including facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, or personal anecdotes that reinforce your arguments.
- Logical Organization: Arrange your main points logically, with the most persuasive ones coming first to guide your audience through your speech smoothly.
Let’s take a look at how this section will look in a speech:
Studies have shown that individuals who volunteer regularly experience personal growth. They develop a greater sense of purpose and fulfillment in their lives. Volunteering provides an opportunity to step out of one's comfort zone and learn new skills, which, in turn, boosts self-confidence and self-esteem. Volunteering has been linked to improved mental health. Engaging in community service can reduce stress levels and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. This is because it fosters a sense of belonging, social connection, and emotional well-being. When you help others, you also help yourself. Volunteering offers an ideal environment for skill development. Whether it's honing teamwork, leadership, communication, or problem-solving skills, volunteers gain practical experience that can benefit them personally and professionally. For example, many successful leaders credit their volunteer experiences for shaping their abilities.
The act of volunteering strengthens social bonds within communities. By working together toward a common goal, volunteers build a sense of unity, trust, and shared purpose. This connectedness contributes to the overall well-being and resilience of the community. Volunteering addresses specific local needs and issues. Community volunteers often play a vital role in solving problems, be it by participating in neighborhood clean-ups, tutoring students, or distributing food to the less fortunate. Their efforts have a direct and positive impact on the lives of community members. Many volunteer initiatives result in long-lasting improvements in communities. Projects like reforestation efforts, urban renewal, and literacy programs have made a significant and enduring impact. The commitment of volunteers to sustained change illustrates the potential for individuals to be catalysts for transformation. |
Persuasive Speech Conclusion Outline
The conclusion of your persuasive speech outline serves the crucial role of bringing your speech to a memorable and impactful close.
Here's how to craft an effective conclusion:
- Restate Thesis and Main Points: Start the conclusion by restating your thesis and summarizing your main points to remind your audience of your key arguments.
- Compelling Closing Statement: End with a compelling closing statement, such as a thought-provoking remark, a call to action, a rhetorical question, or a memorable quote that ties back to your topic and leaves your audience pondering.
Here is how it will look in the speech outline:
In summary, volunteering isn't just a choice; it's a vital component in building compassionate, united, and resilient communities.
Throughout this speech, we've explored the personal benefits of volunteering, its positive impact on community development, and ways to get involved in community service.
As we conclude, remember that your contribution can change lives and communities. So, let's make a commitment to volunteer and be the positive change our communities need. By giving our time and effort, we can create a stronger, more compassionate world for ourselves and future generations. |
Persuasive Speech Outline Examples
Let’s take a look at an example of a persuasive speech outline to give you a better idea of the structure:
Reduction of landfill waste Recycling reduces the burden on landfills and prevents the release of harmful chemicals into the environment. Conservation of natural resourcesRecycling conserves valuable resources like trees, water, and minerals. Energy savingsThe recycling process consumes less energy compared to producing items from raw materials. Job creation Recycling programs create jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing. Cost savings for businessesRecycling reduces production costs and waste disposal fees for businesses. Revenue generationSelling recyclable materials generates revenue for local governments. Household recycling Simple steps like separating recyclables from trash at home can have a big impact. Community involvementEncouraging communities to participate in recycling programs fosters a sense of responsibility. Spreading awarenessAdvocating for recycling through education and community initiatives can create a culture of recycling. Recycling is essential for its environmental benefits, economic advantages, and the role of individuals in making a difference. We've seen how recycling reduces landfill waste, conserves resources, and saves energy. It also creates jobs, saves money for businesses, and generates revenue. As individuals, we play a pivotal role in this effort. Let's commit to making recycling a part of our daily lives and advocate for its importance to create a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future for all. |
View this persuasive speech outline middle school:
Start with a fun fact, a surprising statistic, or a short story to grab attention. Explain why this topic is important to middle school students. Clearly state your main argument or position. Briefly outline the key points you will discuss in your speech.
Explain what the problem is in a simple and clear way. Use examples or stories that are relatable to your audience. Discuss why the problem matters to students, their families, or their school. Mention any consequences of not addressing the problem.
Describe the solution you are proposing in a straightforward manner. Explain how this solution works and why it’s effective. List the positive outcomes of implementing the solution. Use simple examples or illustrations to show how it will help. Acknowledge any possible objections or concerns. Provide clear, easy-to-understand reasons why these concerns are not valid or how they can be addressed. Reiterate the importance of your position and the benefits of your solution. Suggest practical steps the audience can take to support the solution. Offer ways they can get involved or make a difference. End with a strong statement, a motivational quote, or a call to action that encourages the audience to act. |
Here are some amazing outline examples that you can refer to ensure you are on the right track:
Persuasive Speech Outline MLA Format
Body Shaming Persuasive Speech Outline
Problem Solution Persuasive Speech Outline
Animal Testing Persuasive Speech Outline
Death Penalty Persuasive Speech Outline
Mental Health Persuasive Speech Outline
Recycling Persuasive Speech Outline
Persuasive Speech Outline Sample
Sample Persuasive Speech Outline APA Format
Pro-choice Persuasive Speech Outline
Monroe Sequence Persuasive Speech Outline
Persuasive Speech Outline For College Students
Persuasive Speech Outline Template PDF
Drunk Driving Persuasive Speech Outline
School Uniforms Persuasive Speech Outline
Policy Persuasive Speech Outline Examples
Check out more persuasive speech examples to have a better idea of structuring your speech!
Writing Tips for Creating Persuasive Speech Outlines
When it comes to delivering a persuasive speech, the foundation of your success lies in your speech outline.
Here are some writing tips to help you create a compelling and persuasive speech outline:
- Choose a Topic of Your Interest:
Select a persuasive speech topic that genuinely interests and inspires you as it will make your speech more persuasive.
- Identify the Type of Speech:
Knowing the type of persuasive speech you are delivering is crucial. It helps in structuring your outline and shaping your arguments accordingly.
- Address Controversy or Debate:
Topics that involve controversy or ongoing debates often make for persuasive speeches. Presenting different viewpoints and then arguing for your perspective can engage your audience and make your speech more compelling.
- Consider Your Audience:
Think about your target audience's interests, beliefs, and values. Your topic should resonate with them. Tailor your message to address their concerns and align with their perspectives.
- Focus on a Clear and Specific Issue:
A well-defined and specific topic is more persuasive than a broad or vague one. Narrow down your subject to a particular issue or aspect that you can thoroughly address within the allotted time.
- Research and Gather Information:
Ensure that there is enough credible information available on your chosen topic. A well-researched speech with supporting evidence is more persuasive.
- Organize Your Main Points Logically:
Arrange your main points in a logical order that builds your argument effectively. This helps your audience follow your reasoning and enhances the persuasiveness of your speech.
- Create Engaging Transitions:
Use smooth transitions between sections to maintain the flow of your speech. This helps keep your audience engaged and ensures your arguments are coherent.
Mistakes to Avoid in Persuasive Speech Outlines
While crafting a persuasive speech outline, it's equally important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder your effectiveness.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you create a more persuasive and engaging speech:
- Lack of Clarity:
Ensure that your outline defines your main goal and message, making it easy for your audience to understand your intent.
- Overloading with Information:
Providing too much information can overwhelm your audience. Stick to the key points and avoid overwhelming your listeners with excessive data, details, or statistics.
- Weak or Generic Introduction:
A lackluster or generic introduction can fail to capture your audience's attention. Aim for a strong and engaging start that piques the interest or emotions of the audience.
- Neglecting Counterarguments:
Ignoring opposing viewpoints can make your speech appear one-sided. Address counterarguments and offer strong counterpoints to strengthen your position and credibility.
- Ignoring Your Audience's Perspective:
Ensure that your speech addresses their needs and concerns, making it more relevant and persuasive to them.
So there you have it!
We have discussed the components of a persuasive speech outline in detail.
By following the tips we've covered in this blog, you can create persuasive speech outlines that are well-structured and engaging.
The introduction, body, and conclusion work together to grab your audience's attention, make your points convincingly, and leave a strong impression.
However, if you still need help writing your speech, you can get help from professional writers at MyPerfectWords.com.
MyPerfectWords.com is a paper writing service that you can rely on. Our writers are experts at crafting proper speech outlines and writing compelling speeches.
So, why wait? Buy speech at the cheapest prices today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you structure a persuasive speech.
A persuasive speech is typically structured into three main parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. In the introduction , capture the audience's attention with a hook, introduce your topic, and state your thesis. In the body , present your main points logically, supported by evidence, and address counterarguments. Use transitions to maintain flow. In conclusion , summarize your key points, restate your thesis, and end with a strong call to action.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

PHILADELPHIA SEPTEMBER 12-13 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
Persuasive Speech: How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech

Most often, it actually causes the other person to want to play “Devil’s advocate” and argue with you. In this article, we are going to show you a simple way to win people to your way of thinking without raising resentment. If you use this technique, your audience will actually WANT to agree with you! The process starts with putting yourself in the shoes of your listener and looking at things from their point of view.
Background About How to Write a Persuasive Speech. Facts Aren’t Very Persuasive.
Want to beat stage fright, articulate with poise, and land your dream job? Take the 2-minute public speaking assessment and get the Fearless Presenter’s Playbook for FREE!

Most people think that a single fact is good, additional facts are better, and too many facts are just right. So, the more facts you can use to prove your point, the better chance you have of convincing the other person that you are right. The HUGE error in this logic, though, is that if you prove that you are right, you are also proving that the other person is wrong. People don’t like it when someone proves that they are wrong. So, we prove our point, the other person is likely to feel resentment. When resentment builds, it leads to anger. Once anger enters the equation, logic goes right out the window.
In addition, when people use a “fact” or “Statistic” to prove a point, the audience has a natural reaction to take a contrary side of the argument. For instance, if I started a statement with, “I can prove to you beyond a doubt that…” before I even finish the statement, there is a good chance that you are already trying to think of a single instance where the statement is NOT true. This is a natural response. As a result, the thing that we need to realize about being persuasive is that the best way to persuade another person is to make the person want to agree with us. We do this by showing the audience how they can get what they want if they do what we want.
You may also like How to Design and Deliver a Memorable Speech .
A Simple 3-Step Process to Create a Persuasive Presentation

The process below is a good way to do both.
Step One: Start Your Persuasive Speech with an Example or Story
When you write an effective persuasive speech, stories are vital. Stories and examples have a powerful way to capture an audience’s attention and set them at ease. They get the audience interested in the presentation. Stories also help your audience see the concepts you are trying to explain in a visual way and make an emotional connection. The more details that you put into your story, the more vivid the images being created in the minds of your audience members.
This concept isn’t mystical or anything. It is science. When we communicate effectively with another person, the purpose is to help the listener picture a concept in his/her mind that is similar to the concept in the speaker’s mind. The old adage is that a “picture is worth 1000 words.” Well, an example or a story is a series of moving pictures. So, a well-told story is worth thousands of words (facts).
By the way, there are a few additional benefits of telling a story. Stories help you reduce nervousness, make better eye contact, and make for a strong opening. For additional details, see Storytelling in Speeches .
I’ll give you an example.
Factual Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

- 53% of all motor vehicle fatalities from last years were people who weren’t wearing seatbelts.
- People not wearing seatbelts are 30 times more likely to be ejected from the vehicle.
- In a single year, crash deaths and injuries cost us over $70 billion dollars.
These are actual statistics. However, when you read each bullet point, you are likely to be a little skeptical. For instance, when you see the 53% statistic, you might have had the same reaction that I did. You might be thinking something like, “Isn’t that right at half? Doesn’t that mean that the other half WERE wearing seatbelts?” When you see the “30 times more likely” statistic, you might be thinking, “That sounds a little exaggerated. What are the actual numbers?” Looking at the last statistic, we’d likely want to know exactly how the reporter came to that conclusion.
As you can see, if you are a believer that seatbelts save lives, you will likely take the numbers at face value. If you don’t like seatbelts, you will likely nitpick the finer points of each statistic. The facts will not likely persuade you.
Example Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

When I came to, I tried to open my door. The accident sealed it shut. The windshield was gone. So I took my seatbelt off and scrambled out the hole. The driver of the truck was a bloody mess. His leg was pinned under the steering wheel.
The firefighters came a few minutes later, and it took them over 30 minutes to cut the metal from around his body to free him.
A Sheriff’s Deputy saw a cut on my face and asked if I had been in the accident. I pointed to my truck. His eyes became like saucers. “You were in that vehicle?”
I nodded. He rushed me to an ambulance. I had actually ruptured my colon, and I had to have surgery. I was down for a month or so, but I survived. In fact, I survived with very few long-term challenges from the accident.
The guy who hit me wasn’t so lucky. He wasn’t wearing a seatbelt. The initial impact of the accident was his head on the steering wheel and then the windshield. He had to have a number of facial surgeries. The only reason he remained in the truck was his pinned leg. For me, the accident was a temporary trauma. For him, it was a life-long tragedy.
The Emotional Difference is the Key
As you can see, there are major differences between the two techniques. The story gives lots of memorable details along with an emotion that captures the audience. If you read both examples, let me ask you a couple of questions. Without looking back up higher on the page, how long did it take the firefighters to cut the other driver from the car? How many CDs did I have? There is a good chance that these two pieces of data came to you really quickly. You likely remembered this data, even though, the data wasn’t exactly important to the story.
However, if I asked you how much money was lost last year as a result of traffic accidents, you might struggle to remember that statistic. The CDs and the firefighters were a part of a compelling story that made you pay attention. The money lost to accidents was just a statistic thrown at you to try to prove that a point was true.
The main benefit of using a story, though, is that when we give statistics (without a story to back them up,) the audience becomes argumentative. However, when we tell a story, the audience can’t argue with us. The audience can’t come to me after I told that story and say, “It didn’t take 30 minutes to cut the guy out of the car. He didn’t have to have a bunch of reconstructive surgeries. The Deputy didn’t say those things to you! The audience can’t argue with the details of the story, because they weren’t there.
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice
When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil’s advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us. They can agree that the story that we told was true. So, now, finish the story with your point or your opinion. “So, in my opinion, if you wear a seatbelt, you’re more likely to avoid serious injury in a severe crash.”
By the way, this technique is not new. It has been around for thousands of years. Aesop was a Greek slave over 500 years before Christ. His stories were passed down verbally for hundreds of years before anyone ever wrote them down in a collection. Today, when you read an Aesop fable, you will get 30 seconds to two minutes of the story first. Then, at the conclusion, almost as a post-script, you will get the advice. Most often, this advice comes in the form of, “The moral of the story is…” You want to do the same in your persuasive presentations. Spend most of the time on the details of the story. Then, spend just a few seconds in the end with your morale.
Step 3: End with the Benefit to the Audience

So, the moral of the story is to wear your seatbelt. If you do that, you will avoid being cut out of your car and endless reconstructive surgeries .
Now, instead of leaving your audience wanting to argue with you, they are more likely to be thinking, “Man, I don’t want to be cut out of my car or have a bunch of facial surgeries.”
The process is very simple. However, it is also very powerful.
How to Write a Successful Persuasive Speech Using the “Breadcrumb” Approach
Once you understand the concept above, you can create very powerful persuasive speeches by linking a series of these persuasive stories together. I call this the breadcrumb strategy. Basically, you use each story as a way to move the audience closer to the ultimate conclusion that you want them to draw. Each story gains a little more agreement.
So, first, just give a simple story about an easy to agree with concept. You will gain agreement fairly easily and begin to also create an emotional appeal. Next, use an additional story to gain additional agreement. If you use this process three to five times, you are more likely to get the audience to agree with your final conclusion. If this is a formal presentation, just make your main points into the persuasive statements and use stories to reinforce the points.
Here are a few persuasive speech examples using this approach.
An Example of a Persuasive Public Speaking Using Breadcrumbs
Marijuana Legalization is Causing Huge Problems in Our Biggest Cities Homelessness is Out of Control in First States to Legalize Marijuana Last year, my family and I took a mini-vacation to Colorado Springs. I had spent a summer in Colorado when I was in college, so I wanted my family to experience the great time that I had had there as a youth. We were only there for four days, but we noticed something dramatic had happened. There were homeless people everywhere. Keep in mind, this wasn’t Denver, this was Colorado City. The picturesque landscape was clouded by ripped sleeping bags on street corners, and trash spread everywhere. We were downtown, and my wife and daughter wanted to do some shopping. My son and I found a comic book store across the street to browse in. As we came out, we almost bumped into a dirty man in torn close. He smiled at us, walked a few feet away from the door, and lit up a joint. He sat on the corner smoking it. As my son and I walked the 1/4 mile back to the store where we left my wife and daughter, we stepped over and walked around over a dozen homeless people camped out right in the middle of the town. This was not the Colorado that I remembered. From what I’ve heard, it has gotten even worse in the last year. So, if you don’t want to dramatically increase your homelessness population, don’t make marijuana legal in your state. DUI Instances and Traffic Accidents Have Increased in Marijuana States I was at the airport waiting for a flight last week, and the guy next to me offered me his newspaper. I haven’t read a newspaper in years, but he seemed so nice that I accepted. It was a copy of the USA Today, and it was open to an article about the rise in unintended consequences from legalizing marijuana. Safety officials and police in Colorado, Nevada, Washington, and Oregon, the first four state to legalize recreational marijuana, have reported a 6% increase in traffic accidents in the last few years. Although the increase (6%) doesn’t seem very dramatic, it was notable because the rate of accidents had been decreasing in each of the states for decades prior to the law change. Assuming that only one of the two parties involved in these new accidents was under the influence, that means that people who aren’t smoking marijuana are being negatively affected by the legalization. So, if you don’t want to increase your chances of being involved in a DUI incident, don’t legalize marijuana. (Notice how I just used an article as my evidence, but to make it more memorable, I told the story about how I came across the article. It is also easier to deliver this type of data because you are just relating what you remember about the data, not trying to be an expert on the data itself.) Marijuana is Still Largely Unregulated Just before my dad went into hospice care, he was in a lot of pain. He would take a prescription painkiller before bed to sleep. One night, my mom called frantically. Dad was in a catatonic state and wasn’t responsive. I rushed over. The hospital found that Dad had an unusually high amount of painkillers in his bloodstream. His regular doctor had been on vacation, and the fill-in doctor had prescribed a much higher dosage of the painkiller by accident. His original prescription was 2.5 mg, and the new prescription was 10 mg. Since dad was in a lot of pain most nights, he almost always took two tablets. He was also on dialysis, so his kidneys weren’t filtering out the excess narcotic each day. He had actually taken 20 MG (instead of 5 MG) on Friday night and another 20 mg on Saturday. Ordinarily, he would have had, at max, 15 mg of the narcotic in his system. Because of the mistake, though, he had 60 MGs. My point is that the narcotics that my dad was prescribed were highly regulated medicines under a doctor’s care, and a mistake was still made that almost killed him. With marijuana, there is really no way of knowing how much narcotic is in each dosage. So, mistakes like this are much more likely. So, in conclusion, legalizing marijuana can increase homelessness, increase the number of impaired drivers, and cause accidental overdoses.
If you use this breadcrumb approach, you are more likely to get at least some agreement. Even if the person disagrees with your conclusion, they are still likely to at least see your side. So, the person may say something like, I still disagree with you, but I totally see your point. That is still a step in the right direction.
For Real-World Practice in How to Design Persuasive Presentations Join Us for a Class
Our instructors are experts at helping presenters design persuasive speeches. We offer the Fearless Presentations ® classes in cities all over the world about every three to four months. In addition to helping you reduce nervousness, your instructor will also show you secrets to creating a great speech. For details about any of the classes, go to our Presentation Skills Class web page.
For additional details, see Persuasive Speech Outline Example .

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized

How to Write a Persuasive Speech: 7 Tips for Success
- The Speaker Lab
- June 12, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of a persuasive speech is about more than just making an argument. It’s about engaging your audience, tapping into their emotions, and guiding them to your point of view with precision.
In our dive into persuasive speaking, we’ll look at how selecting enthralling topics can captivate listeners from the get-go and ensure they hang on every word. By structuring your thoughts clearly, you’ll convey messages that not only resonate but also inspire action. And as we venture further, expect practical insights on delivering these ideas with confidence.
This guide will equip you for impact whether you’re eyeing higher education debates or business pitches. So—ready to persuade? Let’s start building those skills!
Crafting the Essentials of Persuasive Speech
What makes a persuasive speech not just good, but great? It’s all about nailing the essentials. Let’s talk shop and get into what constitutes a persuasive speech.
Defining Persuasive Speech and Its Significance
A powerful tool in any speaker’s arsenal, a persuasive speech aims to convince your audience to adopt your point of view or take action. But why is this skill so crucial? In various contexts—from boardrooms to auditoriums—mastering persuasion can be the key that unlocks doors, whether you’re advocating for human rights or pitching an innovative product. It’s not just about having facts at your fingertips; it’s also about striking chords with audience members on both logical and emotional levels.
In essence, successful persuasion hinges on blending ethos , pathos , and logos —three rhetorical arguments that make different appeals in order to sway people without crossing ethical lines. Imagine stirring up the kind of passion Martin Luther King, Jr. did with his “I Have A Dream” speech—that’s what we’re aiming for.
The Anatomy of Persuasive Speech
Diving deeper into crafting effective messages requires understanding key elements like thesis statements—a concise summary of your argument. Your speech should also have main points bolstered by supporting evidence. An intriguing thesis acts as a magnet drawing listeners in while logically laid out arguments keep them hooked.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Selecting Captivating Topics for Persuasive Speeches
Choosing the right topic is like picking the perfect outfit for an interview. It’s your first chance to impress and persuade. A good persuasive speech topic isn’t just interesting—it should also resonate with you personally, offer fresh insights, and be relevant to your audience. Your chosen topic should spark curiosity.
Criteria for Choosing Your Topic
Picking out a topic that resonates with you and hooks your audience starts with introspection. Think about what gets you fired up: Is it human rights or health insurance debates? Does discussing violent video games or tobacco products prohibition spark that inner debater in you? Now blend this passion with issues relevant to high school curriculums or hot topics from social media chatter—this fusion ensures relevance and personal engagement.
Next, ensure alignment between your chosen subject matter and specific purpose—a mission statement of sorts for your talk. It should clarify why this issue matters here, now, to these listeners. For example, if organ donation rates are low locally yet awareness is high—an effective persuasive speech could pivot towards addressing myths rather than general advocacy.
Brainstorming Ideas That Spark Interest
To uncover gems among standard persuasive speech ideas requires creativity. Begin by listing down all potential subjects that fascinate you—music therapy’s role in mental health recovery perhaps, or how genetically modified foods affect nutrition security.
Dive deeper into each idea by considering its counter arguments, as well as how you might answer such counterarguments.
Structuring Your Persuasive Speech Outline
A persuasive speech outline is your battle plan. It’s where you lay out the strategies to sway your audience and anchor them to every word.
Main Points in a Persuasive Speech
Your outline should map the journey from opening gambit to final plea, with main points acting as guideposts. Your main points aren’t just there for show but also to convince and convert. These points should be clear, concise, and crafted to push the envelope on what your listeners consider possible.
As most successful persuaders will tell you, a well-structured outline doesn’t simply support an argument; it elevates it. That’s why every point must be backed by evidence support strong enough to withstand counter arguments while remaining ethical—no room for manipulation here.
The Blueprint of Your Argument
An effective persuasive speech starts with a thesis statement bold enough yet plausible enough that even skeptics pause for thought. You then need to connect each section back to this central claim.
The body of your argument should alternate between serving up hard-hitting facts (logos) and plucking at the audience’s heartstrings (pathos). And let’s not forget ethos—audiences should be able to trust what you say because you know this topic inside and out due its personal resonance or professional relevance.
To hammer home your main points, make sure you reiterate them in your conclusion, along with your thesis. This method ensures that audiences don’t lose track of your argument in between points.
Mastering Persuasive Speaking Techniques
To effectively deliver a persuasive speech, it’s all about the blend of strategy and sincerity. Think of your speech as a three-course meal served to engage every sense; you need just the right ingredients mixed with skillful preparation.
The secret sauce? Ethos, pathos, logos—your credibility, their emotions, and logic neatly tied together. Present facts illustrated with tales that tug at heartstrings while showcasing your expertise on the topic. These approaches have been used by great leaders throughout history.
Engaging the Audience’s Emotions in Your Persuasive Speech
A dash of emotion can transform your talk from mundane to memorable. When you speak, aim for the heart to build an emotional connection that lasts beyond those final applause. Tell a personal story or paint scenarios that resonate on an individual level. It makes audience members feel like they’re part of something larger than themselves—a surefire way to keep them listening and ready to adopt your viewpoint.
Using Persuasive Speaking Techniques Effectively
An unforgettable opening ensures you grab attention immediately but remember: this is no time for fluff. Get straight into what matters with clear main points outlined upfront because if there’s one thing we know—it’s that nobody likes being lost in translation (or speeches). Counter arguments proactively so when doubts arise, they’re already addressed head-on.
Your thesis statement isn’t just another sentence; it’s the rudder on your ship of an argument. As such it needs to be strong so that everyone knows why they should care about exotic animals or health insurance debates.
Crafting Messages That Resonate
Persuasion isn’t merely about changing minds temporarily—it’s making ideas stick long after curtains close. So layer stories atop statistics until suddenly—the world views genetically modified foods differently because you’ve shown them both sides using evidence support wrapped in narratives too compelling to ignore.
Overcoming Public Speaking Challenges
Stage fright and nervousness can turn a spotlight into a glaring interrogation lamp. It’s common, but you don’t have to let it derail your speech . Deep breathing exercises before taking the stage can help steady those jitters. Remember, even the pros feel butterflies; they’ve just learned how to make them fly in formation.
Dealing with Stage Fright and Nervousness
Facing an audience can intimidating unless you’re prepared. Preparation is your armor against fear. Know your material inside out, because when you do, confidence isn’t far behind. And if that doesn’t cut it? Picture success: visualize yourself crushing it on stage, leaving audiences hanging onto every word.
If sweaty palms still persist, focus on making connections rather than impressing people—that shift in perspective might just be what keeps nerves from taking center stage.
Handling Difficult Audience Members During Your Speech
Sometimes audience members throw curveballs harder than a major league pitcher, but with tact and grace under pressure, you’ll turn that curveball into a homerun. If someone challenges or interrupts you mid-speech, stay calm. Thank them for their input and transition back to your main points swiftly yet respectfully.
A difficult question? Embrace it as an opportunity to showcase depth of knowledge or gracefully defer it until after the presentation so everyone stays engaged without going off track.
Remember: Persuasion begins where discomfort ends—and overcoming these hurdles will leave listeners remembering not just what was said but who said it with conviction.
Ethical Considerations in Persuasion
When you step onto the stage to deliver a persuasive speech, you’re not just sharing an opinion; you’re asking your audience to trust and follow your guidance. Balancing persuasion with honesty is no small feat, but it’s essential for maintaining credibility. You might be tempted to stretch the truth or hide inconvenient facts, but avoiding manipulation in speaking is crucial.
A successful persuasive speaker knows that ethical concerns in persuasive speaking form the bedrock of genuine connection with your audience members. It’s easy to get lost in crafting arguments so compelling they border on coercive. But ask yourself if what you’re doing serves as a bridge between differing viewpoints or simply bulldozes over counter arguments without regard for their validity.
Steering Clear of Manipulative Tactics
Persuasive speeches should light fires under topics like human rights or health insurance—not ignite controversy through deceitful tactics. Ethos, pathos, and logos can become tools for trickery when used improperly. As a responsible communicator aiming at engaging the audience’s emotions ethically, steer clear from creating emotional whirlwinds devoid of factual basis.
To stay true to ethical persuasion principles means ensuring every fact presented has been verified twice over—no exaggeration, deceit, or rumormongering allowed. Stick firmly within reality’s bounds while discussing controversial subjects such as tobacco products regulation or organ donation processes; this helps maintain an atmosphere where constructive debate thrives.
Maintaining Honesty Throughout Your Speech
Your thesis statement isn’t just there for show—it’s your pledge of integrity throughout your address on music therapy benefits or violent video games’ effects on youth behavior patterns. Weaving personal experience into narratives may bolster relatability yet must never wander off into fabrication territory even if spinning tales better suited for your argument seems tempting.
Ready to Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig?
Download our free 26-page guide and get the 14 exact steps you can follow to book a paid speaking gig right now!
Leveraging Online Platforms t0 Develop Your Skills
The savvy speakers among us know that to stay ahead of the game, sharpening your speaking chops online is not just smart; it’s essential. With an array of top-notch courses, you can fast-track your way to becoming a more persuasive and effective speaker.
Building Public Speaking Skills Online
The journey to mastering public speaking starts with one click. The internet bursts at the seams with resources like Toastmasters International tailored to help you build public speaking skills online. Whether it’s refining thesis statements or practicing eye contact through video feedback, their tools are designed for real-world success without leaving your desk.
In addition to Toastmasters International, the National Speakers Association and SpeakerHub also have a myriad of resources for speakers of all levels. And of course, there are our own resources here at The Speaker Lab , where we offer you speaker training that will get you booked and paid to speak.
Top-Notch Courses for Developing Your Skills
No need to spend hours in traditional classrooms when you can speed up learning on-the-go or from the comfort of home. Top-notch programs, such as this course from the University of Colorado Boulder, turn theory into action faster than ever before. Interactive classes like these engage learners like no other. Just remember though—these resources aren’t magic wands; commitment still tops necessity lists if real growth is what you’re after.
FAQs on Persuasive Speeches
What is a persuasive speech example.
Persuasive speech aims to sway the crowd. Think MLK’s “I Have a Dream” pushing for civil rights.
What are the 5 elements of persuasive speech?
The five key slices: a solid intro, clear message, credible evidence, emotional appeal, and a killer conclusion.
How do I start a persuasive speech?
Kick off with an attention grabber—quote, question or startling stat—to hook your listeners right away.
What is a persuasive way of speaking?
Surefire persuasion speaks directly to interests while mixing logic and emotion to shift opinions.
Mastering a persuasive speech is about connection, clarity, and conviction. Remember the essentials: a well-structured argument supports your message and engaging topics capture attention.
Outline each argument with care, making it easy for listeners to follow, then balance facts with stories that stir emotions.
Hone your delivery like great leaders do. Practice making eye contact; refine those public speaking skills online or in person—it’s how you keep an audience listening.
Ethics matter as much as eloquence does. Persuade honestly without manipulating minds or exploiting fears—that’s true success in persuasion.
In every good persuasive speech lies the power to change views, inspire action, even alter history itself. So take these insights and go forth—persuade ethically, speak confidently!
- Last Updated: June 4, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- Blogging Aloud
- About me/contact
- How to write a persuasive speech
Writing a persuasive speech
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 04-24-2023
Getting started with a 7 point action plan
To help you through the process of writing a persuasive speech from beginning to end, here's a 7 step checklist.
To get the most from it move through it sequentially - point by point. You'll find links to topic suggestion pages, explanations about how to structure your speech and the importance of audience analysis with examples and more.
In my experience, a successful persuasive speech can't be flicked out in five minutes! There may be brilliantly competent speakers who can do it if they know their subject, and their audience inside out. However the rest of us, me included, have to put the time in to achieve what we want to. ☺
Quick links to get around this page easily
Checklist for writing a persuasive speech
1. Selecting a persuasive speech topic
If you've already got a speech topic move on to setting a goal . For those who don't, read on.
A major part of the challenge of writing a persuasive speech can be choosing what to speak about.
If you're preparing the speech as part of a class exercise or for a public speaking club like Toastmasters you have seemingly unlimited choice. And that can be bewildering! The possibilities are vast. How do you narrow them down?
The answer is to choose something that you genuinely care about, fits the occasion AND that you know your audience will be interested in.
Speech topic suggestions to explore

- 100 Persuasive speech ideas
- 50 Good persuasive speech topics
- 105 Fun persuasive speech topics
- 309 'Easy' persuasive speech topics
- 310 Persuasive speech topics for college
- 108 Feminist persuasive speech topics
Return to Top
2. Setting a goal
The goal of writing a persuasive speech is to change or move the audience toward accepting your position on the topic. An essential part of that is knowing exactly what it is you want to achieve.
There are degrees of change. Do you want a little, or a lot?
Most wanted response or MWR
What you decide is called your most wanted response or MWR.
A realistic MWR is reached through analysis of your audience in relation to your topic.
Example: My topic is "obesity in children".
Audience - who are they.
I am speaking to mothers whose children all attend the same kindergarten.
The staff are concerned about the number of children who are over weight for their age.
The children mostly come from homes where both parents work.

Current food habits as reported by kindergarten staff
Food is bought already made up for a variety of reasons including time saving, convenience, and a lack of knowledge about how to prepare it any other way.
'Treat' food (sweets, cake etc.) is also used to pacify and/or to reinforce good behavior.
Fussy or picky eating is allowed principally because the effort and time required to change already established patterns is difficult to find.
The problem is compounded by lack of exercise.
Most Wanted Response (MWR) options
In setting the goal (MWR) for the speech I need to decide what approach will achieve the best results.
Do I want to influence the mothers to open their minds to the idea that allowing a child to establish habitual unhealthy eating patterns is detrimental to their children's growth and development?
Or do I want them to stop using treat and pre-prepared foods immediately and only offer home cooked healthy options instead?
The first approach is softly-softly. The second is direct or hard hitting.
3. Audience analysis
Who is your audience.
How you persuade, and your MWR (goal) is most effectively established when you understand who you are talking to.
In relation to the topic you're going to speak about are they:
- Hostile - actively don't want to hear what you have to say for many reasons which may include prejudice, fear, ignorance, inertia, cultural difference, differing values/beliefs ...
- Neutral - no decided opinion or beliefs and therefore no investment toward maintaining the current state or moving toward a new one. This is the middle ground.
- Motivated - actively seeking to change. These people are already aware of the 'problem' and are looking for solutions. They want to hear what you have to tell them and are likely to be ready to be convinced of the rightness of your solution.
What else do you need to know?
Aside from their anticipated baseline attitude, (hostile, neutral, motivated), toward your speech topic, what else would be useful to know about your audience?
Find out their:
- General Age
- Shared fears, concerns or problems
- Cultural background(s)
- Shared interests, beliefs, values, goals, hopes, desires
- What obstacles there are to adopting the change you desire
The more you can find out, the more you can tailor writing a persuasive speech (including tone and language choice), and your MWR to fit.
For instance, going back to the obesity in children example above, we could decide, given what we've found out about the audience, the hard-hitting approach would generate too many obstacles to overcome.
Therefore we will be writing a persuasive speech with a non-threatening MWR that has mothers accepting a pamphlet on children's healthy snack choices to take home.
4. Keep it local
Where possible draw your examples from local material. The reason is we are more likely to care or respond when we actively know who or what is involved firsthand. We identify, and the more we identify, the more invested we are in finding a solution. The situation becomes real to us and we care.
5. Evidence and empathy
An essential part of putting together a good persuasive speech is finding credible evidence to support your argument.
Seek out reputable, reliable, quotable sources to back the points you make. Without them your speech will fail its purpose.
Persuasion is a synthesis of emotional as well as intellectual appeal.
Emotional content will be dismissed unless it is properly backed. Conversely purely intellectual content will be dismissed if it lacks empathy or feeling. You need both - in equal measure.
6. Balance and obstacles
Seek out and address the opposition's arguments, or obstacles in the path of adopting your course of action, fairly and respectfully. Find the elements you share. Openly acknowledge and be clear about them. This builds credibility and trust and as a result your points of departure are more likely to be listened to.
7. Choosing a structural pattern
Once you've decided your topic and its angle, done your audience analysis, fixed what you want to achieve (MWR), researched for evidence, and addressed the obstacles, you're finally ready to begin writing.
What pattern or model will you use?

There is more than one.
Have a look at each of the four below to see which best suits your topic, speech purpose and audience.
1) Monroe's Motivated Sequence

This is a tried and tested model developed in the 1930's by Allan H Monroe. Monroe's Motivated Sequence follows the normal mind-flow or thought sequence someone goes through when someone else is persuading them to do something.
It's a pattern used over and over again by the professional persuaders: marketers, advertisers, politicians ...
Monroe's Motivated Sequence in action
You can find out more about the five steps involved in writing a persuasive speech using Monroe's Motivated Sequence here. There's an explanation with examples of each step, and a printable blank outline template to download.
There's also an example persuasive speech to read that uses the method.
2) Problem/Solution
This is a two step pattern. The first part outlines/explains the problem and the second provides the solution which includes meeting the obstacles and giving evidence.
3) Comparison
In this pattern the method is to compare an item/object/idea/action against another similar item/object/idea/action and establish why the item/object/idea/action you are supporting is superior.
Example: Why a SBI website is better than a Wordpress site if you want to build an online business
- Reason One Wordpress primarily is a blogging platform and blogging is not a business model
- Reason Two Wordpress does not supply fully integrated step-by-step instructions to build a sustainable e-business
- Reason Three Wordpress does not provide its users with constant and fully tested upgrades/updating
With each comparison point compelling, relevant evidence is provided and obstacles are met.
(If you're curious check out the SBI v Wordpress comparison. There are many more than three reasons why SBI is the preferred online business platform! Wordpress or SBI? And these days you can actually have both through SBI.)
4) Using the negative to persuade
In this model the reasons why you are against the opposition of your chosen topic are highlighted.
Example: The topic is Teenage Binge Drinking and the angle is to persuade parents to take more control
- Leads to anti-social behavior - for example, mindless vandalism, drunk-driving, and unprotected sex
- Impacts on growing brains - an overview of current research
- Has implications for developing addictions - alcoholism, nicotine ...
Each negative reason is backed with evidence. One piles on top the other creating an urgency to solve the problem. Your positive solution coming at the end of the speech clinches the argument.
More speech resources
For more about the processes involved in writing a successful speech check these pages:
- Using storytelling effectively

For more about delivering your persuasive speech persuasively please don't overlook these pages. They are gold! Writing is a only part of the process. How you deliver completes it.
- How to rehearse
- Using vocal variety
- Return to the top of the page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- 10 Tips for the SAT Essay
- Basic Tips for Memorizing Speeches, Skits, and Plays
- Mock Election Ideas For Students
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- How to Write an Interesting Biography
- The Difference Between Liberals and Conservatives
- How to Run for Student Council
- Tips to Write a Great Letter to the Editor
- How to Write a Film Review
- Writing the Parts of a Stage Play Script
- 18 Ways to Practice Spelling Words
An Example of a Persuasive Speech Outline to Win Over Your Audience in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 08 April, 2024 • 6 min read
The art of persuasion is no easy feat. But with a strategic outline guiding your message, you can effectively convince others of your viewpoint on even the most controversial topics.
Today, we're sharing an example of a persuasive speech outline you can use as a template for crafting your own convincing presentations.
Table of Contents
The three pillars of persuasion, 6-minute persuasive speech examples, 3-minute persuasive speech examples, bottom line, frequently asked questions.

Tips for Audience Engagement
- Speech Persuasive Examples
- Short Persuasive Speech Examples
- Use word cloud or live Q&A to survey your audience easier!
- Use brainstorming tool effectively by AhaSlides idea board

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
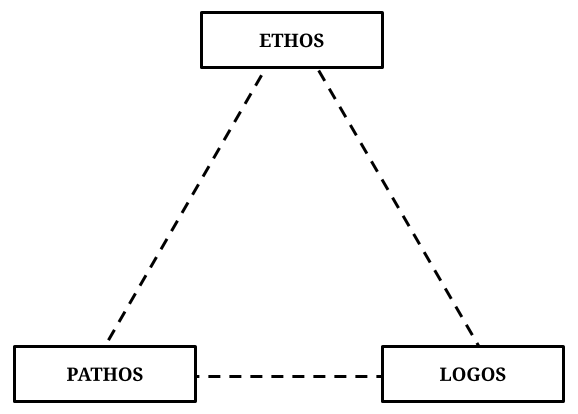
Want to move the masses with your message? Master the magical art of persuasion by tapping into the holy-grail trifecta of ethos, pathos and logos.
Ethos - Ethos refers to establishing credibility and character. Speakers use ethos to convince the audience they are a trusted, knowledgeable source on the topic. Tactics include citing expertise, credentials or experience. The audience is more likely to be swayed by someone they perceive as genuine and authoritative.
Pathos - Pathos utilises emotion to persuade. It aims to tap into the audience's feelings by triggering emotions like fear, happiness, outrage and such. Stories, anecdotes, passionate delivery and language that tugs at the heartstrings are tools used to connect on a human level and make the topic feel relevant. This builds empathy and buy-in.
Logos - Logos relies on facts, statistics, logical reasoning and evidence to rationally convince the audience. Data, expert quotes, proof points and clearly explained critical thinking guide listeners to the conclusion through objective-seeming justifications.
The most effective persuasive strategies incorporate all three approaches - establishing ethos to build speaker credibility, employing pathos to engage emotions, and utilising logos to back assertions through facts and logic.
Example of a Persuasive Speech Outline
Here is an example outline for a 6-minute persuasive speech on why schools should start later:

Title : Starting School Later Will Benefit Students' Health and Performance
Specific Purpose : To persuade my audience that high schools should start no earlier than 8:30 a.m. to align better with teenagers' natural sleep cycles.
I. Introduction A. Adolescents are chronically sleep-deprived due to early start times B. Lack of sleep harms health, safety and learning ability C. Delaying school start by even 30 minutes could make a difference
II. Body Paragraph 1 : Early times contradict biology A. Teens' circadian rhythms shift to late-night/morning pattern B. Most do not get sufficient rest due to obligations like sports C. Studies link lack of sleep to obesity, depression and dangers
III. Body Paragraph 2 : Laters starts to boost academics A. Alert, well-rested teens demonstrate improved test scores B. Attention, focus and memory all benefit from adequate sleep C. Fewer absences and tardies reported at later-starting schools
IV. Body Paragraph 3: Community support available A. American Academy of Pediatrics, medical groups endorse change B. Adjusting schedules is feasible and other districts had success C. Later start times are a small change with a large impact
V. Conclusion A. Prioritising student wellness should motivate policy revision B. Delaying the start by even 30 minutes could transform outcomes C. I urge support for biologically aligned school start times
This is an example of a persuasive speech pitching a business proposal to a potential investor:

Title : Investing in a Mobile Car Wash App
Specific Purpose : To convince investors to back the development of a new on-demand mobile car wash app.
I. Introduction A. My experience in the car care and app development industries B. Gap in the market for a convenient, tech-enabled car wash solution C. Preview of potential and investment opportunity
I I. Body Paragraph 1: Large untapped market A. Majority of car owners dislike traditional wash methods B. On-demand economy has disrupted many industries C. App would remove barriers and attract new customers
III. Body Paragraph 2: Superior customer value proposition A. Schedule washes on the go with just a few taps B. Washers come directly to the customer's location C. Transparent pricing and optional upgrades
IV. Body Paragraph 3: Strong financial projections A. Conservative usage and customer acquisition forecasts B. Multiple revenue streams from washes and add-ons C. Projected 5-year ROI and exit valuation
V. Conclusion: A. Gap in the market represents a huge opportunity B. Experienced team and developed app prototype C. Seeking $500,000 seed funding for the app launch D. This is a chance to get in early on the next big thing

In 3 minutes you need a clear thesis, 2-3 main arguments reinforced with facts/examples, and a concise conclusion recapping your request.
Example 1: Title: schools should switch to a 4-day school week Specific purpose: persuade the school board to adopt a 4-day school week schedule. Main points: longer days can cover required learning, increase teacher retention, and save on transportation costs. A longer weekend means more recovery time.
Example 2: Title: companies should offer a 4-day workweek Specific purpose: persuade my manager to propose a 4-day workweek pilot program to upper management Main points: increased productivity, lower costs from less overtime, higher employee satisfaction and less burnout which benefits retention.
Example 3: Title: high schools should allow cell phones in class Specific purpose: convince the PTA to recommend a change in the cell phone policy at my high school Main points: most teachers now use cell phones as educational tools, they engage digital native students, and an occasional approved personal use boosts mental health.
Example 4: Title: all cafeterias should offer vegetarian/vegan options Specific purpose: persuade the school board to implement a universal vegetarian/vegan option in all public school cafeterias Main points: it's healthier, more environmentally sustainable, and respectful of various student diets and beliefs.
An effective outline serves as the backbone for a persuasive presentation that can inspire change.
It ensures your message is clear, cohesive and backed by strong evidence so that your audience leaves empowered instead of confused.
While crafting compelling content is key, taking the time to strategically structure your outline gives you the best chance of winning hearts and minds.

What should a persuasive speech outline look like?
A persuasive speech outline means each point should support your overall thesis. It includes credible sources/references for evidence and also considers anticipated objections and counterarguments. The language should be clear, concise and conversational for oral delivery.
What is an outline for a speech example?
A speech outline should include these sections: Introduction (attention grabber, thesis, preview), body paragraph (state your points and counterarguments ), and a conclusion (wrap up everything from your speech).
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
How to Write a Persuasive Speech: from Attractive Outline to Effective Closing
Updated 29 Jul 2024
Persuasive speaking is a skill that can transform your ability to influence and persuade others. The point of such a speech format is to sway others to agree with your perspective or support your stance by using compelling arguments, evidence, and persuasive language.
Whether you're a student who needs to deliver a well-crafted self-introduction speech or a seasoned speaker, enhancing your speaking skills can be a game-changer in various aspects of your life.
In this blog post, we'll explore the ins and outs of persuasive speeches, including what they are, how to write them, and the key elements that make them impactful. You’ll learn how to write a persuasive speech and follow tips from renowned speakers to help you elevate your speaking game.
What is a persuasive speech: definition and key parts
At its core, it is a carefully crafted message designed to sway the audience's beliefs, attitudes, or actions. But you should understand that it's not just about sharing information. Otherwise, it's about stirring emotions, building credibility, and appealing to logic. Creating a winning persuasive speech involves mastering the three persuasion pillars: ethos, pathos, and logos.
- Ethos is all about establishing your credibility as a speaker. You need to win the trust of your audience by showcasing your expertise, integrity, and authority on the topic. Share your qualifications, experiences, and credentials to build trust and credibility right from the start.
- Pathos is about tapping into the emotions of your audience. Indeed, stories, anecdotes, and personal connections connect you with people. Share real-life examples, heartwarming stories, or powerful anecdotes that elicit emotions such as empathy, compassion, or passion ─ it will make your talk memorable and impactful.
- Logos is about using logic and reasoning to support your argument. It is where facts, data, evidence, and logical reasoning come into play. Use statistics, research, case studies, and logical arguments to support your points and make your speech persuasive and compelling.
Your message should flow seamlessly from ethos to pathos to logos when you are building an irresistible persuasive speech. Start by establishing your credibility through ethos, then connect with your audience emotionally through pathos, and finally, back up your points with logical reasoning through logos. If you're thinking, "Help me write me a speech ," you can consider seeking professional speech writing services. These services can provide expert assistance in crafting a persuasive speech that seamlessly transitions from ethos to pathos, and finally logos.
Persuasive speech types: useful examples
Speeches come in different flavors, each with a unique focus and purpose. Let's learn about three main types: factual, value, and policy.
Factual persuasive speeches
If you craft a factual type of speech, you want to persuade the audience by presenting information and evidence backed up by facts. The focus is on providing credible data, research findings, and expert opinions to support the speaker's argument. Factual persuasive speeches are often used in informative settings, where the goal is to present information compellingly that influences the audience's perception or understanding of a topic.
Example : Advocating for the importance of regular exercise by citing scientific research on the health benefits and providing statistical data on the risks of sedentary lifestyles.
Value persuasive speeches
These speeches aim to persuade the audience by appealing to their moral or ethical values. The focus is on presenting arguments that align with the audience's beliefs, values, or moral code. Value persuasive speeches often involve discussing subjective or abstract topics, such as social issues, morality, or personal values, and aim to sway the audience's opinions or attitudes based on their values and emotions.
Example : Arguing for promoting diversity and inclusivity in the workplace by appealing to shared values of fairness, equality, and respect for individuals of all backgrounds.
Policy persuasive speeches
The focus here lies in presenting arguments that advocate for a specific policy change or action to be taken. Policy persuasive speeches are often used in political or advocacy settings, where the speaker seeks to influence the audience's actions or decisions on a particular issue or policy.
Example : Proposing a ban on single-use plastics to reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable practices.
Writing a persuasive speech: step-by-step guide
The key to a successful persuasive speech is clearly communicating your message, supporting your arguments with credible evidence, and engaging your audience emotionally and logically. With careful preparation, practice, and confidence, you can deliver a compelling speech that inspires and motivates your audience.
Step 0: Understand your audience.
Understand who you will be talking to, their values, and interests. It helps you tailor your speech to resonate with them and make your arguments more compelling.
Step 1: Choose a topic that inspires you and do the research.
You should be passionate about your topic ─ find what resonates with your audience and yourself. If you are unsure what to discuss, gather topics for a persuasive speech first. Use peer-reviewed journals, websites you can trust, and expert opinions to strengthen your speech.
Step 2: Understand your purpose.
You want your readers to stay engaged throughout the entire speech, which is why you need to state what you will be discussing from the beginning. Understanding your purpose is essential because it guides your message and the strategies you use to persuade your audience. Without one, your speech can lack direction, coherence, and impact. A well-defined purpose helps you to tailor your argument, select the most effective evidence, and use persuasive techniques that are appropriate for your audience.
Step 3: Keep a persuasive speech structure.
A speech typically includes an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The opening should grab your audience's attention: people should see why you are worth listening to and which point you will be supporting. After, you should uncover your point of view and back it up with arguments and examples. In the very end, make a strong call to action.
Step 4: Add persuasive language and techniques.
Choose powerful words and phrases that evoke emotions and create a sense of urgency. Use rhetorical devices such as repetition, rhetorical questions, and anecdotes to make your speech more engaging and memorable. Use persuasive techniques such as ethos (appeal to credibility and authority), pathos (appeal to emotions), and logos (appeal to logic and reason) to strengthen your arguments.
Step 5: Practice and refine your speech.
Rehearse your speech multiple times to become familiar with the content and delivery. Practice speaking slowly, clearly, and with appropriate gestures and facial expressions. Time yourself to ensure that your speech fits within the allocated time. Solicit feedback from others and make necessary revisions to improve your speech's clarity, coherence, and persuasiveness.
You can also consider enlisting the help of professional speech writer . They can assist you in creating a compelling and well-structured speech that effectively communicates your message.
A path to a powerful persuasive speech outline
An outline for your speech may come in handy when you want to ease the stress and pressure of public speaking ─ it helps to organize key arguments, ideals, evidence, and supporting details. You may look at it as a skeleton for the speech that helps you to structure your thoughts and ensure you effectively convey them to your audience. We will look at how to create an outline, taking an example of the mental health issue.
1. Think of a compelling introduction.
Start with a hook that captures your audience's attention and sets the tone for your persuasive message .
"Did you know that mental health affects every aspect of our lives, from physical health to relationships and overall well-being?"
2. Smoothly immerse into the topic.
Provide background information on the topic of mental health to establish its significance.
"Mental health is a critical but often overlooked aspect of our overall health and well-being. It encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being and is crucial in our daily lives."
3. Clearly state your point of view.
Outline the main points or arguments to support your persuasive message about mental health. For example:
Importance of destigmatizing mental illness: Share stories or testimonials from individuals who have experienced stigma related to mental health and highlight the need for a more compassionate and understanding society.
4. Present a solid foundation of facts.
Support your thesis statement with credible facts, statistics, anecdotes, or examples reinforcing your persuasive message. For example:
"As someone who has personally witnessed the impact of mental health challenges in my family, I know firsthand the importance of raising awareness and promoting support for mental health initiatives."
5. Anticipate counterarguments.
Acknowledge potential counterarguments and provide rebuttals to address them. This way, your message will look more reputable.
"Mental health issues are not real illnesses, and people should just 'snap out of it' or 'toughen up.'" Then, offer evidence why it does not work like that.
6. Conclude with a powerful call to action.
Summarize your main points and conclude your speech with a compelling call to action, urging your audience to take specific steps to support your persuasive message.
"Destigmatizing mental illness, promoting mental health awareness, and offering support to those in need are crucial steps towards creating a more compassionate and inclusive society. Let us all take action today to support mental health and make a positive difference in the lives of individuals and communities."
Tips for Writing Persuasive Speech
Don't be confrontational in your argument. People are more likely to change their beliefs or behavior when they feel respected and heard, rather than attacked or belittled. That’s why you don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers. Simple statistics are much more useful because it helps the audience to understand and remember the numbers. By using statistics that are relevant, accurate, and easy to digest, you will only enhance your credibility.
Don't complicate your speech. Going outside the standard "three points" format may complicate your speech. You may want to get creative but do not go overboard by changing the format. The human brain is wired to process information in chunks, and breaking your message down into three main points makes it easier for your audience to absorb and retain.
Master your self-introduction speech. By practicing and creating a solid self-introduction speech, you will establish a connection and create a favorable impression for the audience from the very first minutes.
Learn from famous speakers. Study talks from famous persuasive speakers, such as Martin Luther King Jr., Winston Churchill, or Barack Obama, and learn from their techniques, style, and delivery.
Use storytelling. Tell compelling stories that relate to your topic and resonate with your audience. Stories are powerful tools for conveying emotions, illustrating concepts, and making your speech more engaging and relatable.
Authenticity is a key. When writing a speech, be genuine, sincere, and passionate about your topic. Avoid overly scripted or robotic language, and be yourself throughout your speech.
What is the key to a good persuasive speech?
A persuasion is a set of ethos (credibility), logos (logic), and pathos (emotion) ─ use all three elements in your speech to sound persuasive.
Which opening should I use for a persuasive speech?
It should start with an opening that grabs readers’ attention: it can be a powerful quote, a compelling anecdote, a surprising fact or statistic, a rhetorical question, or a bold statement. Utilizing a commemorative speech is an effective way to engage the audience (check our tips for choosing topics for commemorative speeches ). Once you catch the attention of your audience, make sure to clearly explain your topic idea.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Meredith Anderson
Meredith, a dedicated editor at EduBirdie, specializes in academic writing. Her keen eye for grammar and structure ensures flawless papers, while her insightful feedback helps students improve their writing skills and achieve higher grades.
Related Blog Posts
200+ interesting persuasive speech topics for 2024.
Do you want to inspire others? Do you want to get a chance to have your voice heard? Choosing a good persuasive speech topic enables you to write a...
350+ Informative Speech Topics for Students
Table of contents Informative speech topics about Technology and Science Informative speech topics about Environment Informative spee...
Free 200 Impromptu Speech Topics about Everything
Impromptu speech is task not for faint hearted and may seem more challenging than it actually is! As the name implies, it means speaking in public,...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most

Persuasive Speech Examples: Taking A Stand In Speech

Persuasive speeches have been used throughout history to shape public opinion and shape behavior, and examples abound. Persuasive speech examples include virtually any topic – voting, racism, school uniforms, safety, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
From a teenager asking his parents to go out with friends to an aspiring politician convincing voters to choose him, many people use a persuasive speech to convince their audience members to do something. A successful persuasive speech entails getting someone to take action and be swayed to the speaker’s side.
Table of Contents
What Is A Persuasive Speech?
While an informative speech aims to enlighten the audience about a particular subject, a persuasive speech aims to influence the audience — and convince them to accept a particular point of view.
The central idea is to persuade, whether discussing a persuasive essay or public speaking. This form of communication is a call to action for people to believe in and take action upon something.
Throughout history, persuasive speech ideas and their communicators have played a vital role in driving change, whether on a personal, community, societal, national, or even global level.
We’ve seen leaders and important figures sway public opinions and spark movements. Persuasive speech has been there to raise awareness about a specific issue (e.g., labor rights, gender equality). People have been using such speeches to establish authority, negotiate, and, ultimately, urge the audience to join their side.

What Are Some Examples Of A Persuasive Speech Topic?
There’s a wide range of good persuasive speech topics . To give you an idea, here’s a list of persuasive speech topics:
- Social media is taking a toll on young people’s mental health
- Cell phones and too much screen time are making people lazier
- Violent video games make people more aggressive
- Why authorities must ban fast food for children
- Schools and workplaces should take more action to curb obesity rates
- Why public schools are better than private ones
- College athletes should undergo steroid tests
- There’s more to high school and college students than their GPAs
- Should award-giving bodies rely on the popular vote or the judges’ vote?
- There’s a need to regulate the use of painkillers more heavily
- Cloning must not be legalized
- More government budget should be allocated to health care
- Why businesses must invest in renewable energy
- Should military units be allowed to use drones in warfare?
- How freedom of religion is affecting society
- Libraries are becoming obsolete: A step-by-step guide on keeping them alive
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals, clinical settings, and zoos?
- Developing countries must increase their minimum wage
- Global warming is getting more intense
- The death penalty must be abolished
What Is An Example Of How Start Of A Persuasive Speech?
Persuasion is an art. And when you’re given the chance to make a persuasive speech, one of the first things you must do is to settle down with a thesis statement. Then, you must identify at least two main points, pre-empt counterarguments, and organize your thoughts with a persuasive speech outline.
Remember that your opening (and closing) statements should be strong. Right at the start, you must captivate your audience’s attention. You can give an impactful factual statement or pose a question that challenges conventional views.
The success of a speech doesn’t only end with writing a persuasive one. You must also deliver it with impact. This means maintaining eye contact, keeping your posture open, and using a clear voice and an appropriate facial expression.
What Are The 3 Points To Persuasive Speech?
There are three pillars of a persuasive speech. First is ethos, which taps into the audience’s ethical beliefs. To convince them and establish your credibility, you must resonate with the morals they uphold.
The second one is pathos, which refers to the emotional appeal of your narrative. One approach is to share an anecdote that your audience can relate to. To effectively appeal to your audience’s emotions, you must also use language, tone, diction, and images to paint a better picture of your main point.
On other other hand, logos appeals to logic. This is why it’s important to pepper your speech with facts.
How Are Persuasive Speeches Used?
You may know persuasive speeches as those stirring speeches delivered by politicians and civil rights and business leaders. In reality, you yourself could be using it in everyday life.
There are different types of persuasive speeches. While some mobilize bigger movements, others only persuade a smaller audience or even just one person.
You can use it in a personal context . For example, you’re convincing your parent to extend your curfew or eat at a certain restaurant. In grander ways, you can also use it to advocate for social and political movements. If you’re in business, marketing, or sales, you can use persuasive speech to promote your brand and convince others to buy your product or service.
For example, a teen might try to persuade a parent to let them stay out beyond curfew, while a civil rights leader might use persuasion to encourage listeners to fight racism.
No matter the context of your speech, an effective persuasive speech can compel someone or a group of people to adopt a viewpoint, take a particular action, and change a behavior or belief.

What Are Persuasive Speech Examples?
This AI-created speech about walking shows how a persuasive speech is laid out, using Monroe’s Motivated Sequence (i.e., attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and call to action) to convey the message that walking can overcome the risks of modern life
The introduction sets up the speech:
“Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners… We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?”
Unfortunately, lack of exercise leads to health problems. Walking can overcome the effects of lack of exercise, lethargy, and poor diet. The body of the speech delves into this concept in detail and then concludes with a call to the audience to walk more.
AI pick up the pattern that many living persons have perfected over the year.
Maya Angelou, an American poet and civil rights activist, delivered this compelling poem as a persuasive speech . The performance concludes with this inspiring message about overcoming hardship and discrimination: “Leaving behind nights of terror and fear, I rise/ Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear, I rise/ Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave/ I am the dream and the hope of the slave/ I rise, I rise, I rise.”
What Are Some Historical Examples Of Persuasive Speech?
Maya Angelou is just one of the important figures who have delivered powerful speeches etched in history. These individuals have risen and relayed impactful messages, championing advocacies that would resonate with people during their time — and beyond.
Below are more moving examples of a persuasive speech:
The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
Context: In November 1863, during the American Civil War, US President Abraham Lincoln delivered this speech in commemoration of the dedication of the Gettysburg National Ceremony (also known as the Soldiers’ National Ceremony).
Snippet: “Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We come to dedicate a portion of it as a final resting place for those who died here, that the nation might live. This we may, in all propriety, do.
“ But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate, we can not consecrate, we can not hallow, this ground, The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have hallowed it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note nor long remember what we say here; while it can never forget what they did here.
“ It is rather for us, the living, we here be dedicated to the great task remaining before us that, from these honored dead, we take increased devotion to that cause for which they here, gave the last full measure of devotion that we here highly resolve these dead shall not have died in vain; that the nation, shall have a new birth of freedom, and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.”
The Finest Hour by Winston Churchill
Context: In his nearly 40-minute long speech in June 1940, over a month since Winston Churchill became the British Prime Minister, he sparked hope that they could win the impending Battle of Britain during the Second World War.
Snippet: “What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the Battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this Island or lose the war.
If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free, and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of perverted science. Let us, therefore, brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour.’”
I Have a Dream by Mary Wollstonecraft
Context: In her 1792 speech, the British writer and women’s rights advocate shared her dream — that a day will come when women will be treated as rational human beings.
Snippet: “These may be termed utopian dreams. – Thanks to that Being who impressed them on my soul, and gave me sufficient strength of mind to dare to exert my own reason, till, becoming dependent only on him for the support of my virtue, I view, with indignation, the mistaken notions that enslave my sex.
“ I love man as my fellow; but his scepter, real or usurped, extends not to me unless the reason of an individual demands my homage; and even then, the submission is to reason and not to man. In fact, the conduct of an accountable being must be regulated by the operations of its own reason; or on what foundation rests the throne of God?”
These snippets of their persuasive speech capture the very essence of this form of communication: to convince the audience through compelling and valid reasoning, evoking their feelings and moral principles, and motivating them to act and join a movement, big or small.
Recent Posts
Active Listening Absorbs The Whole Message, Not Just The Words
Active listening goes beyond hearing the words someone is saying to you and understanding the message they are conveying. Many only hear a small percentage of what is being said as they are...
Counteracting Fear Of Public Speaking With Coaching And Therapy
Nearly 75% of people experience the social phobia of fear of public speaking. The result may be nervousness before speaking or a full-blown panic attack. Practicing public speaking may lessen the...
An Impressive Persuasive Speech Outline: Examples & Guide
Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a persuasive speech outline and see great examples.
But first… what is a persuasive speech, after all?
A persuasive speech is a speech that convinces people of certain ideas, values, and beliefs. As its specific purpose is proving a point, it relies on one successful format. You’ll see it here in our persuasive speech outline examples prepared by our experts .
- 🖊️ Make the Creative Process Flow
- ✍🏻 The Components of Ideal Writing
- ✔️ Check This Unique Template
- 🔮 Check 50 Persuasive Speech Topics!
- 📙 Read a Masterpiece of Writing!
1. 🖊️ Persuasive Speech Outline Format: Make the Creative Process Flow
Custom-writing.org prepared this guide on how to develop a perfect persuasive speech outline for you:
- Pick a certain problematic issue you’d like to talk about;
- Think of an unusual way to introduce it to the audience;
- Use an approach grip the readers’ attention;
- Structure your argument to make it a logical sequence;
- Follow the traditional intro – arguments – discussion – conclusion outline;
- Use your imagination and creativity!
2. ✍🏻 The Components of Ideal Writing
Hush! You’re about to learn a secret:
There IS a perfect formula for a format for persuasive speech outline!
Check this:
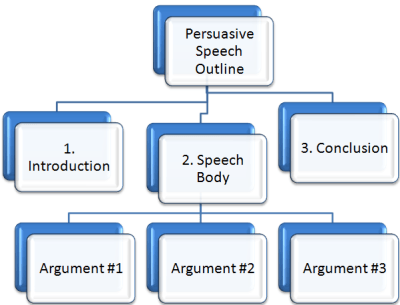
- The Introduction Section:
- Attention-Getter;
- Taking by Storm;
- Building Bonds of Trust.
- The Speech Body: 1st Paragraph:
- The Case in Point;
- The Evidence;
- The Supportive Ideas;
- The Case for the Changes.
- Reasoning #1:
- Reasoning #2:
- The Case for the Changes;
- Reasoning #3:
- The Conclusion
With such an outline, you’ll get a persuasive speech a student can only dream of! All in all, your persuasive speech outline should look the following way:
3. ✔️ Check This Unique Template
Do you want to create the perfect outline for your speech? Follow these tips:
- Think of an unusual and controversial issue;
- Develop your own idea of the issue in question;
- Give credit to opposite opinions;
- Structure an argument on the issue;
- Remember about the AIDA principle;
- Offer a unique solution and draw a conclusion.
That’ll take care of your speech.
All in all, your persuasive speech should answer the question whether something should or should not take place and why.
4. 🔮 Check 50 Persuasive Speech Topics!
Do you know the secret formula of perfect persuasive speeches?
Perfect wording + perfect logics + speech topics + sense of humor = perfect persuasive speech.
You won’t have problems with the sense of humor, that’s quite clear.
What you need though, is a couple of good persuasive speech ideas.
So, read these Top 50 Best Topics for Writing an Unbelievable Persuasive Speech :
- 2012 : why there was no catastrophe coming.
- Being an individual while also remaining part of the group: the mechanics of social behavior .
- Should parents control their children’s online pastimes? The threat of ‘adult’ content.
- Alien life forms: further search for extraterrestrial intelligence should be encouraged.
- Paranormal phenomena: a piece of evidence worth trusting or another make-believe?
- Explain why marijuana should be legal.
- The reasons why minimum wage should be increased in the US.
- Describe the reasons to raise taxes on high-fat food.
- It is necessary to abolish the death penalty.
- Explain why bullies should be expelled from school .
- Explain why the government must revise gun control legislation.
- Give reasons to use animals for research purposes.
- Student-athletes should be paid for participating in sports.
- Clarify your reasons for prohibiting young children from playing tackle football.
- To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee should be taught in schools .
- Elucidate the necessity to make abortion a part of the national healthcare plan.
- The reasons why people should be forbidden to sell their body organs .
- Testing medicines on animals should be strictly prohibited.
- Scare them straight: juvenile delinquency should be dealt with quickly and harshly.
- Explain why it is necessary to teach evolution in schools.
- Arranged marriages are less happy than marriages based on love.
- It’s a good idea to ban American football for being too dangerous.
- The grounds to prohibit the use of cell phones in public places .
- Give the reasons to allow animal transplantation.
- Why online dating must not be considered real dating.
- Canceling grades in schools will bust students’ motivation to study.
- Explain the reasons people should not send expeditions to Mars.
- It is necessary to forbid clear-cutting in rainforests.
- The criminal justice system should try juveniles as adults for serious crimes.
- Why smoking in public places should be made illegal.
- Advocate the necessity to lower TOEFL scores for university admission.
- Celebrities should be positive role models .
- Why tattoos should be considered art.
- Explain why illegal immigrants should have full access to social services.
- Why biometric security should be a primary focus of modern companies.
- The reasons to prohibit the use of cell phones while driving .
- Cameras in public places are necessary for the security of citizens.
- Mandatory job drug tests will increase productivity and improve the working environment.
- Why puppy mills should be outlawed.
- Mandatory overtime has a negative effect on nursing performance and must be prohibited.
- Screen time for children must be strictly limited.
- Give the reasons why higher education should be free.
- The reasons why tobacco products and cigarettes should be banned.
- Explain why the government should revise laws protecting animal welfare .
- Human cloning should be illegal.
- Elucidate the reasons why same-sex marriage should be legal.
- The government should make big corporations participate in crime-prevention programs.
- Explain why vaccination for children should be mandatory.
- It’s impossible to make any immoral behavior illegal .
- Remote work should become a norm.
These persuasive topics will definitely get you an excellent grade! What’s more, they’ll help you create your own topics for persuasive speech!
5. 📙 Read a Masterpiece of Writing!
It’s time to see some examples of persuasive speech writing. Write as professionals do!
A Persuasive Speech on Family Values

In the modern world, the importance of family values has been downshifted by the need to build a career. Busy with climbing up the career ladder, people forget about the essence of the family. And everyone who has ever heard their parents saying, “Not now, darling, Daddy’s busy,” or saw their mothers working late after they went to bed knows how big the problem is.
It is obvious that career development and promotion have become the essence of modern people’s lives. Unfortunately, according to the statistics, in most cases relatives suffer. As reports say (Smith 2011, p. 111), in 60% of the cases, working parents know very little about their children’s social life.
It cannot be argued, however, that a stable career and salary are not the crucial elements of modern life. Without a stable source of money and a career, one is most likely to feel insecure; moreover, the family can suffer financially. Hence, it is obvious that the career must not be forgotten either.
Therefore, it can be suggested that a balance between these two aspects of everyday life must be maintained. According to Johnson (2000, p. 98), 10% of families manage to both lead a happy family life and succeed in their work. Hence, a specific plan is required to remain both a good employee and a good parent.
Among the possible solutions for the situation, splitting responsibilities can do the trick. When scheduling their lives, parents can spend more time with their children and each other. Moreover, work efficiency will increase when following an established plan.
That’s what they call a speech example! Now you’re fully equipped to create the persuasive speech of the decade – so start the writing process!
You might also be interested in:
- Easy Steps to More Persuasive Essays
- Best Sports Persuasive Speech Topics
- Best Easy Persuasive Speech Topics
- Persuasive Speech Outline: The Recipe for a Successful Outcome
- Funny Persuasive Speech Topics: Best Ideas
- Racial Profiling Essay: Argumentative & Persuasive Writing
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![persuasive speech outline Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![persuasive speech outline Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...

You might be wondering about how to write a conclusion paragraph for a research paper. It may seem like your readers should understand your main arguments by the end, so there is no need for it. However, there are several aspects that prove the importance of a conclusion section in...
![persuasive speech outline American Antiquity Style Guide: Citation Rules & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/education-concept-books-laptop-library-284x153.jpg)
American Antiquity is a professional quarterly journal, which contains various papers on the American archeology. It is incredibly popular among archeologists and the students majoring in history. The organization adopted the rules of The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) citation style. As a result: The journal includes numerous references that...

The most tedious and time-consuming part of any school or college written assignment is the bibliography. Sometimes, it can even be challenging! For example, if you’re confused by the variety of citation styles. That is why Custom-Writing experts prepared a brief guide about creating a perfect bibliography for a project....

An appendix is the part of the paper that contains supplementary material. The information from an appendix in paper writing is not essential. If the readers ignore this part, they still have to get the paper’s idea. Appendices help the readers to understand the research better. They might be useful...

Writing an abstract is one of the skills you need to master to succeed in your studies. An abstract is a summary of an academic text. It contains information about the aims and the outcomes of the research. The primary purpose of an abstract is to help readers understand what...

So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.

Looking for relevant sources of information for your research is already a tiring process, but when you also need to pay attention to their credibility, it becomes almost impossible! However, it’s still a quite critical aspect to pay attention to. Using unreliable sites like Wikipedia, even if it’s a two-page...
![persuasive speech outline How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/research-charts-284x153.jpg)
Only two words, but you already feel a chill down your spine. A research paper is no joke. It’s a super detailed piece of academic writing where you analyze a chosen issue in-depth. The main aim of such torture is to show how knowledgeable you are and that your opinion...

A research proposal is a text that suggests a topic or research problem, justifies the need to study it, and describes the ways and methods of conducting the study. Scholars usually write proposals to get funding for their research. In their turn, students might have to do that to get...

It’s longer than your Bachelor’s thesis. It’s more stressful. It’s more important. And you have no clue how to write it. We understand that a lot comes with the responsibility of creating a Master’s thesis from scratch. But no need to stress out; you can get all the help you...
Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples
What is a persuasive speech.
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
| Benefits of healthy foods | Animal testing | Affirmative action |
| Cell phone use while driving | Arts in education | Credit cards |
| Climate change | Capital punishment/death penalty | Fossil fuels |
| Extinction of the dinosaurs | Community service | Fracking |
| Extraterrestrial life | Fast food & obesity | Global warming |
| Gun violence | Human cloning | Gun control |
| Increase in poverty | Influence of social media | Mental health/health care |
| Moon landing | Paying college athletes | Minimum wage |
| Pandemics | Screen time for young children | Renewable energy |
| Voting rights | Violent video games | School choice/private vs. public schools vs. homeschooling |
| World hunger | Zoos & exotic animals | School uniforms |
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”
How a Speech Outline Can Help You Persuade Your Audience
Contrary to many politicians, Winston Churchill wrote all of his speeches. From his famous “We shall fight on the beaches” speech addressed to the House of Commons in 1940 to the scores of others, Churchill wrote and delivered his speeches in his own way. Despite his contemporaries describing him as “a word-spinner,” and, “a second-rate rhetorician,” people remember Winston Churchill’s words even today. And in his hand during a persuasive speech, you could almost certainly see a piece of parchment that was his speech outline.
Why Use a Speech Outline?
An organized speech is also more persuasive. A speech where you show your points in a scattershot manner, even if they’re good points, won’t have the same impact as one where you lay out your main points in a logical, convincing fashion. In other words, writing an outline for a persuasive speech will help your comments stay with your audience for longer.
The Two Outline Types
Preparation outline, speaking outline.
The speaking outline is what many people think of when they hear the term “speech outline.” This is the outline you’ll actually have with you when you deliver your speech. The speaking outline shows all the points you want to hit, including any phrases or quotes you’ll want to say word for word. The points serve as helpful guides, allowing you to navigate your way through the speech without needing to look at your papers constantly. This outline acts as a reference point to make sure you provide all the information you want but still sound natural in your delivery. Many people choose to put this outline on notecards that they carry with them as they give their speeches.
Speech Outline Template
Purpose statement, thesis statement, introduction.
The introduction is what will hook your audience. Once you know how to start a speech, you’ll be able to grab people’s attention so you can begin to persuade them. An introduction also establishes a connection with the audience. It indicates why they should listen to you. Openings can also serve as a preview of what you plan on talking about. Getting the speech introduction right is vital because if you lose the audience initially, it becomes challenging to win their attention back.
Bibliography
Transitions.
While preparing your speech, you should also prepare transitions between each of the above sections. Whether moving from the intro to the body or the main point to a sub-point, transitions help smooth out a speech and keep people following along with little effort. Make sure your transitions flow seamlessly from one point to the next. Without them, a speech can come across as jarring and difficult to understand.
Speech Outline Example
Use a speech outline for next time.
Dale Carnegie once said, “There are always three speeches, for every one you actually gave. The one you practiced, the one you gave, and the one you wish you gave.” By creating a speech outline, you’ll show your audience the poise of a practiced public speaker, even if you still get nervous. An outline will help you give an effective speech, one you can be proud you gave no matter what the topic is about.
Want to learn more skills as a leader? The following articles can help:
Top 18 Conflict Resolution Skills Every Leader Needs

49 Sample Persuasive Speech Outline
Student Example
Persuasive Speech Outline
- This is a student example of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- This student’s outline is well developed, coherent, integrates research, follows a strong organizational pattern, and meets all expectations of an outline in a public speaking course.
- Click on the Google Document provided for a sample speech outline.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Free Persuasive Speech Generator
- ✅ 6 Benefits of the Tool
💬 What Is Persuasive Speech?
📍 how to write a persuasive speech, 💡 top 20 persuasive speech topics, 📝 4 world-famous persuasive speech examples, 🔗 references.
Do you have a pending persuasive speech assignment but need some push to help you do it perfectly? No worries; you can use our persuasive speech generator to create informative speeches quickly.
The free automatic AI generator is one of the best to boost your speech writing on any topic.
✅ 6 Benefits of This Persuasive Speech Generator
How can this instant generator benefit your speech-writing efforts?
Our tool has many benefits, but we focus on the 6 most important ones:
| 🎯 Specialized | Our persuasive speech generator is specifically designed to match all the requirements of drafting a speech of this genre that will be remembered. You can’t go wrong with its matching power. |
| 🔢 Structural | Our speech builder lets you generate logical and well-structured speeches that motivate your listeners to listen to you until the end. |
| 🎨 Creative | This persuasive speech generator ensures you don’t worry about the correct or most suitable vocabulary for your text. It does everything for you and chooses the best vocabulary based on your speech’s theme. |
| 🦄 Inspiring | The online speech maker helps you draft your speech effortlessly and saves you the dreaded writer’s block hassles. |
| 🚀 Quick | The persuasive speech generator saves you precious writing time to enable you to invest that time in other valuable activities. |
| 💸 Free | No longer need to worry about subscription or renewal fees for premium speech builders. You can use our persuasive speech generator free of charge and enjoy its functionality without spending a penny. |
As the name suggests, a persuasive speech influences listeners’ behavior, attitudes, beliefs, and values.
In this speech, a speaker seeks a favorable response that aligns with their convictions or position on a matter.
An orator uses arguments to convince their audience to see a particular issue from their preferred perspective. Convincing arguments incorporate different elements to urge listeners to favor a speaker’s stand.
They follow a three-prong strategy incorporating:
A claim is a statement requiring support through evidence. Your speech should also include a thesis statement, your speech’s overarching idea from which other smaller ideas spring.
Informative vs. Persuasive Speech
An informative speech differs from a persuasive one in many ways.
| Informative speech | Persuasive speech |
|---|---|
So, how do you write a great persuasive speech that makes listeners adopt your preferred position on a matter?
Below are steps to drafting a great convincing speech.
Know Your Audience
Start by familiarizing yourself with your listeners before moving by knowing their needs, tastes, and ability to understand your desired topic.
This way, you will be better positioned to customize your speech to suit their needs and not parade your vast knowledge.
Familiarize Yourself with Your Topic
Get to know your topic to ensure it suits your audience’s needs. If you aren’t familiar with the topic, research it thoroughly to present your readers with facts.
This way, you will be better positioned to present your listeners with sufficient facts to persuade them.
Determine Your Speech’s Goal
A speech is not only about organizing facts in a logical manner; it is usually meant to persuade the audience and deliver a specific message across .
You, as a speaker, should focus on that message and find appropriate means to get it across.
Select the Best Persuasive Approach
Determine the best approach to persuade your listeners. You may lean on either ethos, logos, or pathos to achieve your desired goal. You can also use all of these approaches.
The final selection will depend on your audience.
Outline Your Key Ideas
You need to outline your best points before presenting them to your audience.
This way, you are better placed to know which argument to present first and last.
Start on a Strong Footing
You must begin your speech with a strong, attractive hook to capture your audience’s attention.
Your opening needs a catchy title that whets your audience’s appetite to listen to your speech.
Give Convincing Evidence
Your speech’s main body should include the points you want to use to convince listeners to side with your position.
Give your audience convincing examples and reasons to buy into your perspective.
Address Counter-arguments
Don’t forget to address opposing arguments because others have a right to hold contrary views and not accept your point right away.
While this may not be necessary, you can bolster your case by anticipating and discussing opposing views.
Finish with a Call to Action
Since you defined your speech’s goal, don’t forget to make a relevant call to action .
Remember, this part is like your landing pad.
Below are carefully selected persuasive speech topics to inspire you.
- Martial arts benefit the mind.
- Competitive sports have many mental benefits.
- Games have many positive social benefits.
- Make community service mandatory for college graduation.
- Traits that make up real heroes.
- Letter grades should be replaced with pass or fail .
- The real secret to success.
- Public libraries should filter internet pornography .
- Video games promote violence.
- Should abortions be illegal as a form of homicide ?
- Dirty music promotes immorality.
- Beauty pageants for children should be banned .
- Parents should spend more time with their children.
- Why junk food should cost more than healthy food .
- Tablets are better than laptops.
- Why should there be a four-day workweek ?
- Ban school uniforms.
- The internet should remain open source .
- Security cameras violate privacy.
- Vote by mail: should it be allowed ?
Below are the top four world-famous persuasive speeches to get inspiration from.
I Have a Dream by MLK
This speech embodies the black community’s search for equality. Martin Luther King voiced his opposition to the segregation against Africans when white supremacists sought to keep Africans in inferior positions using the backdoor. The leader envisioned a society where equality would replace racial discrimination.
Ain’t I A Woman by Sojourner Truth
This speech by an African woman embodied the quest for equal human rights during the season when oppression and slavery were at their peak. Truth was one of the leading advocates who fought for women’s rights in the 19th century. She delivered this speech at an 1851 Women’s Rights Convention in Akron, Ohio.
I Am Prepared to Die by Nelson Mandela
This Nelson Mandela speech echoes the struggle to end apartheid in South Africa. Mandela risked his life to fight state-sponsored discrimination against Africans. Mandela was prepared to die for this just cause.
The Audacity of Hope by Barack Obama
This famous speech by the son of a Kenyan student who made it to become a US President shows the power of transformational hope. The speech is based on Obama’s focus on patriotic optimism and determination as change catalysts. This speech catapulted him into the limelight and led to his popular election as America’s first black and youngest president.
❓ Persuasive Speech Generator FAQ
Updated: Jul 19th, 2024
- What Is Persuasive Speech? (Plus 10 Tips for Creating One)
- Persuasive Speaking
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- How to Write a Persuasive Speech: 13 Steps (with Pictures)
- Persuasive Speech Types & Features
- Persuasive Speaking – Speak Out, Call In
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Q&A by Experts
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Editorial Policy
- Job Openings
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- Brand Guidelines
- IvyPanda Shop
- Online Courses
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
IvyPanda's AI-powered Persuasive Speech Generator will quickly create a sample speech you can use for inspiration. Just add the key points and briefly describe your audience. Our free online generator will craft a convincing and engaging speech momentarily.

- VisualStory®
- Duarte DataStory®
- Presentation Principles™
- Slide:ology®
- Slide Design
Speaker Coaching
- Presenting Virtually™
- Illuminate™
- Adaptive Listening™
- Team training
- Learning journeys
- Brand and product storytelling
- Keynotes and events
- Sales enablement
- Communication systems
- Accelerator Lab™
- Our culture
- Our leaders
- Case studies
- Media mentions
- Guides and tools
- Learner support
The art of persuasive speech: How to speak with confidence

Phoebe Perelman
The spoken word is a catalyst for change. From the boardroom, to the newsroom, to the courtroom, to the dining room – words are used not only to inform, but to influence. Every speech you give and conversation you have are opportunities to shape the world around you. In our inundated information economy, the value of your ideas is determined by your ability to persuade.
What is a persuasive speech?
A persuasive speech is a form of communication intended to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and actions of others. Whether you’re an L&D leader shaping organizational culture, a sales manager overseeing a team, or a social media strategist responsible for justifying ad spend, persuasive speaking is an integral part of your job description.
I’m sure you can think of some prime persuasive speech examples. Maybe Martin Luther King, Jr.’s ‘I Have a Dream’ speech comes to mind. Or Al Gore’s ‘Inconvenient Truth.’ Or maybe that time your daughter tried to convince you to adopt a ferret.
Persuasive speeches come in many forms, but some persuasive speeches move masses (or result in new family mascots), while others don’t make a dent. Why?
Why your persuasive speaking might not be working
If you’ve ever failed to foster organizational change, close a deal, or motivate a team, you may be thinking more about what you want to say than what the audience needs to hear. We’ve all been there! But in order to persuade people, you first need to understand them.
Reason #1: Not studying your audience
Put yourself in the audience members’ shoes by answering the following questions:
- Who are they?
- What do they do?
- What do they dream of?
- What keeps them lying awake at night?
- How will your idea, product, or point of view benefit them or solve a problem they care about?
- What are their existing feelings and beliefs about the topic at hand?
By considering what they care about, you can determine the type of content they’ll resonate with. And by acknowledging their resistance points, you can prepare to address any counterarguments or rebuttals.
Reason #2: Not using enough data
Another common pitfall we see is when speakers lean too heavily into emotional content without including any supporting evidence. Your argument will stall quickly if there’s no research, data, or other qualitative and quantitative metrics to back up your Big Idea™.
Reason #3: Not communicating your data well
On the opposite spectrum, speakers can also lean too heavily into logical content, relying solely on facts and figures with no story. “ Data doesn’t speak for itselfe , it needs a good storyteller,” says Nancy Duarte, CEO of Duarte Inc. “The findings [from the data] can stay buried without the help of a communicator.”
Neither instance is ideal. Persuasive speeches and presentations alike require a rhetorical juggling act with three specific elements.
You can learn more about this in our best-selling workshop, Duarte DataStory®. It was specifically designed to help professionals in data-intense roles learn how to communicate better, and tell stories through their data, to win buy-in.
How do you craft a persuasive speech?
Persuasive speeches need three imperative components. And these three persuasive speaking components have held true for over 2,000 years. We all have Aristotle to thank for this timeless wisdom. They are ethos, pathos, and logos, and we’ll go into why they are needed when you begin to structure your persuasive speech.

3 components of a persuasive speech structure
Make sure your persuasive speech structure includes some aspect of the three below elements. They are a huge tool for ensuring your persuasive presentation is a success.
Ethos: Establishing credibility
Establishing credibility as a speaker is crucial to winning over an audience. After all, would you take advice from a doctor who hadn’t gone through medical school? I think not. People are more likely to listen to someone they perceive as:
- Knowledgeable
- Trustworthy
- And ethical
You can establish credibility by demonstrating confidence, conveying your expertise, and sharing relevant experience (in a humble, non-braggy way of course).
Pathos: Emotional appeal
One of the most effective persuasive strategies is tapping into the emotions of your audience. We can learn a lot about emotional appeal by looking at advertisements. Companies aren’t just selling a product – they’re selling a feeling, or a better state of being. Cars become calls to adventure, clothing becomes a boost of confidence, and software becomes a time-saver. These outcomes are illustrated through stories, metaphors, and vivid language or imagery. The same tactics can be incorporated into a persuasive speech.
Logos: Logical appeal
No matter how trustworthy you seem, or how compelling your stories are, most people need tangible proof. That’s why concrete evidence is essential to any speech or presentation. Include facts, statistics, customer examples, and expert validation to bolster your claims and enhance the credibility of your message.
As I said above, it’s important to cover your bases and include elements of all three persuasive appeals when outlining your main messages. Speaking of outlines…
How to use a persuasive speech outline
Now that you have your three components for your persuasive speech structure, it’s time to make your persuasive speech outline.
Step 1. Identify your Big Idea™
Start by determining a Big Idea™ for your talk. What is the main point you want the audience to walk away with? This will serve as a thesis of sorts.

Step 2: Compile content to validate your Big Idea™
Next, determine what key messages you need to make to validate your Big Idea™. These may include problems, solutions, topics, specific events, periods in time, etc. You can then start to organize these messages into chapters.

Step 3: Gather supporting points
Once you’ve defined your chapters, you can add supporting points. Those are your stats, quotes, stories, use cases, metaphors, personal anecdotes, etc.
Step 4: Read it back and fill in gaps
Your outline is probably looking good by now, but you’re not quite done. Review your outline out loud to see how it transitions from one point to the next. This is your chance to rearrange and reconsider your content. Ask yourself:
- Does my outline address the audience-specific questions posed earlier?
- Have I incorporated every side of the rhetorical triangle?
- Does it flow?
- Am I using contrast to keep my audience engaged?
Once you feel good about the messy middle of your presentation, start to brainstorm a captivating hook and compelling call to action.
Step 5: Determine your visual aids for your persuasive speech
Visual aids come in all shapes and sizes. Depending on your audience size, goals, and intent, there are a multitude of options when it comes to selecting the right visual aid for your persuasive speech. We’ve covered the topic of how to choose the right visual aid for your speech, so let’s assume is a presentation (our specialty!)
What is a persuasive presentation?
A persuasive presentation is when you choose to deliver your persuasive speech with the use of a digital presentation deck. This is typically done with slide presentation software, and they usually have helpful features like speaker notes or slide templates to help you tell your story in a visually appealing way.
Presentations offer something that speeches don’t: visuals. Visuals enhance your ability to elicit emotion and provide supporting evidence.
The most persuasive slides are simple, easy to understand, and complementary to your verbal message. So, keep your main message in mind, stick to one idea per slide, and make sure your slides can pass the Glance Test™.
Want more info on slide design principles? Allow me to save you some reading time by directing you to our on-demand webinar: Designing slides and visual aids that pop.
What is a call-to-action speech?
If you don’t intend to move someone with your persuasive presentation, then you might as well send an email. A call-to-action speech is the same as a persuasive speech. It should move your audience into action through the art of persuasion.
At Duarte, we believe that every speech is a persuasive speech, and no persuasive speech is complete without a call to action. A call to action is a directive for the audience based on your end goal. What do you want to achieve with this talk and what do you want the audience to do to help you achieve that goal?
- Champion your brand?
- Complete a training course??
- Schedule a second sales conversation?
A call-to-action could also involve changing belief systems or getting the audience to adopt a new point of view. Maybe you don’t need them to act on something, but instead to feel differently about a person, product, or process.
Before developing your CTA, ask yourself: “who are they when they walk in the room, and who do I want them to be when they leave the room?”
What qualities do you need to improve your persuasive communication?
Persuasive speaking involves more than just content. You could have the most robust, audience-centric script, but without public speaking prowess, your efforts will go to waste. The way you deliver your speech or presentation has everything to do with the likelihood of influencing an audience. Capturing and holding an audience’s attention requires a certain type of stage presence. Fortunately, you don’t need to be born with uncanny charisma – you can learn how to leverage your voice and speak with confidence.

The best way to nail your persuasive speech is with Duarte
There’s a lot that goes into persuasive speaking. And that tracks – it’s not easy to change people’s actions and beliefs! The content you choose, the visuals you use, and the way you deliver all play a role in persuasion. And more often than not, it’s helpful to seek an outside perspective to pressure test your persuasive speech.
Duarte works with the world’s biggest brands to develop persuasive stories and visuals that have won countless hearts and minds. From CEOs giving their keynotes to thousands, to product marketers getting their go-to-market product launches just right, we can help!
So, if you’re prepping for a main-stage or career-defining event where you need to influence an outcome, consider working with a persuasive expert from our agency.
If you’re confident in your content, but not in your persuasive stage presence, hone in on delivery by working with a speaker coach.
Or, if you don’t have a specific persuasive presentation to prepare for, but want to learn how to shape ideas into persuasive narratives, you can enroll in a public speaking and presentation skills course like Resonate® that will teach you how to:
- Analyze your audience so you can deliver value, even when they resist
- Clarify the core of your idea
- Create supporting content with the story structure used by history’s greatest communicators
- Distill and communicate complex ideas with clarity
And that concludes the persuasive speaking basics. Let’s recap. The best way to prepare for persuasive speaking opportunities is to:
- Think audience-first
- Consider counterarguments
- Incorporate ethos, logos, and pathos
- Use an outline
- Craft a clear call to action
- Add visuals if possible
- Refine your delivery
- Pressure test with an external perspective (like ours)
Put these tactics to the test before your next persuasive speech and see just how influential you can be.

Check out these related courses
Captivate™
Improve your public speaking
Overcome bad habits, conquer fears, and increase your confidence in any speaking setting. Discover your strengths and build on them to improve your delivery.
Personalized help for speakers
Up-level your speaking skills with one-on-one support. We’ll help you rehearse your talk, polish your presence, and transform your message delivery.
Presentation Principles™
Learn presentation basics
Follow a step-by-step method to write compelling stories, amplify ideas visually, and present with confidence while learning at your own pace.
Check out these related resources

Why you should absolutely avoid using filler words (and how to actually stop)
Want to learn what are filler words and how to stop using them for good? Use these expert public speaking tips to nail your next board meeting, presentation or keynote and learn to embrace the “pause for effect.”

17 rhetorical devices that will make you sound like Steve Jobs
Want to communicate like Steve Jobs? Join us in an analysis of one of his most famous speeches and how he employed rhetorical devices to make it memorable and moving.

How to stop that stutter: 7 steps to overcome presentation performance anxiety
Whether you stutter or suffer from anxiety before a presentation, learn 7 steps to help you calm the stutter, and your nerves, for your next presentation or big-stage moment.

Walking decks 101: A beginner’s guide and why you need one
Learn everything you need to know about walking decks, what they are, how to use one, and all the use cases for one.

How to design and deliver an investor pitch deck that gets funded
Learn tips and tricks to use for your investor pitch deck from the experts in presentation design and persuasive communication.

How to choose the best presentation coach for your needs
Unlock the key strategies for selecting the best presentation coach tailored to your specific needs to enhance your public speaking abilities.
Outline Templates
Persuasive Speech Outline Template – 15+ Examples, Samples & Formats
The audience is staring at you, ready to hear you speak. They are eager to hear what you have to say. This is your first speech in front of a large crowd, and it is your duty to persuade them. You come with nothing but your brain, assuming that because you are passionate over the subject, you will remember everything you need to say. However, as you start speaking it is clear to you, and to the looks of some of the members listening, that you do not remember everything you needed to remember. You start to mixing-up words and sweating, knowing that you should have filled out a persuasive speech outline template.
All of this could have been avoided with a simple persuasive speech outline template. Persuasive speech outlines help keep things organized and put in a logical form. So, in this article I would like to present some tips on how to make a speech outline format , and some great examples and templates to go with them.
However, the first thing to do is talk about how to write a persuasive speech outline. The first thing you need to do is find out what your topic will be. This should be at the top of your outline template , that way you will remember to stay on topic! Under this there should be an introduction, which has a short amount of information that will help you remember what to say.
From here there should be at least three main points in the speech to talk about, and within each point there should be at least two or three sub-points. Each of these sub-points should be talked about in the speech, and each one should have a short description or some short facts with it.
Finally, there should be a conclusion. Make sure to have something to help you remember to tie everything together and recap a little for the audience.
Here are some templates, samples and formats to help with your persuasive speech, whether it be for a class or for a job. Good luck and remember to have some fun with your speech! It makes all the difference in the world.
Speech Outline Template
A Speech Outline Template organizes your thoughts, ensuring clarity and flow in your speech delivery. By highlighting key points and arranging them logically, it aids in effective communication. Whether you’re a novice speaker or seasoned orator, this free template can help you.

Download Source: https://www.highfile.com/informative-speech-outline-template/
Blank Persuasive Speech Outline Template

Persuasive Speech Outline Format

Persuasive Speech Outline Example in Word

Persuasive Speech Outline Example

Persuasive Speech Outline Sample

I would now like to go over some examples of persuasive speech outlines and why they are important. The first is persuasive speech outlines for college students. I’ll use a dream reason example. If a student is going to make a persuasive speech over dreams and how they enhance our memory, their outline would have something like “Dreams, the memory enhancer”. They would then have and introduction point, where they talk about the importance and relevance of this topic, mainly, that of how it can help with exams in class. Then their first main point would be a bullet point, like a study done. From there they would talk about the implications of this study. This would be the same for the next two points, and then a conclusion, in which a few things are written down to help remember how to tie it all together.
Persuasive Speech Outline for High School Students

Persuasive Speech Outline for College Students

Individual Persuasive Speech Outline Template

Texting and Driving Informative Speech Outline

Persuasive Speech Outline Example on Texting While Driving

Persuasive Speech Outline Sample (Monroe’s Motivated Sequence)

There is also cause and effect persuasive speech outlines, in which you would start out with a title over a topic you have picked, like smoking can cause lung cancer. You would then have an introduction that has the points you will be making and a few words on what the topic is about. The first bullet point should be your most persuasive argument and it should have a few sub-points that speak of the facts and statistics. The next point could be some studies done on it, and the last one could have some examples. Then the conclusion can bring all those together to form a solid argument in your favor.
Persuasive Speech Problem Solution Outline Format

Persuasive Speech Problem Cause Solution Outline Format

These are some persuasive speech problem solution outline examples that are sure to help you in your speaking. Along with these solutions, here are some tips and guides I want to share, that way you will be able to better create an outline that matches your personality. These outline guides are especially helpful for beginners or anyone who is stuck!
Persuasive Speech Outline Template and Guide

How to Plan and Draft Your Persuasive Speech (PowerPoint Slides)

How to Write a Persuasive Speech Outline

Tips for Writing a Persuasive Speech Outline
- Make it short – I have been in a situation before, where I wish I had had that outline. Persuasive speech outlines for college students are important because so many of our classes involve speeches given to our classmates, and trying to convince them of something. However, when you do this you cannot be standing in front of the class staring at a bunch of papers. An outline should be just that, an outline. It is there to help you remember what to say and when to say it! If your speech is on a research then research outline template might be helpful for you or you may also like to see some presentation outline formats .
- Keep it flowing logically – There are also cause and effect persuasive speech outlines. These are especially helpful because cause and effect speeches have a lot of logical ideas in them. Logical ideas, though good, can be hard to remember, and so writing them down in an outline helps a lot. The outline should flow logically, and it should be written in the order of how you are going to speak.
- Always start with an introduction and end with a conclusion – This is so important in any kind of speech. The introduction gives the audience an idea of what you will be talking about, and the conclusion brings it all together. You will be hard pressed to ever find a speaker who does not have an introduction and a conclusion.
Leave a Comment
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the steps to prepare and deliver a persuasive speech, from choosing a topic and angle to building an effective argument and conclusion. See examples of persuasive speech outlines on various topics and get tips on how to write your own.
Learn how to write a persuasive speech outline with tips, topics, and examples. Find out how to structure, deliver, and address counter-arguments in your speech.
Learn how to create an effective persuasive speech outline with examples and tips. Find out the components of a persuasive speech, such as introduction, body, and conclusion, and how to organize them logically.
Learn how to use Monroe's Motivated Sequence, a 5 step pattern for organizing persuasive speeches, with an example on fear of public speaking. Download a blank outline template and get more persuasive speech resources.
Learn how to write an effective persuasive speech outline with tips and tricks on identifying your main objective, organizing key points, selecting topics, enhancing persuasion, and crafting a captivating structure. Find out how to use rhetorical appeals, supporting evidence, counterarguments, and Monroe's Motivated Sequence to convince your audience.
Learn how to write a persuasive speech that makes logical and emotional sense to your audience. Follow a simple 3-step process: start with a story or example, explain your argument, and end with a call to action.
Learn how to craft a persuasive speech outline that guides you from start to finish and convinces your audience with clarity. Find tips on structure, research, transitions, timing, visual aids and more.
Learn how to craft a persuasive speech outline that engages your audience, taps into their emotions, and guides them to your point of view. Find out how to select captivating topics, structure your main points, and master persuasive speaking techniques.
Learn how to write a persuasive speech with a 7 point checklist that covers topic selection, goal setting, audience analysis, evidence, balance, structure and more. Find speech topic suggestions, tips and resources to help you persuade your audience.
Learn how to choose a topic, write a hook statement, and present three main points with evidence to convince your audience. Follow the standard speech format with an introduction, body, and summary.
Creating a Persuasive Speech Which Calls For Action Using an Outline Format Before you begin: We already know that your purpose is to persuade. The purpose statement expresses the goal of the speech. Formulating it lets you identify precisely what you want the speech to accomplish. In the case of your speech, what do you want the governing body ...
Example of a persuasive speech outline. In 3 minutes you need a clear thesis, 2-3 main arguments reinforced with facts/examples, and a concise conclusion recapping your request. Example 1: Title: schools should switch to a 4-day school week. Specific purpose: persuade the school board to adopt a 4-day school week schedule.
Learn how to craft a persuasive speech that appeals to ethos, pathos, and logos. Follow a step-by-step guide and get tips from experts on choosing a topic, structuring your speech, and using persuasive language and techniques.
Persuasive speeches have been used throughout history to shape public opinion and shape behavior, and examples abound. Persuasive speech examples include virtually any topic - voting, racism, school uniforms, safety, organ donation, recycling, and so on. From a teenager asking his parents to go out with friends to an aspiring politician ...
An Impressive Persuasive Speech Outline: Examples & Guide. (17 votes) Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you'll deal with the last one. You're about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing.
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy. A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective.
A preparation outline is also known as a practice or a working outline. As you can probably guess by the name, this outline helps you prepare your persuasive speech. While writing this outline, you can develop a solid thesis and call to action for your speech while also writing down the main and supporting points you need to include.
Persuasive Speech Outline. This is a student example of Monroe's Motivated Sequence. This student's outline is well developed, coherent, integrates research, follows a strong organizational pattern, and meets all expectations of an outline in a public speaking course. Click on the Google Document provided for a sample speech outline.
This persuasive speech generator ensures you don't worry about the correct or most suitable vocabulary for your text. It does everything for you and chooses the best vocabulary based on your speech's theme. 🦄 Inspiring. The online speech maker helps you draft your speech effortlessly and saves you the dreaded writer's block hassles.
How to use a persuasive speech outline. Now that you have your three components for your persuasive speech structure, it's time to make your persuasive speech outline. Step 1. Identify your Big Idea™ Start by determining a Big Idea™ for your talk. What is the main point you want the audience to walk away with? This will serve as a thesis ...
Persuasive Speech Outline Template - 15+ Examples, Samples & Formats. The audience is staring at you, ready to hear you speak. They are eager to hear what you have to say. This is your first speech in front of a large crowd, and it is your duty to persuade them. You come with nothing but your brain, assuming that because you are passionate ...
Health-science document from University of Maryland, Baltimore, 4 pages, DIABETES SELF-MANAGEMENT TRAINING Persuasive Speech: Expanding Access to Diabetes Self-Management Training Act NDNP 710: Evidence-Informed Health Policy & Advocacy University of Maryland School of Nursing March 14, 2023 1 DIABETES SELF-MANAGEMENT TRAININ