

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
What is problem solving, definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.
StrategyPunk
Introduction.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
Step 1: Define the Problem
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Step 4: Workplan
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template, multi-chapter growth strategy framework (free template), lidl swot analysis: free ppt template and in-depth insights.
Discover Lidl's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with our free PowerPoint template. This in-depth SWOT analysis provides valuable insights to help you understand Lidl's market position and strategic direction.
Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Pestle analysis: decoding reddit's landscape (free ppt).
40 problem-solving techniques and processes
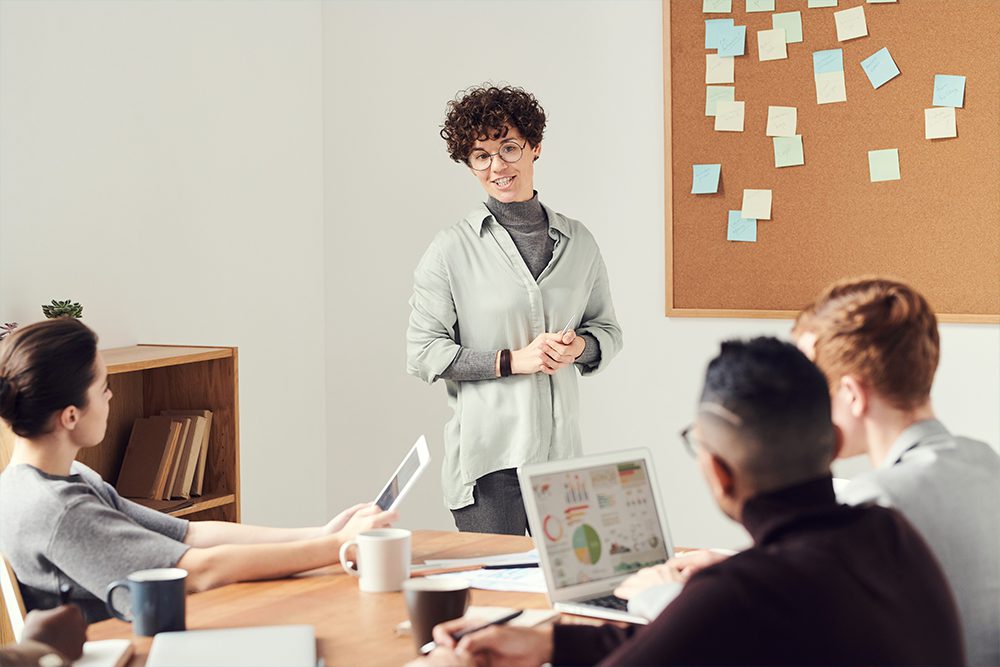

All teams and organizations encounter challenges. Approaching those challenges without a structured problem solving process can end up making things worse.
Proven problem solving techniques such as those outlined below can guide your group through a process of identifying problems and challenges , ideating on possible solutions , and then evaluating and implementing the most suitable .
In this post, you'll find problem-solving tools you can use to develop effective solutions. You'll also find some tips for facilitating the problem solving process and solving complex problems.
Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, 54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
What is problem solving?
Problem solving is a process of finding and implementing a solution to a challenge or obstacle. In most contexts, this means going through a problem solving process that begins with identifying the issue, exploring its root causes, ideating and refining possible solutions before implementing and measuring the impact of that solution.
For simple or small problems, it can be tempting to skip straight to implementing what you believe is the right solution. The danger with this approach is that without exploring the true causes of the issue, it might just occur again or your chosen solution may cause other issues.
Particularly in the world of work, good problem solving means using data to back up each step of the process, bringing in new perspectives and effectively measuring the impact of your solution.
Effective problem solving can help ensure that your team or organization is well positioned to overcome challenges, be resilient to change and create innovation. In my experience, problem solving is a combination of skillset, mindset and process, and it’s especially vital for leaders to cultivate this skill.

What is the seven step problem solving process?
A problem solving process is a step-by-step framework from going from discovering a problem all the way through to implementing a solution.
With practice, this framework can become intuitive, and innovative companies tend to have a consistent and ongoing ability to discover and tackle challenges when they come up.
You might see everything from a four step problem solving process through to seven steps. While all these processes cover roughly the same ground, I’ve found a seven step problem solving process is helpful for making all key steps legible.
We’ll outline that process here and then follow with techniques you can use to explore and work on that step of the problem solving process with a group.
The seven-step problem solving process is:
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem(s) you need to solve. This often looks like using group discussions and activities to help a group surface and effectively articulate the challenges they’re facing and wish to resolve.
Be sure to align with your team on the exact definition and nature of the problem you’re solving. An effective process is one where everyone is pulling in the same direction – ensure clarity and alignment now to help avoid misunderstandings later.
2. Problem analysis and refinement
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . Choosing the right problem to solve means you are on the right path to creating the right solution.
At this stage, you may look deeper at the problem you identified to try and discover the root cause at the level of people or process. You may also spend some time sourcing data, consulting relevant parties and creating and refining a problem statement.
Problem refinement means adjusting scope or focus of the problem you will be aiming to solve based on what comes up during your analysis. As you analyze data sources, you might discover that the root cause means you need to adjust your problem statement. Alternatively, you might find that your original problem statement is too big to be meaningful approached within your current project.
Remember that the goal of any problem refinement is to help set the stage for effective solution development and deployment. Set the right focus and get buy-in from your team here and you’ll be well positioned to move forward with confidence.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or techniquess designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can often come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
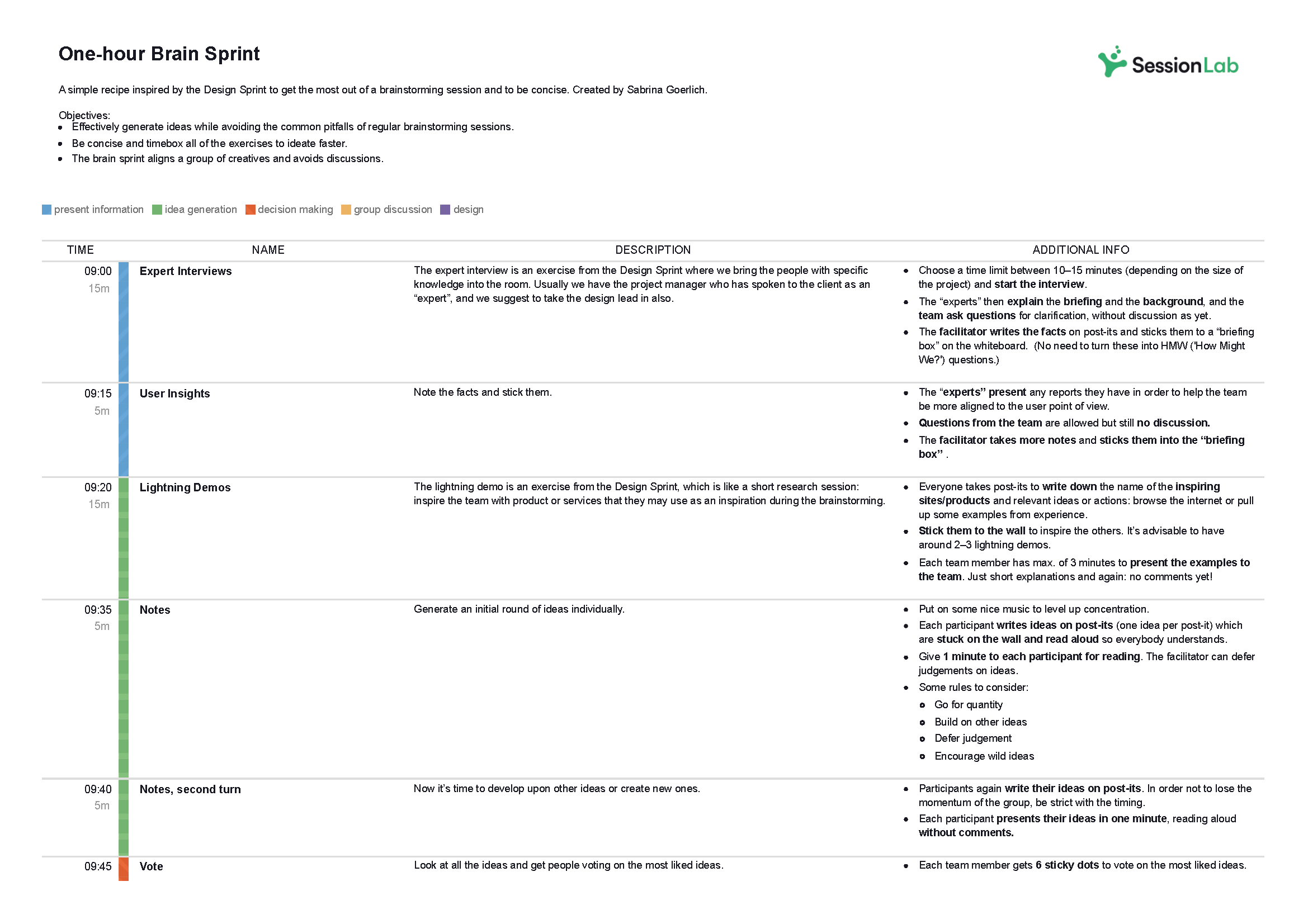
4. Solution development
No solution is perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your front-running solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making and planning
Nearly there! Once you’ve got a set of possible, you’ll need to make a decision on which to implement. This can be a consensus-based group decision or it might be for a leader or major stakeholder to decide. You’ll find a set of effective decision making methods below.
Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution, there are some additional actions that also need to be decided upon. You’ll want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
Set clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups for your chosen solution. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving processes have the end goal of implementing an effective and impactful solution that your group has confidence in.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way. For some solutions, you might also implement a test with a small group and monitor results before rolling it out to an entire company.
You should have a clear owner for your solution who will oversee the plans you made together and help ensure they’re put into place. This person will often coordinate the implementation team and set-up processes to measure the efficacy of your solution too.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling it’s been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback.
You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s also worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time.
What does an effective problem solving process look like?
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . In our experience, a well-structured problem solving workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
The format of a workshop ensures that you can get buy-in from your group, encourage free-thinking and solution exploration before making a decision on what to implement following the session.
This Design Sprint 2.0 template is an effective problem solving process from top agency AJ&Smart. It’s a great format for the entire problem solving process, with four-days of workshops designed to surface issues, explore solutions and even test a solution.
Check it for an example of how you might structure and run a problem solving process and feel free to copy and adjust it your needs!
For a shorter process you can run in a single afternoon, this remote problem solving agenda will guide you effectively in just a couple of hours.
Whatever the length of your workshop, by using SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Complete problem-solving methods
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly It doesn’t matter where you work and what your job role is, if you work with other people together as a team, you will always encounter the same challenges: Unclear goals and miscommunication that cause busy work and overtime Unstructured meetings that leave attendants tired, confused and without clear outcomes. Frustration builds up because internal challenges to productivity are not addressed Sudden changes in priorities lead to a loss of focus and momentum Muddled compromise takes the place of clear decision- making, leaving everybody to come up with their own interpretation. In short, a lack of structure leads to a waste of time and effort, projects that drag on for too long and frustrated, burnt out teams. AJ&Smart has worked with some of the most innovative, productive companies in the world. What sets their teams apart from others is not better tools, bigger talent or more beautiful offices. The secret sauce to becoming a more productive, more creative and happier team is simple: Replace all open discussion or brainstorming with a structured process that leads to more ideas, clearer decisions and better outcomes. When a good process provides guardrails and a clear path to follow, it becomes easier to come up with ideas, make decisions and solve problems. This is why AJ&Smart created Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ). It’s a simple and short, but powerful group exercise that can be run either in-person, in the same room, or remotely with distributed teams.
Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
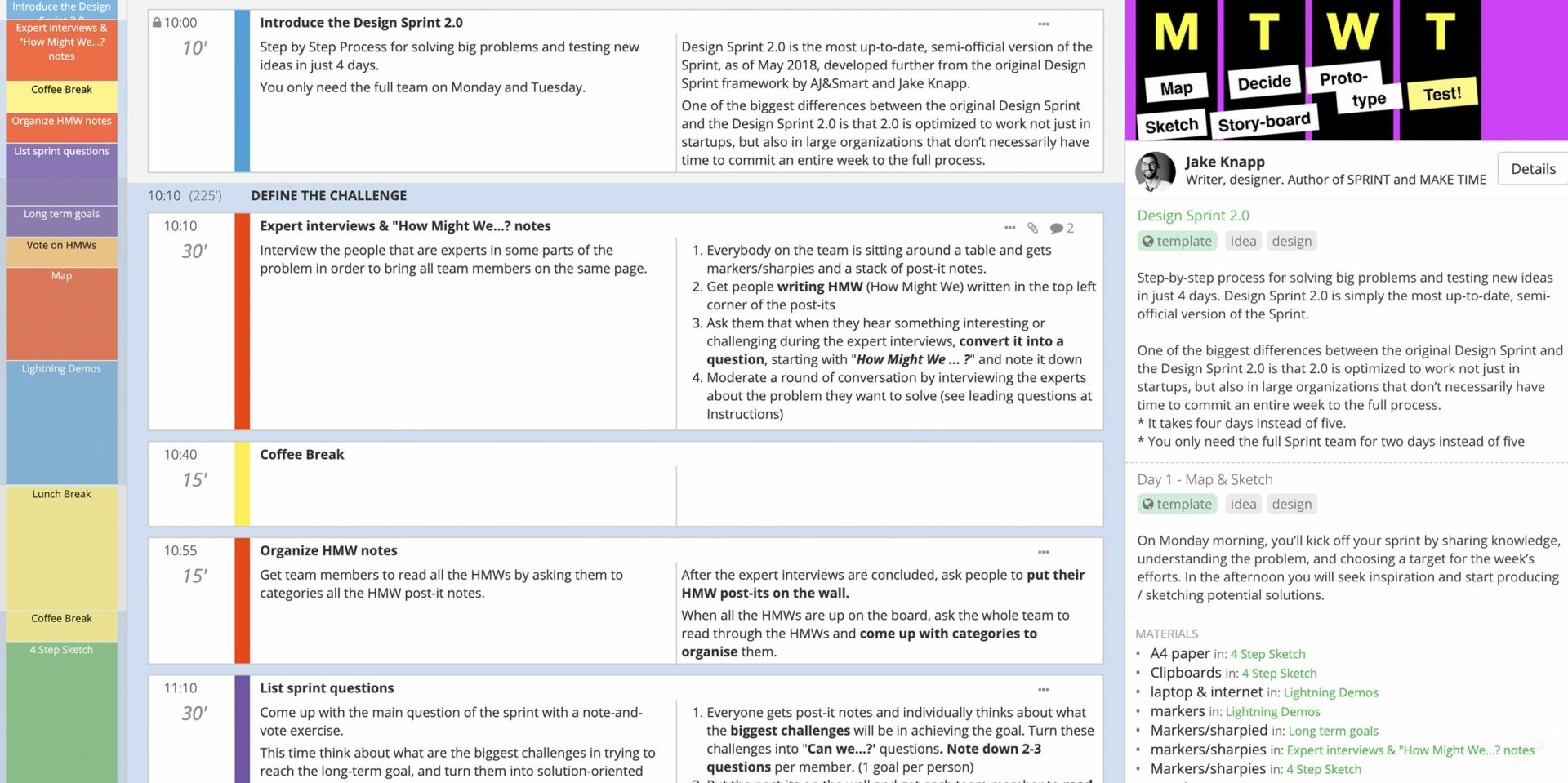
Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for brainstorming solutions
Now you have the context and background of the problem you are trying to solving, now comes the time to start ideating and thinking about how you’ll solve the issue.
Here, you’ll want to encourage creative, free thinking and speed. Get as many ideas out as possible and explore different perspectives so you have the raw material for the next step.
Looking at a problem from a new angle can be one of the most effective ways of creating an effective solution. TRIZ is a problem-solving tool that asks the group to consider what they must not do in order to solve a challenge.
By reversing the discussion, new topics and taboo subjects often emerge, allowing the group to think more deeply and create ideas that confront the status quo in a safe and meaningful way. If you’re working on a problem that you’ve tried to solve before, TRIZ is a great problem-solving method to help your team get unblocked.
Making Space with TRIZ #issue analysis #liberating structures #issue resolution You can clear space for innovation by helping a group let go of what it knows (but rarely admits) limits its success and by inviting creative destruction. TRIZ makes it possible to challenge sacred cows safely and encourages heretical thinking. The question “What must we stop doing to make progress on our deepest purpose?” induces seriously fun yet very courageous conversations. Since laughter often erupts, issues that are otherwise taboo get a chance to be aired and confronted. With creative destruction come opportunities for renewal as local action and innovation rush in to fill the vacuum. Whoosh!
Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Idea and Concept Development
Brainstorming without structure can quickly become chaotic or frustrating. In a problem-solving context, having an ideation framework to follow can help ensure your team is both creative and disciplined.
In this method, you’ll find an idea generation process that encourages your group to brainstorm effectively before developing their ideas and begin clustering them together. By using concepts such as Yes and…, more is more and postponing judgement, you can create the ideal conditions for brainstorming with ease.
Idea & Concept Development #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation Ideation and Concept Development is a process for groups to work creatively and collaboratively to generate creative ideas. It’s a general approach that can be adapted and customized to suit many different scenarios. It includes basic principles for idea generation and several steps for groups to work with. It also includes steps for idea selection and development.
Problem-solving techniques for developing and refining solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to develop and refine your ideas in order to bring them closer to a solution that actually solves the problem.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team think through their ideas and refine them as part of your problem solving process.
Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
Ensuring that everyone in a group is able to contribute to a discussion is vital during any problem solving process. Not only does this ensure all bases are covered, but its then easier to get buy-in and accountability when people have been able to contribute to the process.
1-2-4-All is a tried and tested facilitation technique where participants are asked to first brainstorm on a topic on their own. Next, they discuss and share ideas in a pair before moving into a small group. Those groups are then asked to present the best idea from their discussion to the rest of the team.
This method can be used in many different contexts effectively, though I find it particularly shines in the idea development stage of the process. Giving each participant time to concretize their ideas and develop them in progressively larger groups can create a great space for both innovation and psychological safety.
1-2-4-All #idea generation #liberating structures #issue analysis With this facilitation technique you can immediately include everyone regardless of how large the group is. You can generate better ideas and more of them faster than ever before. You can tap the know-how and imagination that is distributed widely in places not known in advance. Open, generative conversation unfolds. Ideas and solutions are sifted in rapid fashion. Most importantly, participants own the ideas, so follow-up and implementation is simplified. No buy-in strategies needed! Simple and elegant!
15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Problem-solving techniques for making decisions and planning
After your group is happy with the possible solutions you’ve developed, now comes the time to choose which to implement. There’s more than one way to make a decision and the best option is often dependant on the needs and set-up of your group.
Sometimes, it’s the case that you’ll want to vote as a group on what is likely to be the most impactful solution. Other times, it might be down to a decision maker or major stakeholder to make the final decision. Whatever your process, here’s some techniques you can use to help you make a decision during your problem solving process.
How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
Straddling the gap between decision making and planning, MoSCoW is a simple and effective method that allows a group team to easily prioritize a set of possible options.
Use this method in a problem solving process by collecting and summarizing all your possible solutions and then categorize them into 4 sections: “Must have”, “Should have”, “Could have”, or “Would like but won‘t get”.
This method is particularly useful when its less about choosing one possible solution and more about prioritorizing which to do first and which may not fit in the scope of your project. In my experience, complex challenges often require multiple small fixes, and this method can be a great way to move from a pile of things you’d all like to do to a structured plan.
MoSCoW #define intentions #create #design #action #remote-friendly MoSCoW is a method that allows the team to prioritize the different features that they will work on. Features are then categorized into “Must have”, “Should have”, “Could have”, or “Would like but won‘t get”. To be used at the beginning of a timeslot (for example during Sprint planning) and when planning is needed.
When it comes to managing the rollout of a solution, clarity and accountability are key factors in ensuring the success of the project. The RAACI chart is a simple but effective model for setting roles and responsibilities as part of a planning session.
Start by listing each person involved in the project and put them into the following groups in order to make it clear who is responsible for what during the rollout of your solution.
- Responsibility (Which person and/or team will be taking action?)
- Authority (At what “point” must the responsible person check in before going further?)
- Accountability (Who must the responsible person check in with?)
- Consultation (Who must be consulted by the responsible person before decisions are made?)
- Information (Who must be informed of decisions, once made?)
Ensure this information is easily accessible and use it to inform who does what and who is looped into discussions and kept up to date.
RAACI #roles and responsibility #teamwork #project management Clarifying roles and responsibilities, levels of autonomy/latitude in decision making, and levels of engagement among diverse stakeholders.
Problem-solving warm-up activities
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process. Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Closing activities for a problem-solving process
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Tips for effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Create psychologically safe spaces for discussion
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner.
It can be tough for people to stand up and contribute if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions and where possible, create regular opportunities for challenges to be brought up organically.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
Save time and effort creating an effective problem solving process
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
James Smart is Head of Content at SessionLab. He’s also a creative facilitator who has run workshops and designed courses for establishments like the National Centre for Writing, UK. He especially enjoys working with young people and empowering others in their creative practice.
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Your list of techniques for problem solving can be helpfully extended by adding TRIZ to the list of techniques. TRIZ has 40 problem solving techniques derived from methods inventros and patent holders used to get new patents. About 10-12 are general approaches. many organization sponsor classes in TRIZ that are used to solve business problems or general organiztational problems. You can take a look at TRIZ and dwonload a free internet booklet to see if you feel it shound be included per your selection process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Problem Solving Methodologies
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Hi im Daniel continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma and over 10 years of real-world experience across a range sectors, I have a passion for optimizing processes and creating a culture of efficiency. I wanted to create Learn Lean Siigma to be a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights and provide all the guides, tools, techniques and templates I looked for in one place as someone new to the world of Lean Six Sigma and Continuous improvement.

Preparation Strategies for the Green Belt Exam

What Every Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Should Know
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

Understanding Process Performance: Pp and Ppk
Understand Process Performance (Pp) and Process Performance Index (Ppk) to assess and improve manufacturing processes.…
LIFO or FIFO for Stock Management?
Choosing between LIFO and FIFO for stock management depends on factors like product nature, market…
Are There Any Official Standards for Six Sigma?
Are there any official standards for Six Sigma? While Six Sigma is a well-defined methodology…
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

- Quality Improvement
- Talk To Minitab
The Basics of Structured Problem-Solving Methodologies: DMAIC & 8D
Topics: Minitab Engage
When it comes to solving a problem, organizations want to get to the root cause of the problem, as quickly as possible. They also want to ensure that they find the most effective solution to that problem, make sure the solution is implemented fully, and is sustained into the future so that the problem no longer occurs. The best way to do this is by implementing structured problem-solving. In this blog post, we’ll briefly cover structured problem-solving and the best improvement methodologies to achieve operational excellence. Before we dive into ways Minitab can help, let’s first cover the basics of problem-solving.
WHAT IS STRUCTURED PROBLEM-SOLVING?
Structured problem-solving is a disciplined approach that breaks down the problem-solving process into discrete steps with clear objectives. This method enables you to tackle complex problems, while ensuring you’re resolving the right ones. It also ensures that you fully understand those problems, you've considered the reasonable solutions, and are effectively implementing and sustaining them.
WHAT IS A STRUCTURED PROBLEM-SOLVING METHODOLOGY?
A structured problem-solving methodology is a technique that consists of a series of phases that a project must pass through before it gets completed. The goal of a methodology is to highlight the intention behind solving a particular problem and offers a strategic way to resolve it. WHAT ARE THE BEST PROBLEM-SOLVING METHODOLOGIES?
That depends on the problem you’re trying to solve for your improvement initiative. The structure and discipline of completing all the steps in each methodology is more important than the specific methodology chosen. To help you easily visualize these methodologies, we’ve created the Periodic Table of Problem-Solving Methodologies. Now let’s cover two important methodologies for successful process improvement and problem prevention: DMAIC and 8D .
8D is known as the Eight Disciplines of problem-solving. It consists of eight steps to solve difficult, recurring, or critical problems. The methodology consists of problem-solving tools to help you identify, correct, and eliminate the source of problems within your organization. If the problem you’re trying to solve is complex and needs to be resolved quickly, 8D might be the right methodology to implement for your organization. Each methodology could be supported with a project template, where its roadmap corresponds to the set of phases in that methodology. It is a best practice to complete each step of a given methodology, before moving on to the next one.
MINITAB ENGAGE, YOUR SOLUTION TO EFFECTIVE PROBLEM-SOLVING
Minitab Engage TM was built to help organizations drive innovation and improvement initiatives. What makes our solution unique is that it combines structured problem-solving methodologies with tools and dashboards to help you plan, execute, and measure your innovation initiatives! There are many problem-solving methodologies and tools to help you get started. We have the ultimate end-to-end improvement solution to help you reach innovation success.
Ready to explore structured problem-solving?
Download our free eBook to discover the top methodologies and tools to help you accelerate your innovation programs.

See how our experts can train your company to better understand and utilize data. Find out more about our Training Services today!
You Might Also Like
- Trust Center
© 2023 Minitab, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Settings
The 8-Step Problem-Solving Method

- November 22, 2021
Table Of Contents
What is the 8-step problem-solving method, the 8 steps and the problem-solving process, the culture of problem-solving.
- Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA)
- Gain Problem-Solving Support
As a manufacturing professional, you know how important it is to stay organized, keep your goals in mind and strive for success. But with all of the responsibilities and daily tasks piling up, it takes effort to find and stick to a process that can keep you on track.
Luckily, there’s a tried and trusted way to achieve success in the manufacturing industry.
The eight-step problem-solving process is a structured method that guides you through the various steps of solving issues. Unlike other problem-solving processes that are often broad, the eight-step method takes you through each individual step, from identifying the problem to taking actionable steps to success.
Instead of changing a few things at a middling level that will probably break down again later, you can unearth the roots of problems and build success from the ground up.
For a fundamental breakdown of how to fix problems and lead your manufacturing team to success, here are the eight steps of the problem-solving process.
1. Identify the Problem
The first step in the process is to identify the problem. Identify why this is a problem, how you discovered it and how it impacts your business. Also note when the problem started and how long it has been going on.
If the problem is small, you can try to contain it and may not need additional steps to fix it. However, if the problem is complex, move forward through the process.
2. Define the Problem
The next step involves breaking down the problem and defining what it is. It’s important to be as clear as you can with this step — a vague problem will hinder the process, whereas a clearly defined issue will allow you to take actionable steps to fix it.
Analyze factors like how high of a priority it is to solve the problem. You can also look to data and other resources to clarify or help you understand the concern.
3. Make a Goal
Create an end goal. Envision what fixing this problem would look like and feel like. What would it accomplish? How would it help you? Map out all the ways fixing this problem would benefit you and use it for motivation to achieve your goal. Set a timeline to figure how long it will take to accomplish that goal.
4. Find the Root of the Problem
Often problems are byproducts of deeper, more central problems, so make sure you dig deep enough to find out what is really causing the issue. If the problem is large and complex, break it down into individual parts.
Gather information and use it to identify the deeper issues of the problem and validate what you think the real concern may be. Take time at this step to really focus on the deep problem — executing this step effectively will save you a lot of time down the road.

5. Develop Actionable Steps
Create a list of realistic steps you can take to combat the problem. You can start with a large list and combine or subtract steps, but it’s important you come up with various ways to attack the problem. Use this action plan to draw up a strategy to get at the root of the problem. Each step should be specific and detail-focused — any steps that are vague or tedious will only take up time and cause confusion.
6. Execute Steps
Now that the plan is in place, all you have to do is follow through on your actionable steps. Illustrate the steps you’re taking to your team, explain why you’re taking them and delegate any steps that another employee has to perform to execute your plan.
Communication is key in this step. In most cases, you won’t be executing the plan all by yourself, so make sure you’re expressing the goals and motives of each step with your team so they can see how it connects to the bigger picture.
7. Observe and Evaluate
Monitor your strategy carefully and see how it relates to the original problem. Is it working? Is it only creating more problems? Gather data, talk to your team and be thorough and objective in your evaluation. You might have to readjust your plan as you gain new information, or you may meet your goals and the plan will be successful.
8. Continue the Process
If the plan worked, find ways to continue integrating these steps into your team’s daily routine. If they didn’t work, go back to the goal-setting process or identify some more aspects of the problem — there may be a deeper concern you missed the first time around. Communicate to your team about how the plan went.
In the future, continue using the eight-step process to solve issues and build momentum with your team.
It’s important to build a culture of problem-solving in your manufacturing plant. It can be easy to fall into the trap of “Band-Aid” solutions — quick fixes without digging into the deeper problems.
It’s believed that the eight-step problem-solving process was actually created by the Toyota Motor Corporation to achieve their admired production standards.
From the lore of Toyota, we get some great eight-step problem-solving examples. Taiichi Ohno , the father of the Toyota Production System, observed his workers fixing only the first level of cause when their machines stopped working. To combat this, he developed a problem-solving method to methodically break down each problem of the machine until he found the root cause. Only then could he truly fix the machine.
It’s one of many eight-step problem-solving examples, and it shows the importance of creating a process to increase productivity.
Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) and the 8-Step Problem-Solving Process Differences
The eight-step problem-solving process is an expanded version of the Plan, Do, Check, Act cycle . The first five steps of the 8-step process fall under the planning step, while steps six, seven and eight all correspond to the do, check and act steps. The eight-step process is a more detailed, methodical version of PDCA problem-solving, and converts a vague cycle into something a bit more specific and actionable.

Gain the Problem-Solving Support You Need With MANTEC
MANTEC is the best resource center for manufacturing companies in South Central Pennsylvania. We’re a non-profit that solves any problems a manufacturing facility could have, including sales and marketing , process improvement , manufacturing technology and workforce engagement .
Our expert staff has had vast experience in the manufacturing industry, and we can provide the guidance you need to get your business running at top efficiency. Our services are affordable and extremely valuable. Contact us today!
Related Posts

Struggling to manage multiple payment systems for different business needs (B2B, B2C, D2C)? Payment Hub…

In the dynamic landscape of business, achieving and maintaining an International Organization for Standardization (ISO)…

Manufacturers need to build agility into their businesses and processes to respond and recover faster…


Brain Power
5 steps (and 4 techniques) for effective problem solving.
Problem solving is the process of reviewing every element of an issue so you can get to a solution or fix it. Problem solving steps cover multiple aspects of a problem that you can bring together to find a solution. Whether that’s in a group collaboratively or independently, the process remains the same, but the approach and the steps can differ.
To find a problem solving approach that works for you, your team, or your company, you have to take into consideration the environment you’re in and the personalities around you.
Knowing the characters in the room will help you decide on the best approach to try and ultimately get to the best solution.
Table of Contents
5 problem solving steps, 4 techniques to encourage problem solving, the bottom line.
No matter what the problem is, to solve it, you nearly always have to follow these problem solving steps. Missing any of these steps can cause the problem to either resurface or the solution to not be implemented correctly.
Once you know these steps, you can then get creative with the approach you take to find the solutions you need.
1. Define the Problem
You must define and understand the problem before you start, whether you’re solving it independently or as a group. If you don’t have a single view of what the problem is, you could be fixing something that doesn’t need fixing, or you’ll fix the wrong problem.
Spend time elaborating on the problem, write it down, and discuss everything, so you’re clear on why the problem is occurring and who it is impacting.
Once you have clarity on the problem, you then need to start thinking about every possible solution . This is where you go big and broad, as you want to come up with as many alternative solutions as possible. Don’t just take the first idea; build out as many as you can through active listening, as the more you create, the more likely you’ll find a solution that has the best impact on the team.
3. Decide on a Solution
Whichever solution you pick individually or as a team, make sure you think about the impact on others if you implement this solution. Ask questions like:
- How will they react to this change?
- Will they need to change anything?
- Who do we need to inform of this change?
4. Implement the Solution
At this stage of problem solving, be prepared for feedback, and plan for this. When you roll out the solution, request feedback on the success of the change made.
5. Review, Iterate, and Improve
Making a change shouldn’t be a one time action. Spend time reviewing the results of the change to make sure it’s made the required impact and met the desired outcomes.
Make changes where needed so you can further improve the solution implemented.
Each individual or team is going to have different needs and may need a different technique to encourage each of the problem solving steps. Try one of these to stimulate the process.
1-2-4 All Approach + Voting
The 1-2-4-All is a good problem solving approach that can work no matter how large the group is. Everyone is involved, and you can generate a vast amount of ideas quickly.
Ideas and solutions are discussed and organized rapidly, and what is great about this approach is the attendees own their ideas, so when it comes to implementing the solutions, you don’t have more work to gain buy-in.
As a facilitator, you first need to present the group with a question explaining the problem or situation. For example, “What actions or ideas would you recommend to solve the company’s lack of quiet working areas?”
With the question clear for all to see, the group then spends 5 minutes to reflect on the question individually. They can jot down their thoughts and ideas on Post-Its.
Now ask the participants to find one or two other people to discuss their ideas and thoughts with. Ask the group to move around to find a partner so they can mix with new people.
Ask the pairs to spend 5 minutes discussing their shared ideas and thoughts.
Next, put the group into groups of two or three pairs to make groups of 4-6. Each group shouldn’t be larger than six as the chances of everyone being able to speak reduces.
Ask the group to discuss one interesting idea they’ve heard in previous rounds, and each group member shares one each.
The group then needs to pick their preferred solution to the problem. This doesn’t have to be voted on, just one that resonated most with the group.
Then ask for three actions that could be taken to implement this change.
Bring everyone back together as a group and ask open questions like “What is the one thing you discussed that stood out for you?” or “Is there something you now see differently following these discussions?”
By the end of the session, you’ll have multiple approaches to solve the problem, and the whole group will have contributed to the future solutions and improvements.
The Lightning Decision Jam
The Lightning Decision Jam is a great way to solve problems collaboratively and agree on one solution or experiment you want to try straight away. It encourages team decision making, but at the same time, the individual can get their ideas and feedback across. [1]
If, as a team, you have a particular area you want to improve upon, like the office environment, for example, this approach is perfect to incorporate in the problem solving steps.
The approach follows a simple loop.
Make a Note – Stick It on The Wall – Vote – Prioritize
Using sticky notes, the technique identifies major problems, encourages solutions, and opens the group up for discussion. It allows each team member to play an active role in identifying both problems and ways to solve them.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a fantastic visual thinking tool that allows you to bring problems to life by building out the connections and visualizing the relationships that make up the problem.
You can use a mind map to quickly expand upon the problem and give yourself the full picture of the causes of the problem, as well as solutions [2] .

The goal of a mind map is to simplify the problem and link the causes and solutions to the problem.
To create a mind map, you must first create the central topic (level 1). In this case, that’s the problem.
Next, create the linked topics (level 2) that you place around and connect to the main central topic with a simple line.
If the central topic is “The client is always changing their mind at the last minute,” then you could have linked topics like:
- How often does this happen?
- Why are they doing this?
- What are they asking for?
- How do they ask for it?
- What impact does this have?
Adding these linking topics allows you to start building out the main causes of the problem as you can begin to see the full picture of what you need to fix. Once you’re happy that you’ve covered the breadth of the problem and its issues, you can start to ideate on how you’re going to fix it with the problem solving steps.
Now, start adding subtopics (level 3) linking to each of the level 2 topics. This is where you can start to go big on solutions and ideas to help fix the problem.
For each of the linked topics (level 2), start to think about how you can prevent them, mitigate them, or improve them. As this is just ideas on paper, write down anything that comes to mind, even if you think the client will never agree to it!
The more you write down, the more ideas you’ll have until you find one or two that could solve the main problem.
Once you run out of ideas, take a step back and highlight your favorite solutions to take forward and implement.
The 5 Why’s
The five why’s can sound a little controversial, and you shouldn’t try this without prepping the team beforehand.
Asking “why” is a great way to go deep into the root of the problem to make the individual or team really think about the cause. When a problem arises, we often have preconceived ideas about why this problem has occurred, which is usually based on our experiences or beliefs.
Start with describing the problem, and then the facilitator can ask “Why?” fives time or more until you get to the root of the problem. It’s tough at first to keep being asked why, but it’s also satisfying when you get to the root of the problem [3] .
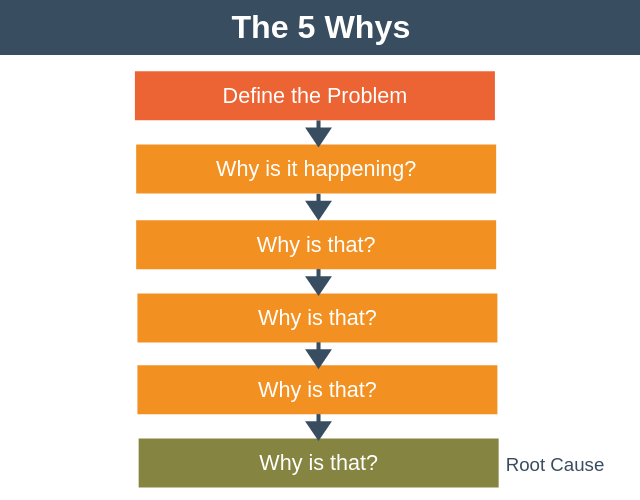
As a facilitator, although the basic approach is to ask why, you need to be careful not to guide the participant down a single route.
To help with this, you can use a mind map with the problem at the center. Then ask a why question that will result in multiple secondary topics around the central problem. Having this visual representation of the problem helps you build out more useful why questions around it.
Once you get to the root of the problem, don’t forget to be clear in the actions to put a fix in place to resolve it.
Learn more about how to use the five why’s here .
To fix a problem, you must first be in a position where you fully understand it. There are many ways to misinterpret a problem, and the best way to understand them is through conversation with the team or individuals who are experiencing it.
Once you’re aligned, you can then begin to work on the solutions that will have the greatest impact through effective problem solving steps.
For the more significant or difficult problems to solve, it’s often advisable to break the solution up into smaller actions or improvements.
Trial these improvements in short iterations, and then continue the conversations to review and improve the solution. Implementing all of these steps will help you root out the problems and find useful solutions each time.
| [1] | ^ | UX Planet: |
| [2] | ^ | Focus: |
| [3] | ^ | Expert Program Management: |

How to Use a Planner Effectively

How to Be a Better Planner: Avoid the Planning Fallacy

5 Best Apps to Help You Delegate Tasks Easily

Delegating Leadership Style: What Is It & When To Use It?

The Fear of Delegating Work To Others

Why Is Delegation Important in Leadership?
7 Best Tools for Prioritizing Work

How to Deal with Competing Priorities Effectively
What Is the RICE Prioritization Model And How Does It Work?
4 Exercises to Improve Your Focus

What Is Chronic Procrastination and How To Deal with It

How to Snap Out of Procrastination With ADHD

Are Depression And Procrastination Connected?

Procrastination And Laziness: Their Differences & Connections

Bedtime Procrastination: Why You Do It And How To Break It

15 Books on Procrastination To Help You Start Taking Action

Productive Procrastination: Is It Good or Bad?

The Impact of Procrastination on Productivity

How to Cope With Anxiety-Induced Procrastination

How to Break the Perfectionism-Procrastination Loop

15 Work-Life Balance Books to Help You Take Control of Life
Work Life Balance for Women: What It Means & How to Find It

6 Essential Mindsets For Continuous Career Growth

How to Discover Your Next Career Move Amid the Great Resignation

The Key to Creating a Vibrant (And Magical Life) by Lee Cockerell

9 Tips on How To Disconnect From Work And Stay Present

Work-Life Integration vs Work-Life Balance: Is One Better Than the Other?

How To Practice Self-Advocacy in the Workplace (Go-to Guide)

How to Boost Your Focus And Attention Span
What Are Distractions in a Nutshell?

What Is Procrastination And How To End It

Prioritization — Using Your Time & Energy Effectively

Delegation — Leveraging Your Time & Resources

Your Guide to Effective Planning & Scheduling

The Ultimate Guide to Achieving Goals

How to Find Lasting Motivation
Complete Guide to Getting Back Your Energy

How to Have a Good Life Balance
Explore the time flow system.

About the Time Flow System

Key Philosophy I: Fluid Progress, Like Water
Key Philosophy II: Pragmatic Priorities

Key Philosophy III: Sustainable Momentum

Key Philosophy IV: Three Goal Focus
How the Time Flow System Works
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving, a guide to the 7-step mckinsey problem solving process.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
In this guide you'll learn:
Overview of the mckinsey approach to problem solving, problem solving process, problem definition.
- Problem Statement
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Structure the problem, hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, communicate, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, request the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem.
In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
Constraints can be a good thing (e.g., limit solutions to actions within the available budget.) And constraints can be a bad thing (e.g., eliminating the possibility of creative ideas.) So choose wisely.
The problem statement may ignore many issues to focus on the priority that should be addressed. The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution.
Example scenario – A family on Friday evening :
A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend.
The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
Potential problem definitions – A family on Friday evening :
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Given one set of facts, it is possible to come up with many possible problem statements. The choice of problem statement constrains the range of possible solutions.
Before starting to solve the problem, the family first needs to agree on what problem they want to solve.
- What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
- How can the family schedule their activities this weekend to accomplish everything planned given that they only have one vehicle available?
- How can the family increase income or reduce expenses to allow them to save $75K over the next 12 months to pay for the planned addition to their house?
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
Here are three different templates for a workplan:
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Once the recommendations have been crafted in the problem-solving process, it’s vital to effectively communicate those findings and recommendations.
An executive summary is a great slide to use for this. See more on executive summary slides, including 30 templates, at our Ultimate Guide to Executive Summary Slides .
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2024 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Soft skills
- What is a credential?
- Why do a credential?
- How do credentials work?
- Selecting your level
- How will I be assessed?
- Benefits for professionals
- Benefits for organisations
- Benefits for postgraduates
Problem solving techniques: Steps and methods

Posted on May 29, 2019
Constant disruption has become a hallmark of the modern workforce and organisations want problem solving skills to combat this. Employers need people who can respond to change – be that evolving technology, new competitors, different models for doing business, or any of the other transformations that have taken place in recent years.
In addition, problem solving techniques encompass many of the other top skills employers seek . For example, LinkedIn’s list of the most in-demand soft skills of 2019 includes creativity, collaboration and adaptability, all of which fall under the problem-solving umbrella.
Despite its importance, many employees misunderstand what the problem solving method really involves.
What constitutes effective problem solving?
Effective problem solving doesn’t mean going away and coming up with an answer immediately. In fact, this isn’t good problem solving at all, because you’ll be running with the first solution that comes into your mind, which often isn’t the best.
Instead, you should look at problem solving more as a process with several steps involved that will help you reach the best outcome. Those steps are:
- Define the problem
- List all the possible solutions
- Evaluate the options
- Select the best solution
- Create an implementation plan
- Communicate your solution
Let’s look at each step in a little more detail.

1. Define the problem
The first step to solving a problem is defining what the problem actually is – sounds simple, right? Well no. An effective problem solver will take the thoughts of everyone involved into account, but different people might have different ideas on what the root cause of the issue really is. It’s up to you to actively listen to everyone without bringing any of your own preconceived notions to the conversation. Learning to differentiate facts from opinion is an essential part of this process.
An effective problem solver will take the opinions of everyone involved into account
The same can be said of data. Depending on what the problem is, there will be varying amounts of information available that will help you work out what’s gone wrong. There should be at least some data involved in any problem, and it’s up to you to gather as much as possible and analyse it objectively.
2. List all the possible solutions
Once you’ve identified what the real issue is, it’s time to think of solutions. Brainstorming as many solutions as possible will help you arrive at the best answer because you’ll be considering all potential options and scenarios. You should take everyone’s thoughts into account when you’re brainstorming these ideas, as well as all the insights you’ve gleaned from your data analysis. It also helps to seek input from others at this stage, as they may come up with solutions you haven’t thought of.
Depending on the type of problem, it can be useful to think of both short-term and long-term solutions, as some of your options may take a while to implement.

3. Evaluate the options
Each option will have pros and cons, and it’s important you list all of these, as well as how each solution could impact key stakeholders. Once you’ve narrowed down your options to three or four, it’s often a good idea to go to other employees for feedback just in case you’ve missed something. You should also work out how each option ties in with the broader goals of the business.
There may be a way to merge two options together in order to satisfy more people.
4. Select an option
Only now should you choose which solution you’re going to go with. What you decide should be whatever solves the problem most effectively while also taking the interests of everyone involved into account. There may be a way to merge two options together in order to satisfy more people.
5. Create an implementation plan
At this point you might be thinking it’s time to sit back and relax – problem solved, right? There are actually two more steps involved if you want your problem solving method to be truly effective. The first is to create an implementation plan. After all, if you don’t carry out your solution effectively, you’re not really solving the problem at all.
Create an implementation plan on how you will put your solution into practice. One problem solving technique that many use here is to introduce a testing and feedback phase just to make sure the option you’ve selected really is the most viable. You’ll also want to include any changes to your solution that may occur in your implementation plan, as well as how you’ll monitor compliance and success.
6. Communicate your solution
There’s one last step to consider as part of the problem solving methodology, and that’s communicating your solution . Without this crucial part of the process, how is anyone going to know what you’ve decided? Make sure you communicate your decision to all the people who might be impacted by it. Not everyone is going to be 100 per cent happy with it, so when you communicate you must give them context. Explain exactly why you’ve made that decision and how the pros mean it’s better than any of the other options you came up with.
Prove your problem solving skills with Deakin
Employers are increasingly seeking soft skills, but unfortunately, while you can show that you’ve got a degree in a subject, it’s much harder to prove you’ve got proficiency in things like problem solving skills. But this is changing thanks to Deakin’s micro-credentials. These are university-level micro-credentials that provide an authoritative and third-party assessment of your capabilities in a range of areas, including problem solving. Reach out today for more information .
7 Steps to an Effective Problem-Solving Process
September 1, 2016 | Leadership Articles

An effective problem-solving process is one of the key attributes that separate great leaders from average ones.
Being a successful leader doesn’t mean that you don’t have any problems. Rather, it means that you know how to solve problems effectively as they arise. If you never had to deal with any problems, chances are pretty high that your company doesn’t really need you. They could hire an entry-level person to do your job!
Unfortunately, there are many examples of leaders out there who have been promoted to management or leadership positions because they are competent and excel in the technical skills needed to do the work. These people find themselves suddenly needing to “think on their feet” and solve problems that are far more high-level and complicated than they’ve ever really had to deal with before. Are there tools available to these people to help them solve the problem correctly and effectively? Absolutely!
Today, I am going to introduce you to the Seven Steps of Effective Problem Solving that Bullet Proof® Managers are learning about, developing, and implementing in their teams.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
What are things like when they are the way we want them to be?
This question helps you find the standard against which we’re going to measure where we are now. If things were going the way we want them to go, what does that look like? If this person were doing the job we want him or her to do, what would they be doing?
And then ask this important question: How much variation from the norm is tolerable?
Therein lies the problem. From an engineering perspective, you might have very little tolerance. From a behavioral perspective, you might have more tolerance. You might say it’s okay with me when this person doesn’t do it exactly as I say because I’m okay with them taking some liberty with this. Some other issue you may need 100% compliance.
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
At what stage is this problem? This helps you identify the urgency of the problem, and there are generally three stages.
The emergent stage is where the problem is just beginning to happen. It does not cause an immediate threat to the way business operates every day. It is just beginning to happen and you have time on your side to be able to correct it without it causing much damage to the processes it is affecting. The mature stage is where this problem is causing more than just minor damage. Some amount of damage has been done, and you need to jump on it immediately to fix it before it becomes a problem where the consequences may be greater, deeper, and more expensive if we don’t solve this problem fast.
The third stage is the crisis stage, when the problem is so serious it must be corrected immediately. At this stage, real damage has been done to company processes, reputation, finances, etc. that will have potentially long-term effects on your ability to do business.
Step 3: Describe the Problem
You should be able to describe a problem by writing it in the form of a statement and you should do it in 12 words or less, assuming it’s not a complicated, scientific problem. This way, you have clarity exactly what the issue is. Then, perhaps try distributing it to your team to ensure they agree that this is the root of the problem, that it makes sense, and everyone that is working toward a solution is working toward the same goal.
The most important question of all, when describing your problem: Is your premise correct?
Let me give you an example of what I mean. We’ve all heard – or read – the story of the engineer’s take on the old “half empty, half full” question. A speaker holds up the glass of water and asks if the glass is half empty or half full, a discussion within the group ensues, and you generally expect some sort of lesson in optimism, etc. from it. In this version, an engineer is in the room and answers, “I see this glass of water as being twice the size it needs to be.”
You see, sometimes when you are the one in charge of the problem, you tend to set the premise of the problem from your own perspective. But, that premise may not be accurate, or it may just need an alternate perspective from which to see it. If your premise is not correct, or at least incomplete, you are not fully understanding the problem and considering all the best options for a solution.
Step 4: Look for Root Causes
This step involves asking and answering a lot of questions. Ask questions like: What caused this problem? Who is responsible for this problem? When did this problem first emerge? Why did this happen? How did this variance from the standard come to be? Where does it hurt us the most? How do we go about resolving this problem?
Also, ask the most important question: Can we solve this problem for good so it will never occur again? Because an important aspect to leadership is coming up with solutions that people can use for a long-term benefit, rather than having to deal with the same problems over and over and over.
Step 5: Develop Alternate Solutions
Just about any problem you have to deal with has more solutions to it than the one that you think of first. So, it is best to develop a list of alternate solutions that you and your team can assess and decide which one will be the best for the particular problem. I often use the ⅓ + 1 Rule to create consensus around one – or the top two or three solutions – that will be best for everyone involved.
Then rank those solutions based on efficiency, cost, long-term value, what resources you have and that you can commit to the solution of the problem. Then, look at every one of those solutions carefully and decide what you believe to be the best solution to this problem at this time.
Step 6: Implement the Solution
Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn’t work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part in making the solution work, that there are timelines for execution, and also that you have a system in place to track whether or not the solution has corrected the problem.
Step 7: Measure the Results
From your implementation plan in step 6, make sure you track and measure the results so you can answer questions such as: Did it work? Was this a good solution? Did we learn something here in the implementation that we could apply to other potential problems?
These seven simple steps will help you become a more effective, efficient problem solver in your organization. As you practice this process and develop the skills, these steps will become more natural to you until the point that you are using them without noticing!
About Crestcom International, LLC.
Crestcom International, LLC is an international leadership development organization, training more than one million leaders for 25,000 businesses in over 60 countries across the globe. Crestcom achieves this through a blend of live-facilitated multimedia video, interactive exercises, and shared learning experiences. Crestcom implements action plans and coaching accountability sessions to ensure measured development in key leadership competency areas. For more information, please contact your local Crestcom representative found here .
Interested in a free Leadership Skills Workshop with your team?
- Address instantly fixable issues that impact customer perceptions and employee morale.
- Learn and practice a habit that will raise employee performance.
- Set actions with specific and measurable steps that they'll gladly be accountable to achieve.
- Case Studies
- Leadership Articles
- Multi-Generational Leadership
- Owning a franchise
- Press Releases
Latest Posts

Stay Updated
Browse by topic.
[st-tag-cloud]
Privacy Overview

The Five-Step Problem-Solving Process
Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from…

Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from routine will help you think creatively and objectively. Doing too much at the same time increases the chances of burnout.
Solving problems is easier when you align your thoughts with your actions. If you’re in multiple places at once mentally, you’re more likely to get overwhelmed under pressure. So, a problem-solving process follows specific steps to make it approachable and straightforward. This includes breaking down complex problems, understanding what you want to achieve, and allocating responsibilities to different people to ease some of the pressure.
The problem-solving process will help you measure your progress against factors like budget, timelines and deliverables. The point is to get the key stakeholders on the same page about the ‘what’, ‘why’ and ‘how’ of the process. ( Xanax ) Let’s discuss the five-step problem-solving process that you can adopt.
Problems at a workplace need not necessarily be situations that have a negative impact, such as a product failure or a change in government policy. Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also “problems” that need to be “solved”.
Here are the steps of a problem-solving process:
1. Defining the Problem
The first step in the process is often overlooked. To define the problem is to understand what it is that you’re solving for. This is also where you outline and write down your purpose—what you want to achieve and why. Making sure you know what the problem is can make it easier to follow up with the remaining steps. This will also help you identify which part of the problem needs more attention than others.
2. Analyzing the Problem
Analyze why the problem occurred and go deeper to understand the existing situation. If it’s a product that has malfunctioned, assess factors like raw material, assembly line, and people involved to identify the problem areas. This will help you figure out if the problem will persist or recur. You can measure the solution against existing factors to assess its future viability.
3. Weighing the Options
Once you’ve figured out what the problem is and why it occurred, you can move on to generating multiple options as solutions. You can combine your existing knowledge with research and data to come up with viable and effective solutions. Thinking objectively and getting inputs from those involved in the process will broaden your perspective of the problem. You’ll be able to come up with better options if you’re open to ideas other than your own.
4. Implementing The Best Solution
Implementation will depend on the type of data at hand and other variables. Consider the big picture when you’re selecting the best option. Look at factors like how the solution will impact your budget, how soon you can implement it, and whether it can withstand setbacks or failures. If you need to make any tweaks or upgrades, make them happen in this stage.
5. Monitoring Progress
The problem-solving process doesn’t end at implementation. It requires constant monitoring to watch out for recurrences and relapses. It’s possible that something doesn’t work out as expected on implementation. To ensure the process functions smoothly, you can make changes as soon as you catch a miscalculation. Always stay on top of things by monitoring how far you’ve come and how much farther you have to go.
You can learn to solve any problem—big or small—with experience and patience. Adopt an impartial and analytical approach that has room for multiple perspectives. In the workplace, you’re often faced with situations like an unexpected system failure or a key employee quitting in the middle of a crucial project.
Problem-solving skills will help you face these situations head-on. Harappa Education’s Structuring Problems course will show you how to classify and categorize problems to discover effective solutions. Equipping yourself with the right knowledge will help you navigate work-related problems in a calm and competent manner.
Explore topics such as Problem Solving , the PICK Chart , How to Solve Problems & the Barriers to Problem Solving from our Harappa Diaries blog section and develop your skills.

Adopting the right problem-solving approach
May 4, 2023 You’ve defined your problem, ensured stakeholders are aligned, and are ready to bring the right problem-solving approach and focus to the situation to find an optimal solution. But what is the right problem-solving approach? And what if there is no single ideal course of action? In our 2013 classic from the Quarterly , senior partner Olivier Leclerc highlights the value of taking a number of different approaches simultaneously to solve difficult problems. Read on to discover the five flexons, or problem-solving languages, that can be applied to the same problem to generate richer insights and more innovative solutions. Then check out more insights on problem-solving approaches, and dive into examples of pressing challenges organizations are contending with now.
Five routes to more innovative problem solving
Author Talks: Get on the performance curve
Strategy to beat the odds
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Digital performance management: From the front line to the bottom line
Addressing employee burnout: Are you solving the right problem?
Business’s ‘It’s not my problem’ IT problem
TEST YOUR SKILLS
Take the McKinsey Problem Solving Test
Solve, McKinsey’s assessment game
- How to Overcome Challenges in Statistics Homework
How to Understand and Overcome Challenges in Statistics Homework

Solving your statistics homework can be a daunting task, but with the right approach and techniques, you can solve them effectively. This guide will provide you with a step-by-step approach to solving homework similar to the examples provided, focusing on regression analysis, descriptive statistics, and value assessment. These tips and techniques will help you navigate through any statistics homework with confidence.
1. Understanding the Problem Statement
The first step in solving any statistics homework is to thoroughly understand the problem statement. Break down the homework into smaller, manageable parts and identify the key objectives. For example, in the given homework, you might need to:
- Analyze data to make informed decisions.
- Develop regression models to predict outcomes.
- Summarize data using descriptive statistics.
- Interpret statistical results to draw meaningful conclusions.
.webp)
2. Data Preparation
Before diving into the analysis, it is crucial to prepare your data. This includes:
- Cleaning the data: Remove any missing or inconsistent values.
- Structuring the data: Organize the data into a format suitable for analysis (e.g., data frames in R or Python).
- Understanding the variables: Identify the types of variables (categorical or continuous) and their relationships.
3. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics provide a summary of the data and are the foundation of any statistical analysis. Here’s how you can approach it:
- Central Tendency: Calculate the mean, median, and mode to understand the central point of the data.
- Dispersion: Measure the spread of the data using range, variance, and standard deviation.
- Visualization: Use graphs like histograms, box plots, and scatter plots to visualize the data distribution and detect patterns or outliers.
Example: In the homework regarding Fortune magazine’s 100 best companies to work for, you could:
- Calculate the mean and median salaries for salaried and hourly employees.
- Compare salary distributions across different company sizes using box plots.
For students seeking help with descriptive statistics homework , consider utilizing resources or tools that provide step-by-step guidance on these calculations. This can include statistical software, online tutorials, or consulting with a tutor for personalized assistance.
4. Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a powerful tool for predicting outcomes and understanding relationships between variables. and if you need further assistance, consider the following steps:
- Simple Linear Regression: Start with a basic model to predict a dependent variable using one independent variable.
- Multiple Regression: Incorporate multiple independent variables to improve the accuracy of your predictions.
- Dummy Variables: Use dummy variables to include categorical data in your regression models.
Steps to develop a regression model:
- Formulate the model: Identify the dependent variable (what you want to predict) and independent variables (predictors).
- Estimate the coefficients: Use statistical software to estimate the coefficients of the regression equation.
- Evaluate the model: Check the goodness-of-fit (R-squared value) and perform hypothesis tests (t-tests) to assess the significance of the predictors.
- Interpret the results: Understand the implications of the regression coefficients and the overall model.
Example: In the homework involving Environment Canada’s Fuel Economy Guide, you could:
- Develop a regression model to predict highway MPG based on engine displacement, type of fuel, and type of drive.
- Interpret the coefficients to understand the impact of each variable on fuel efficiency.
5. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing helps determine whether the relationships observed in the data are statistically significant. Common tests include:
- T-tests: Compare the means of two groups.
- ANOVA: Compare the means of three or more groups.
- Chi-square tests: Test relationships between categorical variables.
Example: In the car value assessment homework, you might:
- Test whether the type of car (small, family, upscale) significantly affects the cost per mile.
- Determine if smaller cars provide better value than larger cars using regression analysis and hypothesis testing.
6. Model Refinement
After developing your initial models, refine them by:
- Removing insignificant variables: Use p-values to identify and remove predictors that do not significantly contribute to the model.
- Checking for multicollinearity: Ensure that independent variables are not highly correlated, which can distort the results.
- Cross-validation: Validate the model using different subsets of the data to ensure its robustness.
7. Reporting and Interpretation
Finally, present your findings in a clear and concise manner. Your report should include:
- Introduction: Briefly describe the purpose of the analysis and the data used.
- Methodology: Explain the steps taken to prepare the data, conduct the analysis, and develop the models.
- Results: Present the key findings, including descriptive statistics, regression coefficients, and hypothesis test results.
- Discussion: Interpret the results, discuss their implications, and make recommendations based on your analysis.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and suggest areas for further research or analysis.
Example: In the car value assessment homework, your report might conclude that smaller cars generally offer better value than larger cars, supported by statistical evidence from your regression models and hypothesis tests.
Tools and Software
Leverage statistical software such as R , Python (with libraries like Pandas and Statsmodels), SPSS , or Excel for your analysis. These tools provide powerful functions for data manipulation, visualization, and statistical modeling.
By following these steps, you can effectively solve complex statistics homework and provide meaningful insights from your analysis. Remember to stay organized, validate your models, and clearly communicate your findings. With practice, you’ll become proficient in tackling any statistics homework that comes your way.
Post a comment...
How to overcome challenges in statistics homework submit your homework, attached files.
| File | Actions |
|---|

Similar Problems from Web Search
Failure Analysis of Automotive Drive System: A Six Sigma DMADV Approach
- Tools and Techniques
- Published: 24 August 2024
Cite this article

- Shivagond Teli 1 ,
- Vinod Surange ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3388-9489 2 &
- Lokpriya Gaikwad 3
10 Accesses
Explore all metrics
This study outlines the application of the Six Sigma methodology to rectify oil seal leaks in an automobile company's hollow drive shafts. Persistent issues with oil seepage through the shaft's oil seal led to clutch malfunctions, power failures, and subsequent breakdowns, resulting in high warranty costs, which negatively impacted the status of a firm in the market and the level of fulfillment experienced by its clients. Projects are crucial for translating an organization's strategic goals into achievable outcomes, serving as the cornerstone of success. We implemented a quality-driven effort using Six Sigma and the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) to foster a culture of continuous improvement. Utilizing the procedures-oriented DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) technique, the oil seal leakage issue was addressed and resolved successfully from the gearbox. The Pugh matrix was used to choose a new design from various alternatives, a KANO model to evaluate customer demands, and a cause-and-effect diagram to analyze possible failure situations. The overall aim was to determine the failure situations that were most likely to occur. Through its deployment, we intended to improve both the product's dependability and the production process's efficiency. Following the design improvements, the defects observed in the assemblies dropped to 58, with no occurrences of oil seal leakage. It is plausible to conclude that these techniques can significantly enhance product quality. The study demonstrates the efficacy of Six Sigma methodologies in tackling intricate situations.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
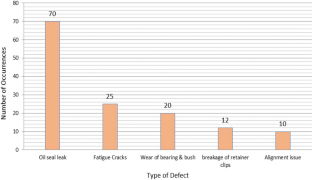
Similar content being viewed by others

Application of 7-Step Problem-Solving Methodology for Defect Elimination: A Case Study in an Automotive Industry

Advanced RCM Industry Case—Modeling and Advanced Analytics (ELMAS) for Improved Availability and Cost-Efficiency

Integrating Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability Issues for Analyzing Failures in Fuel Injection Pump
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
S. Thawani, Six Sigma—strategy for organizational excellence. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 15 (5–6), 655–664 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/14783360410001680143
Article Google Scholar
S.D.R. Perera, Failure on an automobile rear axle shaft. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 22 (3), 934–939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-022-01412-x
I. Daniyan, A. Adeodu, K. Mpofu, R. Maladzhi, M.G. Kana-Kana Katumba, Application of lean Six Sigma methodology using DMAIC approach for the improvement of bogie assembly process in the railcar industry. Heliyon. 8 (3), e09043 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09043
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
L.M. Gaikwad, S.N. Teli, V.S. Majali, U.M. Bhushi, An application of Six Sigma to reduce supplier quality cost. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. C. 97 (1), 93–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-015-0200-2
M. Singh, R. Rathi, Investigation of critical success factors associated with Lean Six Sigma implementation in MSMEs using best worst method. Int. J. Six Sigma Compet. Advant. 12 (2/3), 209–233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSCA.2020.110976
K.M. Suresh, P. Asokan, S. Vinodh, Application of design for Six Sigma methodology to an automotive component. Int. J. Six Sigma Compet. Advant. 10 (1), 1–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSCA.2016.080446
D.S. Jiju Antony, J.J. Dahlgaard, Lean Six Sigma and innovation: an exploratory study among UK organisations. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 27 (1–2), 124–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2014.959255
V.G. Surange, Implementation of Six Sigma to reduce cost of quality: a case study of automobile sector. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 15 (2), 282–294 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9927-6
L.M. Gaikwad, U. Bhushi, S.N. Teli, Implementation of Six Sigma methodologies to gain a competitive advantage: a case study approach (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ASET53988.2022.9735103
A. Trubetskaya, O. McDermott, P. Durand, D.J. Powell, Improving value chain data lifecycle management utilising design for Lean Six Sigma methods. TQM J. 36 (9), 136–154 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-01-2024-0020
S.G. Bidikar, S.B. Rane, P.R. Potdar, Product development using design for Six Sigma approach: case study in switchgear industry. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 13 (1), 203–230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01199-4
F.-K. Wang, C.-T. Yeh, T.-P. Chu, Using the design for Six Sigma approach with TRIZ for new product development. Comput. Ind. Eng. 98 , 522–530 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.06.014
D.M. Wu, C.K.P. Luk, W.Z. Fei, Quality control of low-cost electric machines for electric vehicles by DOE assisted six sigma DMADV method, in 2017 7th International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications: Smart Mobility, Power Transfer & Security (PESA) (2017), pp. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/PESA.2017.8277740
K. Guler, D.M. Petrisor, A Pugh Matrix based product development model for increased small design team efficiency. Cogent Eng. 8 (1), 1923383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2021.1923383
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Bharati Vidyapeeth College of Engineering, Navi Mumbai, India
Shivagond Teli
Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Nagpur, Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, India
Vinod Surange
SIES Graduate School of Technology, Navi Mumbai, India
Lokpriya Gaikwad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Vinod Surange .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Teli, S., Surange, V. & Gaikwad, L. Failure Analysis of Automotive Drive System: A Six Sigma DMADV Approach. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-024-02003-8
Download citation
Received : 21 March 2024
Revised : 06 July 2024
Accepted : 21 July 2024
Published : 24 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-024-02003-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Automotive manufacturing
- TRIZ methodology
- Critical-to-Quality (CTQ)
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
The Problem-Solving Process. In order to effectively manage and run a successful organization, leadership must guide their employees and develop problem-solving techniques. Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below.
Problem-solving is an important component of any business or organization. It entails identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems in order to improve processes, drive results, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. A3 Problem solving is one of the most effective problem-solving methodologies. A3 Problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to ...
A problem solving process is a step-by-step framework from going from discovering a problem all the way through to implementing a solution. With practice, this framework can become intuitive, and innovative companies tend to have a consistent and ongoing ability to discover and tackle challenges when they come up.
In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that's a problem-solving methodology.
The Problem-Solving Process. The process of problem-solving is a methodical approach that involves several distinct stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in navigating from the initial recognition of a problem to its final resolution. Let's explore each of these stages in detail. Step 1: Identifying the Problem. This is the foundational ...
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner. The 8D process consists of the following steps:
The problem solving process typically includes: Pinpointing what's broken by gathering data and consulting with team members. Figuring out why it's not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem. Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution. While skills like active listening ...
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious ...
The McKinsey guide to problem solving. Become a better problem solver with insights and advice from leaders around the world on topics including developing a problem-solving mindset, solving problems in uncertain times, problem solving with AI, and much more.
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
DMAIC is best suited for a complex problem, or if the risk is high. 8D is known as the Eight Disciplines of problem-solving. It consists of eight steps to solve difficult, recurring, or critical problems. The methodology consists of problem-solving tools to help you identify, correct, and eliminate the source of problems within your organization.
The 8 Steps and the Problem-Solving Process. The Culture of Problem-Solving. Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) Gain Problem-Solving Support. As a manufacturing professional, you know how important it is to stay organized, keep your goals in mind and strive for success. But with all of the responsibilities and daily tasks piling up, it takes effort to ...
Problem solving is the process of reviewing every element of an issue so you can get to a solution or fix it. Problem solving steps cover multiple aspects of a problem that you can bring together to find a solution. Whether that's in a group collaboratively or independently, the process remains the same, but the approach and the steps can differ.
The eight disciplines (8D) model is a problem solving approach typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals, and is most commonly used by the automotive industry but has also been successfully applied in healthcare, retail, finance, government, and manufacturing. The purpose of the 8D methodology is to identify, correct, and ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
1. Problem definition. A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem. 2. The problem-solving process. Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations. 3. Distinctiveness practices.
Evaluate the options. Select the best solution. Create an implementation plan. Communicate your solution. Let's look at each step in a little more detail. The first solution you come up with won't always be the best - taking the time to consider your options is an essential problem solving technique. 1.
Step 6: Implement the Solution. Implementing the solution you decide on can include creating an implementation plan. It could also include planning on what happens next if something goes wrong with the solution if it doesn't work out the way you thought it would. Implementation means that everyone on your team knows and understands their part ...
Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also "problems" that need to be "solved". Here are the steps of a problem-solving process: 1. Defining the Problem. The first step in the process is often ...
Here are the seven steps of the rational approach: Define the problem. Identify possible causes. Brainstorm options to solve the problem. Select an option. Create an implementation plan. Execute the plan and monitor the results. Evaluate the solution. Read more: Effective Problem Solving Steps in the Workplace.
Then check out more insights on problem-solving approaches, and dive into examples of pressing challenges organizations are contending with now. Five routes to more innovative problem solving. Author Talks: Get on the performance curve. Strategy to beat the odds. How to master the seven-step problem-solving process. Want better strategies?
What is problem-solving? Problem-solving is both an ability and a process. As an ability, problem-solving can help resolve issues in different environments, such as home, school, abroad, and social situations. As a process, problem-solving involves a series of steps for finding solutions to questions or concerns that arise throughout life.
Design thinking is in contrast to more traditional problem-solving methods. Historically, many fields and industries employed a more linear process (sometimes called "Waterfall"), which defined a problem from a business standpoint and approached it with a rigid, one-step-after-the-other procedure. Truly creative solutions are less ordered.
1. Understanding the Problem Statement. The first step in solving any statistics homework is to thoroughly understand the problem statement. Break down the homework into smaller, manageable parts and identify the key objectives. For example, in the given homework, you might need to: Analyze data to make informed decisions.
A couple tackled the $4.3 million renovation of their mahogany-clad Nevada home, including the addition of a guesthouse and garage—but they didn't always see eye to eye on the approach.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. ... x = 0 Step by step solution : Step 1 :Solving a Single Variable Equation : 1.1 Solve : -15x = 0 Multiply both sides of the ... 3x(x-15) https://www.tiger-algebra.com ...
The steps are defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, controlling (DMAIC), and defining, measuring, analyzing, designing, and verifying (DMADV). The following studies are available to focus further on the application of the DMADV steps. Authors Wang et al. incorporated DMADV steps with the Theory of Inventive Problem-Solving (TRIZ) method ...