- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify
Table of Contents

Research Gap
Definition:
Research gap refers to an area or topic within a field of study that has not yet been extensively researched or is yet to be explored. It is a question, problem or issue that has not been addressed or resolved by previous research.
How to Identify Research Gap
Identifying a research gap is an essential step in conducting research that adds value and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. Research gap requires critical thinking, creativity, and a thorough understanding of the existing literature . It is an iterative process that may require revisiting and refining your research questions and ideas multiple times.
Here are some steps that can help you identify a research gap:
- Review existing literature: Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in your research area. This will help you identify what has already been studied and what gaps still exist.
- Identify a research problem: Identify a specific research problem or question that you want to address.
- Analyze existing research: Analyze the existing research related to your research problem. This will help you identify areas that have not been studied, inconsistencies in the findings, or limitations of the previous research.
- Brainstorm potential research ideas : Based on your analysis, brainstorm potential research ideas that address the identified gaps.
- Consult with experts: Consult with experts in your research area to get their opinions on potential research ideas and to identify any additional gaps that you may have missed.
- Refine research questions: Refine your research questions and hypotheses based on the identified gaps and potential research ideas.
- Develop a research proposal: Develop a research proposal that outlines your research questions, objectives, and methods to address the identified research gap.
Types of Research Gap
There are different types of research gaps that can be identified, and each type is associated with a specific situation or problem. Here are the main types of research gaps and their explanations:
Theoretical Gap
This type of research gap refers to a lack of theoretical understanding or knowledge in a particular area. It can occur when there is a discrepancy between existing theories and empirical evidence or when there is no theory that can explain a particular phenomenon. Identifying theoretical gaps can lead to the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones.
Empirical Gap
An empirical gap occurs when there is a lack of empirical evidence or data in a particular area. It can happen when there is a lack of research on a specific topic or when existing research is inadequate or inconclusive. Identifying empirical gaps can lead to the development of new research studies to collect data or the refinement of existing research methods to improve the quality of data collected.
Methodological Gap
This type of research gap refers to a lack of appropriate research methods or techniques to answer a research question. It can occur when existing methods are inadequate, outdated, or inappropriate for the research question. Identifying methodological gaps can lead to the development of new research methods or the modification of existing ones to better address the research question.
Practical Gap
A practical gap occurs when there is a lack of practical applications or implementation of research findings. It can occur when research findings are not implemented due to financial, political, or social constraints. Identifying practical gaps can lead to the development of strategies for the effective implementation of research findings in practice.
Knowledge Gap
This type of research gap occurs when there is a lack of knowledge or information on a particular topic. It can happen when a new area of research is emerging, or when research is conducted in a different context or population. Identifying knowledge gaps can lead to the development of new research studies or the extension of existing research to fill the gap.
Examples of Research Gap
Here are some examples of research gaps that researchers might identify:
- Theoretical Gap Example : In the field of psychology, there might be a theoretical gap related to the lack of understanding of the relationship between social media use and mental health. Although there is existing research on the topic, there might be a lack of consensus on the mechanisms that link social media use to mental health outcomes.
- Empirical Gap Example : In the field of environmental science, there might be an empirical gap related to the lack of data on the long-term effects of climate change on biodiversity in specific regions. Although there might be some studies on the topic, there might be a lack of data on the long-term effects of climate change on specific species or ecosystems.
- Methodological Gap Example : In the field of education, there might be a methodological gap related to the lack of appropriate research methods to assess the impact of online learning on student outcomes. Although there might be some studies on the topic, existing research methods might not be appropriate to assess the complex relationships between online learning and student outcomes.
- Practical Gap Example: In the field of healthcare, there might be a practical gap related to the lack of effective strategies to implement evidence-based practices in clinical settings. Although there might be existing research on the effectiveness of certain practices, they might not be implemented in practice due to various barriers, such as financial constraints or lack of resources.
- Knowledge Gap Example: In the field of anthropology, there might be a knowledge gap related to the lack of understanding of the cultural practices of indigenous communities in certain regions. Although there might be some research on the topic, there might be a lack of knowledge about specific cultural practices or beliefs that are unique to those communities.
Examples of Research Gap In Literature Review, Thesis, and Research Paper might be:
- Literature review : A literature review on the topic of machine learning and healthcare might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the use of machine learning for early detection of rare diseases.
- Thesis : A thesis on the topic of cybersecurity might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the effectiveness of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing cyber attacks.
- Research paper : A research paper on the topic of natural language processing might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the use of natural language processing techniques for sentiment analysis in non-English languages.
How to Write Research Gap
By following these steps, you can effectively write about research gaps in your paper and clearly articulate the contribution that your study will make to the existing body of knowledge.
Here are some steps to follow when writing about research gaps in your paper:
- Identify the research question : Before writing about research gaps, you need to identify your research question or problem. This will help you to understand the scope of your research and identify areas where additional research is needed.
- Review the literature: Conduct a thorough review of the literature related to your research question. This will help you to identify the current state of knowledge in the field and the gaps that exist.
- Identify the research gap: Based on your review of the literature, identify the specific research gap that your study will address. This could be a theoretical, empirical, methodological, practical, or knowledge gap.
- Provide evidence: Provide evidence to support your claim that the research gap exists. This could include a summary of the existing literature, a discussion of the limitations of previous studies, or an analysis of the current state of knowledge in the field.
- Explain the importance: Explain why it is important to fill the research gap. This could include a discussion of the potential implications of filling the gap, the significance of the research for the field, or the potential benefits to society.
- State your research objectives: State your research objectives, which should be aligned with the research gap you have identified. This will help you to clearly articulate the purpose of your study and how it will address the research gap.
Importance of Research Gap
The importance of research gaps can be summarized as follows:
- Advancing knowledge: Identifying research gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge in a particular field. By identifying areas where additional research is needed, researchers can fill gaps in the existing body of knowledge and contribute to the development of new theories and practices.
- Guiding research: Research gaps can guide researchers in designing studies that fill those gaps. By identifying research gaps, researchers can develop research questions and objectives that are aligned with the needs of the field and contribute to the development of new knowledge.
- Enhancing research quality: By identifying research gaps, researchers can avoid duplicating previous research and instead focus on developing innovative research that fills gaps in the existing body of knowledge. This can lead to more impactful research and higher-quality research outputs.
- Informing policy and practice: Research gaps can inform policy and practice by highlighting areas where additional research is needed to inform decision-making. By filling research gaps, researchers can provide evidence-based recommendations that have the potential to improve policy and practice in a particular field.
Applications of Research Gap
Here are some potential applications of research gap:
- Informing research priorities: Research gaps can help guide research funding agencies and researchers to prioritize research areas that require more attention and resources.
- Identifying practical implications: Identifying gaps in knowledge can help identify practical applications of research that are still unexplored or underdeveloped.
- Stimulating innovation: Research gaps can encourage innovation and the development of new approaches or methodologies to address unexplored areas.
- Improving policy-making: Research gaps can inform policy-making decisions by highlighting areas where more research is needed to make informed policy decisions.
- Enhancing academic discourse: Research gaps can lead to new and constructive debates and discussions within academic communities, leading to more robust and comprehensive research.
Advantages of Research Gap
Here are some of the advantages of research gap:
- Identifies new research opportunities: Identifying research gaps can help researchers identify areas that require further exploration, which can lead to new research opportunities.
- Improves the quality of research: By identifying gaps in current research, researchers can focus their efforts on addressing unanswered questions, which can improve the overall quality of research.
- Enhances the relevance of research: Research that addresses existing gaps can have significant implications for the development of theories, policies, and practices, and can therefore increase the relevance and impact of research.
- Helps avoid duplication of effort: Identifying existing research can help researchers avoid duplicating efforts, saving time and resources.
- Helps to refine research questions: Research gaps can help researchers refine their research questions, making them more focused and relevant to the needs of the field.
- Promotes collaboration: By identifying areas of research that require further investigation, researchers can collaborate with others to conduct research that addresses these gaps, which can lead to more comprehensive and impactful research outcomes.
Disadvantages of Research Gap
While research gaps can be advantageous, there are also some potential disadvantages that should be considered:
- Difficulty in identifying gaps: Identifying gaps in existing research can be challenging, particularly in fields where there is a large volume of research or where research findings are scattered across different disciplines.
- Lack of funding: Addressing research gaps may require significant resources, and researchers may struggle to secure funding for their work if it is perceived as too risky or uncertain.
- Time-consuming: Conducting research to address gaps can be time-consuming, particularly if the research involves collecting new data or developing new methods.
- Risk of oversimplification: Addressing research gaps may require researchers to simplify complex problems, which can lead to oversimplification and a failure to capture the complexity of the issues.
- Bias : Identifying research gaps can be influenced by researchers’ personal biases or perspectives, which can lead to a skewed understanding of the field.
- Potential for disagreement: Identifying research gaps can be subjective, and different researchers may have different views on what constitutes a gap in the field, leading to disagreements and debate.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

How To Find A Research Gap, Quickly
A step-by-step guide for new researchers
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | April 2023
If you’ve got a dissertation, thesis or research project coming up, one of the first (and most important) things you’ll need to do is find a suitable research gap . In this post, we’ll share a straightforward process to help you uncover high-quality, original research gaps in a very time-efficient manner.
Overview: Finding Research Gaps
- What exactly is a research gap?
- Research gap vs research topic
- How to find potential research gaps
- How to evaluate research gaps (and topics)
- Key takeaways
What is a research gap?
As a starting point, it’s useful to first define what we mean by research gap, to ensure we’re all on the same page. The term “research gap” gets thrown around quite loosely by students and academics alike, so let’s clear that up.
Simply put, a research gap is any space where there’s a lack of solid, agreed-upon research regarding a specific topic, issue or phenomenon. In other words, there’s a lack of established knowledge and, consequently, a need for further research.
Let’s look at a hypothetical example to illustrate a research gap.
Within the existing research regarding factors affect job satisfaction , there may be a wealth of established and agreed-upon empirical work within a US and UK context , but very little research within Eastern nations such as Japan or Korea . Given that these nations have distinctly different national cultures and workforce compositions compared to the West, it’s plausible that the factors that contribute toward job satisfaction may also be different. Therefore, a research gap emerges for studies that explore this matter.
This example is purely hypothetical (and there’s probably plenty of research covering this already), but it illustrates the core point that a research gap reflects a lack of firmly established knowledge regarding a specific matter . Given this lack, an opportunity exists for researchers (like you) to go on and fill the gap.
So, it’s the same as a research topic?
Not quite – but they are connected. A research gap refers to an area where there’s a lack of settled research , whereas a research topic outlines the focus of a specific study . Despite being different things, these two are related because research gaps are the birthplace of research topics. In other words, by identifying a clear research gap, you have a foundation from which you can build a research topic for your specific study. Your study is unlikely to resolve the entire research gap on it’s own, but it will contribute towards it .
If you’d like to learn more, we’ve got a comprehensive post that covers research gaps (including the different types of research gaps), as well as an explainer video below.
How to find a research gap
Now that we’ve defined what a research gap is, it’s time to get down to the process of finding potential research gaps that you can use as a basis for potential research topics. Importantly, it’s worth noting that this is just one way (of many) to find a research gap (and consequently a topic). We’re not proposing that it’s the only way or best way, but it’s certainly a relatively quick way to identify opportunities.
Step 1: Identify your broad area of interest
The very first step to finding a research gap is to decide on your general area of interest . For example, if you were undertaking a dissertation as part of an MBA degree, you may decide that you’re interested in corporate reputation, HR strategy, or leadership styles. As you can see, these are broad categories – there’s no need to get super specific just yet. Of course, if there is something very specific that you’re interested in, that’s great – but don’t feel pressured to narrow it down too much right now.
Equally important is to make sure that this area of interest is allowed by your university or whichever institution you’ll be proposing your research to. This might sound dead obvious, but you’ll be surprised how many times we’ve seen students run down a path with great excitement, only to later learn that their university wants a very specific area of focus in terms of topic (and their area of interest doesn’t qualify).

Step 2: Do an initial literature scan
Once you’ve pinned down your broad area (or areas) of interest, the next step is to head over to Google Scholar to undertake an initial literature scan . If you’re not familiar with this tool, Google Scholar is a great starting point for finding academic literature on pretty much any topic, as it uses Google’s powerful search capabilities to hunt down relevant academic literature. It’s certainly not the be-all and end-all of literature search tools, but it’s a useful starting point .
Within Google Scholar, you’ll want to do a few searches using keywords that are relevant to your area of interest. Sticking with our earlier example, we could use the key phrase “job satisfaction”, or we may want to get a little more specific – perhaps “job satisfaction for millennials” or “job satisfaction in Japan”.
It’s always a good idea to play around with as many keywords/phrases as you can think up. Take an iterative approach here and see which keywords yield the most relevant results for you. Keep each search open in a new tab, as this will help keep things organised for the next steps.
Once you’ve searched for a few different keywords/phrases, you’ll need to do some refining for each of the searches you undertook. Specifically, you’ll need to filter the results down to the most recent papers . You can do this by selecting the time period in the top left corner (see the example below).

Filtering to the current year is typically a good choice (especially for fast-moving research areas), but in some cases, you may need to filter to the last two years . If you’re undertaking this task in January or February, for example, you’ll likely need to select a two-year period.
Need a helping hand?
Step 3: Review and shortlist articles that interest you
Once you’ve run a few searches using different keywords and phrases, you’ll need to scan through the results to see what looks most relevant and interesting to you. At this stage, you can just look at the titles and abstracts (the description provided by Google Scholar) – don’t worry about reading the actual article just yet.
Next, select 5 – 10 articles that interest you and open them up. Here, we’re making the assumption that your university has provided you with access to a decent range of academic databases. In some cases, Google Scholar will link you directly to a PDF of the article, but in most cases, you’ll need paid access. If you don’t have this (for example, if you’re still applying to a university), you can look at two options:
Open-access articles – these are free articles which you can access without any journal subscription. A quick Google search (the regular Google) will help you find open-access journals in your area of interest, but you can also have a look at DOAJ and Elsevier Open Access.
DeepDyve – this is a monthly subscription service that allows you to get access to a broad range of journals. At the time of shooting this video, their monthly subscription is around $50 and they do offer a free trial, which may be sufficient for your project.
Step 4: Skim-read your article shortlist
Now, it’s time to dig into your article shortlist and do some reading. But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the articles from start to finish – you just need to focus on a few key sections.
Specifically, you’ll need to pay attention to the following:
- The abstract (which you’ve probably already read a portion of in Google Scholar)
- The introduction – this will give you a bit more detail about the context and background of the study, as well as what the researchers were trying to achieve (their research aims)
- The discussion or conclusion – this will tell you what the researchers found
By skimming through these three sections for each journal article on your shortlist, you’ll gain a reasonable idea of what each study was about, without having to dig into the painful details. Generally, these sections are usually quite short, so it shouldn’t take you too long.
Step 5: Go “FRIN hunting”
This is where the magic happens. Within each of the articles on your shortlist, you’ll want to search for a few very specific phrases , namely:
- Future research
- Further research
- Research opportunities
- Research directions
All of these terms are commonly found in what we call the “FRIN” section . FRIN stands for “further research is needed”. The FRIN is where the researchers explain what other researchers could do to build on their study, or just on the research area in general. In other words, the FRIN section is where you can find fresh opportunities for novel research . Most empirical studies will either have a dedicated FRIN section or paragraph, or they’ll allude to the FRIN toward the very end of the article. You’ll need to do a little scanning, but it’s usually pretty easy to spot.
It’s worth mentioning that naturally, the FRIN doesn’t hand you a list of research gaps on a platter. It’s not a silver bullet for finding research gaps – but it’s the closest thing to it. Realistically, the FRIN section helps you shortcut the gap-hunting process by highlighting novel research avenues that are worth exploring.
This probably sounds a little conceptual, so let’s have a look at a few examples:
The impact of overeducation on job outcomes: Evidence from Saudi Arabia (Alzubaidi, 2020)
If you scroll down to the bottom of this article, you’ll see there’s a dedicated section called “Limitations and directions for future research”. Here they talk about the limitations of the study and provide suggestions about how future researchers could improve upon their work and overcome the limitations.
Perceived organizational support and job satisfaction: a moderated mediation model of proactive personality and psychological empowerment (Maan et al, 2020)
In this article, within the limitations section, they provide a wonderfully systematic structure where they discuss each limitation, followed by a proposal as to how future studies can overcome the respective limitation. In doing so, they are providing very specific research opportunities for other researchers.
Medical professionals’ job satisfaction and telemedicine readiness during the COVID-19 pandemic: solutions to improve medical practice in Egypt (El-Mazahy et al, 2023)
In this article, they don’t have a dedicated section discussing the FRIN, but we can deduct it based on the limitations section. For example, they state that an evaluation of the knowledge about telemedicine and technology-related skills would have enabled studying their independent effect on the perception of telemedicine.
Follow this FRIN-seeking process for the articles you shortlisted and map out any potentially interesting research gaps . You may find that you need to look at a larger number of articles to find something interesting, or you might find that your area of interest shifts as you engage in the reading – this is perfectly natural. Take as much time as you need to develop a shortlist of potential research gaps that interest you.
Importantly, once you’ve developed a shortlist of potential research gaps, you need to return to Google Scholar to double-check that there aren’t fresh studies that have already addressed the gap. Remember, if you’re looking at papers from two years ago in a fast-moving field, someone else may have jumped on it . Nevertheless, there could still very well be a unique angle you could take – perhaps a contextual gap (e.g. a specific country, industry, etc.).
Ultimately, the need for originality will depend on your specific university’s requirements and the level of study. For example, if you’re doing an undergraduate research project, the originality requirements likely won’t be as gruelling as say a Masters or PhD project. So, make sure you have a clear understanding of what your university’s expectations are. A good way to do this is to look at past dissertations and theses for your specific programme. You can usually find these in the university library or by asking the faculty.
How to evaluate potential research gaps
Once you’ve developed a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant potential research topics) that interest you, you’ll need to systematically evaluate them to choose a winner. There are many factors to consider here, but some important ones include the following:
- Originality and value – is the topic sufficiently novel and will addressing it create value?
- Data access – will you be able to get access to the sample of interest?
- Costs – will there be additional costs involved for data collection and/or analysis?
- Timeframes – will you be able to collect and analyse the data within the timeframe required by your university?
- Supervisor support – is there a suitable supervisor available to support your project from start to finish?
To help you evaluate your options systematically, we’ve got a topic evaluation worksheet that allows you to score each potential topic against a comprehensive set of criteria. You can access the worksheet completely free of charge here .

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered quite a lot of ground in this post. Here are the key takeaways:
- A research gap is any space where there’s a lack of solid, agreed-upon research regarding a specific topic/issue/phenomenon.
- Unique research topics emerge from research gaps , so it’s essential to first identify high-quality research gaps before you attempt to define a topic.
- To find potential research gaps, start by seeking out recent journal articles on Google Scholar and pay particular attention to the FRIN section to identify novel opportunities.
- Once you have a shortlist of prospective research gaps and resultant topic ideas, evaluate them systematically using a comprehensive set of criteria.
If you’d like to get hands-on help finding a research gap and research topic, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey, step by step.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Very useful for me, but i am still confusing review of literature review, how to find out topic related previous research.
Powerful notes! Thanks a lot.
This is helpful. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for this. It is really a great opportunity for me to learn the research journey.
Very Useful
It nice job
You have sharpened my articulations of these components to the core. Thanks so much.
It’s educative and an inspiring way of impacting research knowledge…
Thanks to the writer
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Identifying Research Gaps to Pursue Innovative Research
This article is an excerpt from a lecture given by my Ph.D. guide, a researcher in public health. She advised us on how to identify research gaps to pursue innovative research in our fields.
What is a Research Gap?
Today we are talking about the research gap: what is it, how to identify it, and how to make use of it so that you can pursue innovative research. Now, how many of you have ever felt you had discovered a new and exciting research question , only to find that it had already been written about? I have experienced this more times than I can count. Graduate studies come with pressure to add new knowledge to the field. We can contribute to the progress and knowledge of humanity. To do this, we need to first learn to identify research gaps in the existing literature.
A research gap is, simply, a topic or area for which missing or insufficient information limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question. It should not be confused with a research question, however. For example, if we ask the research question of what the healthiest diet for humans is, we would find many studies and possible answers to this question. On the other hand, if we were to ask the research question of what are the effects of antidepressants on pregnant women, we would not find much-existing data. This is a research gap. When we identify a research gap, we identify a direction for potentially new and exciting research.

How to Identify Research Gap?
Considering the volume of existing research, identifying research gaps can seem overwhelming or even impossible. I don’t have time to read every paper published on public health. Similarly, you guys don’t have time to read every paper. So how can you identify a research gap?
There are different techniques in various disciplines, but we can reduce most of them down to a few steps, which are:
- Identify your key motivating issue/question
- Identify key terms associated with this issue
- Review the literature, searching for these key terms and identifying relevant publications
- Review the literature cited by the key publications which you located in the above step
- Identify issues not addressed by the literature relating to your critical motivating issue
It is the last step which we all find the most challenging. It can be difficult to figure out what an article is not saying. I like to keep a list of notes of biased or inconsistent information. You could also track what authors write as “directions for future research,” which often can point us towards the existing gaps.
Different Types of Research Gaps
Identifying research gaps is an essential step in conducting research, as it helps researchers to refine their research questions and to focus their research efforts on areas where there is a need for more knowledge or understanding.
1. Knowledge gaps
These are gaps in knowledge or understanding of a subject, where more research is needed to fill the gaps. For example, there may be a lack of understanding of the mechanisms behind a particular disease or how a specific technology works.
2. Conceptual gaps
These are gaps in the conceptual framework or theoretical understanding of a subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand the relationship between two concepts or to refine a theoretical framework.
3. Methodological gaps
These are gaps in the methods used to study a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to develop new research methods or to refine existing methods to address specific research questions.
4. Data gaps
These are gaps in the data available on a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to collect data on a specific population or to develop new measures to collect data on a particular construct.
5. Practical gaps
These are gaps in the application of research findings to practical situations. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand how to implement evidence-based practices in real-world settings or to identify barriers to implementing such practices.
Examples of Research Gap
Limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms of a disease:.
Despite significant research on a particular disease, there may be a lack of understanding of the underlying mechanisms of the disease. For example, although much research has been done on Alzheimer’s disease, the exact mechanisms that lead to the disease are not yet fully understood.
Inconsistencies in the findings of previous research:
When previous research on a particular topic has inconsistent findings, there may be a need for further research to clarify or resolve these inconsistencies. For example, previous research on the effectiveness of a particular treatment for a medical condition may have produced inconsistent findings, indicating a need for further research to determine the true effectiveness of the treatment.
Limited research on emerging technologies:
As new technologies emerge, there may be limited research on their applications, benefits, and potential drawbacks. For example, with the increasing use of artificial intelligence in various industries, there is a need for further research on the ethical, legal, and social implications of AI.
How to Deal with Literature Gap?
Once you have identified the literature gaps, it is critical to prioritize. You may find many questions which remain to be answered in the literature. Often one question must be answered before the next can be addressed. In prioritizing the gaps, you have identified, you should consider your funding agency or stakeholders, the needs of the field, and the relevance of your questions to what is currently being studied. Also, consider your own resources and ability to conduct the research you’re considering. Once you have done this, you can narrow your search down to an appropriate question.
Tools to Help Your Search
There are thousands of new articles published every day, and staying up to date on the literature can be overwhelming. You should take advantage of the technology that is available. Some services include PubCrawler , Feedly , Google Scholar , and PubMed updates. Stay up to date on social media forums where scholars share new discoveries, such as Twitter. Reference managers such as Mendeley can help you keep your references well-organized. I personally have had success using Google Scholar and PubMed to stay current on new developments and track which gaps remain in my personal areas of interest.
The most important thing I want to impress upon you today is that you will struggle to choose a research topic that is innovative and exciting if you don’t know the existing literature well. This is why identifying research gaps starts with an extensive and thorough literature review . But give yourself some boundaries. You don’t need to read every paper that has ever been written on a topic. You may find yourself thinking you’re on the right track and then suddenly coming across a paper that you had intended to write! It happens to everyone- it happens to me quite often. Don’t give up- keep reading and you’ll find what you’re looking for.
Class dismissed!
How do you identify research gaps? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research gap can be identified by looking for a topic or area with missing or insufficient information that limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Identifying a research gap is important as it provides a direction for potentially new research or helps bridge the gap in existing literature.
Gap in research is a topic or area with missing or insufficient information. A research gap limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Thank u for your suggestion.
Very useful tips specially for a beginner
Thank you. This is helpful. I find that I’m overwhelmed with literatures. As I read on a particular topic, and in a particular direction I find that other conflicting issues, topic a and ideas keep popping up, making me more confused.
I am very grateful for your advice. It’s just on point.
The clearest, exhaustive, and brief explanation I have ever read.
Thanks for sharing
Thank you very much.The work is brief and understandable
Thank you it is very informative
Thanks for sharing this educative article
Thank you for such informative explanation.
Great job smart guy! Really outdid yourself!
Nice one! I thank you for this as it is just what I was looking for!😃🤟
Thank you so much for this. Much appreciated
Thank you so much.
Thankyou for ur briefing…its so helpful
Thank you so much .I’ved learn a lot from this.❤️
Very exciting and useful piece for researchers.
Your are awesome, it’s a great article.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications
10 Ways to Help Students Restore Focus on Learning
Switching Your Major As a Researcher: Things to Consider Before Making the Decision

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?

Text for Mobile
What Is A Research Gap? (With Tips + Examples)
A research gap is a specific area within a field of study that remains unexplored or under-explored. Identifying a research gap involves recognizing where existing research is lacking or where there are unanswered questions that could provide opportunities for further investigation. Understanding research gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge, as it helps scholars and researchers focus their efforts on areas that can contribute significantly to their field.

What Is A Research Gap?
It is actually a question or any issue that needs to be solved by any pre-existing work or research in your area of study. A research gap can also exist where some new idea still needs to be studied.
Tips on Identifying Research Gap
Research always plays an essential role in acquiring more knowledge and addressing the gaps in different fields. When you are identifying a research gap, you are taking a very important step in the whole research process. This aids the researchers in contributing meaningful insights and triggers the knowledge boundaries.
Understanding the Literature You Are Studying: In order to identify any research gap, it is essential to have an excellent advertising of the preexisting literature in your study field.
Here, you need to conduct a review of many books, scholarly articles, conferences, and other relevant sources. In this way, you can get a good foundation as well as insights into any present state of in-depth knowledge in your own study area.
Defining Your Own Research Question: After getting a good knowledge of the pre-existing literature, you need to define a concise and clear idea of the research question. This research question needs to be very specific, attainable, measurable, time-bound and relevant. An acronym for this entire thing is known as SMART. This also needs to address any significant issue that still needs to be fully solved or adequately answered.
Identifying Your Study Objectives: Here, you need to identify the major objectives of your research paper. All these objectives need to be aligned with the identified research gap. These objectives always guide the researcher and aid you in determining the direction and scope of your research study.
Analyze the Existing Studies: Here, you need to analyze very carefully all the existing studies that are related to your research question. Here, it would help if you looked at the most common recurring findings, themes, and patterns of the discussed literature. Here, you also need to pay a lot of attention to the conflicted areas with the results, unanswered questions, and contradictory theories. These areas show the research gaps that can be explored later.
Consider The Practical Relevance: You always need to evaluate the very practical relevance of the research question as well as its potential impact on society. Here, it would help if you always considered the importance of addressing your own research gap as you identified it.
Here, you also need to assess whether your findings can contribute to the original theoretical framework and offer all the practical solutions for leading to the policy recommendations. These practical ads are relevant to the research paper and trigger its impact.
Consulting With the Experts and Peers: You always need to engage you’re discussing with your mentors, peers, and experts in your own field of study. Here, you always need to seek their opinions and perspectives on the research question to identify potential research gaps.
These can provide valuable insights into assumption challenges, and this helps you refine your research work. Your peers and experts can give you a new idea and help you identify the errors in your thinking.
Conducting Your Pilot Study: You need to conduct it to test the viability and feasibility of the research question. This pilot study provides you with feedback and data on the research design, approach and methodology.
This also helps you identify the potential limitations or challenges that need to be solved before conducting the full research studies.
Reflecting and Refining: You need to vividly reflect on the research progress to refine your research preferences. You need to add the objectives. As you go deeper into your research process, additional research gaps may be uncovered to refine your own research needs.
If you follow this process, you can adapt your own approach to ensure the research gaps.
As per the example of the research gap, identifying your research gap allows your research to contribute to gaining more knowledge to address the pre-existing limitations.
This way, you will understand the existing literature to define a crystal clear research statement. You can identify the research gaps by analyzing the existing studies to consider their relevance. According to the research gap finder, if you consult with your peers, doing all the pilot studies reflects on your research process progress.
If you follow the guide mentioned above, you can always embark on meaningful research studies to trigger your knowledge in your subject area and make a prominent contribution to your field.
Also Read: Struggling with Research Paper Writing?
Different Types of Research Gaps
Identifying research gaps is essential for advancing knowledge in any field. Research gaps are areas where more information is available or existing research needs to be more consistent or conclusive. Here are different types of research gaps:

- Evidence Gap
This gap occurs when no empirical evidence supports certain theories, practices, or interventions. It can also refer to areas where existing studies need to sufficiently cover the topic or lack rigorous methodological approaches.
Example: A need for randomized controlled trials on the effectiveness of a new drug.
- Knowledge Gap
This gap refers to areas where there is a deficiency in understanding or awareness about a particular topic. It can be due to outdated information, incomplete research, or the absence of research on emerging issues.
Example: Limited knowledge about the long-term effects of exposure to new environmental pollutants.
- Theoretical Gap
Theoretical gaps arise when existing theories do not fully explain certain phenomena or when there is a lack of theoretical frameworks to guide research in a particular area.
Example: More theoretical models need to be developed to explain the psychological impacts of social media usage on teenagers.
- Methodological Gap
Methodological gaps exist when current research methods are inadequate for addressing certain research questions or when there is a need for new or improved methodologies.
Example: More robust qualitative methods are needed to study the experiences of marginalized communities.
- Population Gap
This type of gap occurs when certain populations are underrepresented in research. It can involve demographics like age, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, or geographic location.
Example: Lack of research on the mental health of older adults living in rural areas.
Geographical Gap
Geographical gaps refer to areas or regions that are under-researched. These gaps highlight the need for studies in different geographic contexts to understand local issues better.
Example: Limited studies on the effects of climate change in the Arctic regions.

Strategies to Identify Research Gaps:
- Literature Reviews: Comprehensive reviews can help identify where current research is lacking or inconsistent.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: These methods provide a structured approach to synthesize existing research and identify gaps.
- Expert Consultations: Discussions with experts in the field can uncover areas that require further investigation.
- Research Databases: Utilizing databases and citation analysis tools to track research trends and identify under-researched areas.
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: Engaging with multiple disciplines can reveal gaps that are not apparent within a single field.
Understanding and addressing these gaps is crucial for advancing research and knowledge across various domains.
Read More: How To Get A+ Grade In Research Paper?
What is a Research Gap Example?
A Research Paper Example gives you a very clear idea of how to find your research gaps and examples in textual forms. A few examples are given below:
- Context Healthcare: Although there have been enough researchers on the management of diabetes, there has been a research gap in understanding the impact of digital health interventions in the rural areas of Europe.
- Content environmental science: In a wealth of research regarding the huge environmental pollution caused by the use of plastics, there are fewer findings of how the plastic material really accumulates in certain areas like lakes, rivers, etc. and why these materials are never biodegradable.
- Context Education: The empirical research surrounding the online mode has become tremendously popular over the past few years. However, there needs to be more solid studies regarding the impact of the online learning process on the students who need special education. In each of these examples, you can see that the writer begins by acknowledging the preexisting reach results and then explains thoroughly the present area where the research gap really exists.

Also Read: Why Research Is Essential For Students? 20 Common Reasons!
How to Find a Research Gap?
After getting a very clear idea of various types of research gaps, the vet’s next question comes to mind is how to find a research gap. There is a basic 2 step strategy to find the research gap.
In the beginning, you need to find a lot of literature reviews, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews covering your research area of interest. Moreover, it would help if you dug into the very recent journals for wrapping your head in your own knowledge area.
Here, you can also study the current theses and dissertations, especially those in the doctoral degree courses. A number of dissertation databases, such as Open Access, EBSCO, Pro-Quest, etc., are very useful in this regard. Here. You also need to ensure that you are always looking for the most recent sources.
After gathering a good collection of these resources, you need to focus on further research opportunities. In this section, you need to state explicitly where more studies are needed. It would help if you also looked at the present research study’s limitation areas and where the research gaps might exist.
Following this procedure will help you become oriented to the present research area. This can serve as a foundation for finding the potential research gaps. Then, you need to shortlist the main ideas and evaluate them as per the given topic. It would help if you also looked only for the recent articles here.
Also Read: Expert Literature Review Writing Services
How to Deal with Literature Gap?
In any project, a literature review is always very important. It helps you in identifying your excusing knowledge, methods and theories in your own field. However, conducting a literature review has its own challenges.
- Defiling your research question: The very first step is to define your own research question very clearly and briefly. It will help you narrow your scope and focus on the crucial sources. It would help if you used less information here. Your research must always be very specific, answerable, and original. The research project always needs to have real objectives and a purpose.
- Searching and selecting the sources: Your next step is to search and select the sources. That is very much reliable and relevant to your research field. There are a number of databases, like keywords, search engines, etc., related to your study field. However, there are also a lot of limitations to these tools, like currency, coverage, and quality of the sources. Here, certain criteria have to be applied to filter the sources, such as relevance, authority, timeline, and accuracy of the information.
- Analyzing and synthesizing the literature: This is the third step, where you need to analyze and synthesize the literature you selected. Here, you need to summarize the sources and compare, contrast and critique them. In this section, you also need to look for the similarities and differences, the strengths and weaknesses, and the gaps and inconsistencies of the literature review paper. The writers can also identify the major trends, themes, and debates in the discussed field. These should also be related to your research question.
- Fill in the gaps after identifying them: This is the 4th step to filling the literature review research paper. This gap needs to be addressed or is under the researched area and is to be addressed by you with the help of your knowledge. These gaps can be filled by looking for the limitations, contradictions or controversies in the review. You can also do this by asking new questions or proposing new ideas. The gaps can also be filled by providing the newest evidence, arguments or even insights related to your field of study.
- Organizing and structuring the literature review: This is the 5th step of your review, where you need to organize and structure the whole paper in a compact and logical manner. Here, you always need to follow certain guidelines as given by your institute and use the best style and font. Proper headings, subheading citations, and traditions should also be used here. This will help your readers follow your arguments and understand what you want to say. A very clear introduction should also be written, along with a good conclusion and summary to highlight your writing.
- Refining and Revising: The literature review is the final step of writing your literature review. Here, you need to ensure that your review is quite accurate, concise and clear. You must check your literature review thoroughly to make it free from errors, gaps, or inconsistencies in language, content, or presentation. Here, you can also seek feedback from your peers, experts or supervisors in your own field. Their suggestions will help you in performing well. The whore literature review should be thoroughly proofread and edited before the final submission.
Last but not least, never copy from any source; it will be considered plagiarism, and your paper will be cancelled then and there. Thus, write only from your own creativity and not from the writing and articles of other writers.

Read More: Dissertation Literature Review For Masters & PhD
Final Words
Writing a research paper is a challenging task. It would help if you had a lot of Research Skills to accomplish it. You will be given a Research topic on which you have to write. Your ultimate aim in writing the research paper is to get the top grade. This can be done by availing of the best online Case Study Help Service from a reliable provider. The Casestudyhelp is the best choice for you in this respect.
Why CaseStudyHelp?
- We will provide you with the best research gap example in the thesis
- Top online Research Paper Writing Service is provided by us with the most reasonable service charges
- Top grades are always assured by the online Dissertation Help service provided by us
- Our experts provide 24/7 hours of online help and support
- We have the top experts to work with us
- We provide a hundred per cent original and plagiarism-free research paper
- Our papers are also free from any errors
Clients all over the world are very happy and satisfied with our services. Thus, join us soon.
Author Bio:

Hi, I am Lyana Jones, the author of this blog. I am a well-experienced academic writer. We’ll help make your writing shine.
Please contact us anytime, tell us about your topic, and receive a 100% plagiarism-free paper with impeccable grammar and formatting.
View All Post
RELATED POST:
145+ Best Social Work Research Topics and Ideas to Use
130+ education research topics & ideas you must know, top 100+ accounting dissertation topics ideas for student, 7 advantages of dissertation writing you must know, 120+ tourism and hospitality dissertation topics.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Identify a Research Gap

5-minute read
- 10th January 2024
If you’ve been tasked with producing a thesis or dissertation, one of your first steps will be identifying a research gap. Although finding a research gap may sound daunting, don’t fret! In this post, we will define a research gap, discuss its importance, and offer a step-by-step guide that will provide you with the essential know-how to complete this critical step and move on to the rest of your research project.
What Is a Research Gap?
Simply put, a research gap is an area that hasn’t been explored in the existing literature. This could be an unexplored population, an untested method, or a condition that hasn’t been investigated yet.
Why Is Identifying a Research Gap Important?
Identifying a research gap is a foundational step in the research process. It ensures that your research is significant and has the ability to advance knowledge within a specific area. It also helps you align your work with the current needs and challenges of your field. Identifying a research gap has many potential benefits.
1. Avoid Redundancy in Your Research
Understanding the existing literature helps researchers avoid duplication. This means you can steer clear of topics that have already been extensively studied. This ensures your work is novel and contributes something new to the field.
2. Guide the Research Design
Identifying a research gap helps shape your research design and questions. You can tailor your studies to specifically address the identified gap. This ensures that your work directly contributes to filling the void in knowledge.
3. Practical Applications
Research that addresses a gap is more likely to have practical applications and contributions. Whether in academia, industry, or policymaking, research that fills a gap in knowledge is often more applicable and can inform decision-making and practices in real-world contexts.
4. Field Advancements
Addressing a research gap can lead to advancements in the field . It may result in the development of new theories, methodologies, or technologies that push the boundaries of current understanding.
5. Strategic Research Planning
Identifying a research gap is crucial for strategic planning . It helps researchers and institutions prioritize areas that need attention so they can allocate resources effectively. This ensures that efforts are directed toward the most critical gaps in knowledge.
6. Academic and Professional Recognition
Researchers who successfully address significant research gaps often receive peer recognition within their academic and professional communities. This recognition can lead to opportunities for collaboration, funding, and career advancement.
How Do I Identify a Research Gap?
1. clearly define your research topic .
Begin by clearly defining your research topic. A well-scoped topic serves as the foundation for your studies. Make sure it’s not too broad or too narrow; striking the right balance will make it easier to identify gaps in existing literature.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
2. Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review is a vital step in any research. Dive deep into the existing research related to your topic. Look for patterns, recurring themes, and consensus among scholars. Pay attention to areas where conflicting opinions or gaps in understanding emerge.
3. Evaluate Existing Studies
Critically evaluate the studies you encounter during your literature review. Assess the paradigms , methodologies, findings, and limitations of each. Note any discrepancies, unanswered questions, or areas where further investigation is warranted. These are potential indicators of research gaps.
4. Identify Unexplored Perspectives
Consider the perspectives presented in the existing literature. Are there alternative viewpoints or marginalized voices that haven’t been adequately explored? Identifying and incorporating diverse perspectives can often lead to uncharted territory and help you pinpoint a unique research gap.
Additional Tips
Stay up to date with emerging trends.
The field of research is dynamic, with new developments and emerging trends constantly shaping the landscape. Stay up to date with the latest publications, conferences, and discussions in your field and make sure to regularly check relevant academic search engines . Often, identifying a research gap involves being at the forefront of current debates and discussions.
Seek Guidance From Experts
Don’t hesitate to reach out to experts in your field for guidance. Attend conferences, workshops, or seminars where you can interact with seasoned researchers. Their insights and experience can provide valuable perspectives on potential research gaps that you may have overlooked. You can also seek advice from your academic advisor .
Use Research Tools and Analytics
Leverage tech tools to analyze patterns and trends in the existing literature. Tools like citation analysis, keyword mapping, and data visualization can help you identify gaps and areas with limited exploration.
Identifying a research gap is a skill that evolves with experience and dedication. By defining your research topic, meticulously navigating the existing literature, critically evaluating studies, and recognizing unexplored perspectives, you’ll be on your way to identifying a research gap that will serve as the foundation for your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
If you need any help with proofreading your research paper , we can help with our research paper editing services . You can even try a sample of our services for free . Good luck with all your research!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
Free email newsletter template (2024).
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

The Best Method In Identifying Research Gap: An In-depth Analysis
What is research gap.
A research gap refers to an area or topic that has not been sufficiently explored or studied, leaving unanswered questions or unresolved issues. This article will provide an overview of the research gaps concept and their significance in the research process. It will also discuss the importance of identifying research gaps and how they can be used to formulate research objectives and problem statements. Additionally, this section will explore various techniques and strategies for conducting research gap analysis and bridging the gap between existing knowledge and future research endeavors.

Background of Research Gap
In the world of research, identifying and addressing research gaps is a crucial step towards advancing knowledge and understanding in a particular field. A research gap refers to an area in the existing body of knowledge where there is a lack of research or unanswered questions. In other words, it is a gap in the literature that needs to be addressed through further research.
Research gaps can occur for various reasons, such as a lack of studies on a specific topic, contradictory findings in existing research, or the emergence of new ideas or concepts that have not been explored. Identifying research gaps is crucial for the advancement of knowledge and the development of new research questions. By filling these gaps, researchers can contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address unanswered questions.
Furthermore, research gaps provide opportunities for researchers to make significant contributions to their field by conducting innovative and impactful studies. Understanding the background of research gaps is essential for researchers to identify areas where their research can make a meaningful impact.
Significance of Research Gap
The research gap plays a crucial role in the field of academia and scientific research. It holds significant importance for researchers, scholars, and the overall advancement of knowledge.
Contributing to Knowledge and Developing New Theories
One of the primary reasons why the research gap is significant is that it identifies areas where there is a lack of knowledge or understanding. It highlights the gaps in existing research, indicating the need for further investigation and exploration. By identifying research gaps, researchers can contribute to the existing body of knowledge by filling in the missing pieces. This leads to the development of new theories, concepts, and insights that can enhance our understanding of a particular subject or field.
Fostering Innovation and Progress through Unexplored Areas
Furthermore, the significance of research gaps lies in their potential to drive innovation and progress. When researchers identify areas that have not been extensively studied, they have the opportunity to explore new ideas, methodologies, and approaches. This can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various disciplines.
Efficient Utilization of Resources to Avoid Duplication
Moreover, research gaps also help in avoiding duplication of efforts. By identifying what has already been studied and what areas are yet to be explored, researchers can focus their efforts on addressing the gaps rather than repeating existing research. This ensures that resources are utilized effectively and efficiently.
Impacting Practical Applications and Real-World Solutions
Additionally, the significance of research gaps extends to the practical application of research findings. By addressing the gaps in existing knowledge, researchers can provide valuable insights and solutions to real-world problems. This can have a direct impact on industries, policy-making, and decision-making processes. In conclusion, the significance of research gaps cannot be overstated. They serve as catalysts for knowledge advancement, innovation, and practical application. By identifying and addressing these gaps, researchers contribute to the growth and development of their respective fields, ultimately benefiting society as a whole.
Research Gap Examples
Identifying research gaps is crucial for pursuing innovative research. There are various types of research gaps that can be found in existing literature.
Knowledge gaps
Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn’t been studied at all. For example, in the field of psychology, there might be a lack of research on the effects of social media on mental health in adolescents.
Conceptual gaps
Conceptual gaps occur when there is a lack of understanding or clarity about a particular concept or theory. For instance, in the field of economics, there might be a research gap in understanding the relationship between income inequality and economic growth.
Methodological gaps
Methodological gaps refer to the absence of appropriate research methods or techniques to study a specific phenomenon. For example, in the field of biology, there might be a research gap in developing a reliable method to detect a certain type of genetic mutation.
Data gaps occur when there is a lack of available data or insufficient data to address a research question. For instance, in the field of climate science, there might be a research gap in obtaining long-term temperature data for a specific region.
Practical gaps
Practical gaps exist when there is a discrepancy between theoretical knowledge and practical application. For example, in the field of education, there might be a research gap in implementing effective teaching strategies for students with learning disabilities.
Research Gap Analysis Techniques
Carry out a comprehensive literature review.
There are several techniques that can be used to identify research gaps. One common technique is conducting a comprehensive literature review, where researchers examine existing research papers, articles, books, and other relevant sources. By analyzing these materials, researchers can pinpoint what has already been explored and identify areas that require further investigation.
Examining Limitations and Contradictions in Existing Studies
During the literature review, researchers should pay attention to the limitations and gaps in the existing studies. These limitations can include unanswered research questions, contradictory findings, methodological issues, or areas that have not been explored in depth. Researchers can also gain insights by comparing and contrasting the findings, methodologies, and conclusions of different studies within their field, which helps in building a more complete understanding of the topic.
Exploring Interdisciplinary Insights to Identify Gaps
Additionally, researchers can seek inspiration from interdisciplinary fields or related disciplines to identify research gaps. Sometimes, a research gap in one field may have been addressed in another field, and researchers can draw upon these insights to identify areas that have not been explored within their own field. It is important to note that identifying research gaps is not a one-time process. As new studies are published and the field evolves, new gaps may emerge. Therefore, researchers should continuously update their knowledge and review the literature to stay informed about the latest developments and identify new research gaps.
Utilizing Surveys and Interviews for Direct Insights
Another technique is conducting surveys or interviews . This allows researchers to gather information directly from individuals who are knowledgeable in the field. Surveys can be distributed to a large number of participants, while interviews provide more in-depth insights from a smaller group of experts. By collecting data through surveys or interviews, researchers can identify gaps in knowledge or areas where more research is needed. Focus groups are another effective technique for conducting a research gap analysis. In a focus group, a small group of individuals with relevant expertise or experience is brought together to discuss a specific topic. Through group discussions and interactions, researchers can gain valuable insights and identify gaps in knowledge or areas that require further investigation.
Employing Quantitative Analysis to Discover Data Gaps
Quantitative analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis, can also be used to identify research gaps. By analyzing existing data sets, researchers can identify patterns, trends, or gaps in the data that may indicate areas where further research is needed. This type of analysis can provide valuable insights into the gaps in existing knowledge and guide future research directions.
Applying Gap Analysis Frameworks for Structured Assessment
In addition to these techniques, researchers can also use gap analysis frameworks or models to systematically identify and analyze research gaps. These frameworks provide a structured approach to assess the current state of knowledge, determine the desired future state, and identify the gaps that need to be addressed. By using a framework, researchers can ensure a comprehensive analysis of research gaps and develop strategies to bridge those gaps.
Research Gap and Problem Statement
A research problem is a specific issue or question that a researcher wants to investigate. It is the foundation of a research study and provides a clear direction for the research process. The identification of a research gap often leads to the formulation of a research problem.
The problem statement is a constructed sentence that defines the research problem and guides the research question. It helps to clarify the purpose of the study and provides a framework for the research design and research methodology. By addressing the research gap through the problem statement, researchers can contribute to the existing body of knowledge and fill the void in the literature. The research problem becomes the focal point of the study, and the research gap serves as the motivation for conducting the research.
Identifying a research gap and formulating a problem statement are crucial steps in the research process. They ensure that the research study is relevant, meaningful, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field. As a key component of the research framework , the problem statement integrates directly into the overall structure that guides the entire research process, ensuring that all aspects of the investigation are aligned with the identified gaps and research questions.
Bridging the Research Gap
Bridging the research gap is crucial for the advancement of knowledge and the improvement of various fields. It involves closing the divide between research findings and their practical application in real-world settings. By bridging this gap, researchers can ensure that their work has a meaningful impact on society and that it is effectively utilized by practitioners and policymakers.
Effective Collaboration between Researchers and Practitioners
There are several strategies and approaches that can be employed to bridge the research gap. One practical way is to establish collaborations and partnerships between researchers and practitioners. By working together, researchers can gain valuable insights from practitioners’ experiences and expertise, while practitioners can benefit from the latest research findings and evidence-based practices. This collaboration can lead to the development of more relevant and effective solutions to real-world problems.
For facilitating such connections and collaborations, platforms like Researchmate.net are invaluable resources, providing the tools and community needed to bring together researchers and practitioners from diverse fields.
Intermediary Organizations in Facilitating Research Application
Another approach to bridging the research gap is through the use of intermediary organizations. These organizations act as a bridge between researchers and practitioners, facilitating the translation and dissemination of research findings into practical applications. They can provide training, resources, and support to practitioners, helping them to implement evidence-based practices in their work. Intermediary organizations also play a crucial role in promoting knowledge exchange and collaboration between researchers and practitioners.
Enhancing Communication and Knowledge Transfer in Research
Furthermore, bridging the research gap requires effective communication and knowledge transfer. Researchers need to communicate their findings in a clear and accessible manner, using language that is understandable to practitioners and policymakers. This can be achieved through the use of plain language summaries, policy briefs, and other forms of knowledge translation.
Engaging with Practitioners and Policymakers
Additionally, researchers should actively engage with practitioners and policymakers, seeking their input and feedback to ensure that research findings are relevant and applicable to real-world contexts.
In conclusion, exploring the research gap is a critical step in the research process. It helps researchers identify areas where further investigation is needed, contributes to the advancement of knowledge, and drives innovation. By understanding the research gap, researchers can make meaningful contributions to their field and address unanswered questions. Bridging the research gap requires collaboration and commitment from all stakeholders, but the potential benefits are immense.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

7 Easy Step-By-Step Guide of Using ChatGPT: The Best Literature Review Generator for Time-Saving Academic Research

Writing Engaging Introduction in Research Papers : Tips and Tricks!

Understanding Comparative Frameworks: Their Importance, Components, Examples and 8 Best Practices

Revolutionizing Effective Thesis Writing for PhD Students Using Artificial Intelligence!

3 Types of Interviews in Qualitative Research: An Essential Research Instrument and Handy Tips to Conduct Them

Highlight Abstracts: An Ultimate Guide For Researchers!

Crafting Critical Abstracts: 11 Expert Strategies for Summarizing Research

Crafting the Perfect Informative Abstract: Definition, Importance and 8 Expert Writing Tips
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Identify Gaps in Research: Tips to Speed Up the Process
If you have ever wondered how to identify research gaps, well, you’re not alone. All researchers looking to make a solid contribution to their field need to start by identifying a topic or issue that hasn’t been tackled before and coming up with possible solutions for it. This is where learning what is a research gap, knowing about some research gap examples, and knowing how to identify research gaps becomes important. Through this article, we will try answering these questions for you.
Table of Contents
What is a research gap ?
Research gaps are areas requiring more studies or research. 1 They can be:
- an unsolved question or problem within your field.
- a case where inconclusive or contradictive results exist.
- a new concept or idea that hasn’t been studied.
- a new/updated research to replace the outdated existing research.
- a specific demographic or location that has not been well studied.
Why is it important to identify research gaps ?
Identifying and prioritizing research gaps is an essential part of any research for the following reasons. 2 This can help you:
- ensure the rapid generation of subsequent research that is informed by input from previous research studies.
- understand areas of uncertainty within the research problem.
- establish the research problem and scope of the study.
- determine the scope of funding opportunities.
Identifying research gaps : A challenge for early researchers
Coming up with original, innovative ideas in your chosen area of research can be tricky, especially if you are an early career researcher, for the following reasons: 3,4
- Enormous information available : The introduction, discussion, and future research sections in published research articles provide information about gaps in the research field. It is easy to get overwhelmed and feel confused about which one to address. Using digital tools can help you seek out popular topics or the most cited research papers.
- Difficulty in organizing the data : One can quickly lose ideas if not appropriately noted. Mapping the question to the resource and maintaining a record can help narrow research gap s.
- Fear of challenging the existing knowledge : Beginner researchers may not feel confident to question established norms in their field. A good plan of action would be discussing such ideas with your advisor and proceeding according to their feedback or suggestions.
- Lack of direction and motivation : Early researchers have reported negative emotions regarding academic research, including feeling directionless or frustrated with the effort required in identifying research topics. Again a good advisor can help you stay focused. Mentors can help novice researchers avoid cases with a high risk of failure, from misunderstanding the literature, weak design, or too many unknowns. Talking with other fellow researchers can also help overcome some of the anxiety.

How to identify research gaps in the literature
More than 7 million papers get published annually. 5 Considering the volume of existing research, identifying research gaps from existing literature may seem a daunting task. While there are no hard rules for identifying research gaps, the literature has provided some guidelines for identifying problems worth investigating.
1. Observe : Personal interests and experiences can provide insight into possible research problems. For example, a researcher interested in teaching may start with a simple observation of students’ classroom behavior and observe the link with learning theories. Developing the habit of reading literature using smart apps like R Discovery can keep you updated with the latest trends and developments in the field.
2. Search : Exploring existing literature will help to identify if the observed problem is documented. One approach is identifying the independent variables used to solve the researcher’s topic of interest (i.e., the dependent variable). Databases such as Emerald, ProQuest, EbscoHost, PubMed, and ScienceDirect can help potential researchers explore existing research gaps. The following steps can help with optimizing the search process once you decide on the key research question based on your interests.
-Identify key terms.
-Identify relevant articles based on the keywords.
-Review selected articles to identify gaps in the literature.
3. Map : This involves mapping key issues or aspects across the literature. The map should be updated whenever a researcher comes across an article of interest.
4. Synthesize : Synthesis involves integrating the insights of multiple but related studies. A research gap is identified by combining results and findings across several interrelated studies. 6
5. Consult: Seeking expert feedback will help you understand if the research gaps identified are adequate and feasible or if improvements are required.
6. Prioritize : It is possible that you have identified multiple questions requiring answers. Prioritize the question that can be addressed first, considering their relevance, resource availability, and your research strengths.
7. Enroll : Research Skills Development Programs, including workshops and discussion groups within or outside the research institution, can help develop research skills, such as framing the research problem. Networking and corroborating in such events with colleagues and experts might help you know more about current issues and problems in your research domain.
While there is no well-defined process to identify gaps in knowledge, curiosity, judgment, and creativity can help you in identifying these research gaps . Regardless of whether the research gaps identified are large or small, the study design must be sufficient to contribute toward advancing your field of research.
References
- Dissanayake, D. M. N. S. W. (2013). Research, research gap and the research problem.
- Nyanchoka, L., Tudur-Smith, C., Porcher, R., & Hren, D. Key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences with defining, identifying and displaying gaps in health research: a qualitative study. BMJ open , 10 (11), e039932 (2020).
- Müller-Bloch, C., & Kranz, J. (2015). A framework for rigorously identifying research gaps in qualitative literature reviews.
- Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2017). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . Sage publications.
- Fire, M., & Guestrin, C. Over-optimization of academic publishing metrics: observing Goodhart’s Law in action. GigaScience , 8 (6), giz053 (2019).
- Ellis, T. J., & Levy, Y. Framework of problem-based research: A guide for novice researchers on the development of a research-worthy problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline Volume 11, 2008 ).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question: How can research gaps be addressed?
Research gaps can be addressed by conducting further studies, experiments, or investigations that specifically target the areas where knowledge is lacking or incomplete. This involves conducting a thorough literature review to identify existing gaps, designing research methodologies to address these gaps, and collecting new data or analyzing existing data to fill the void. Collaboration among researchers, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative research designs can also help bridge research gaps and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field.
Question: Can research gaps change over time?
Yes, research gaps can change over time. As new studies are conducted, technologies advance, and societal needs evolve, gaps in knowledge may be identified or existing gaps may become more pronounced. Research gaps are dynamic and subject to shifts as new discoveries are made, new questions arise, and priorities change. It is crucial for researchers to continuously assess and update their understanding of the field to identify emerging research gaps and adapt their research efforts accordingly.
Question: Are research gaps specific to a particular discipline or field?
Research gaps can exist within any discipline or field. Each discipline has its own unique body of knowledge and areas where understanding may be limited. Research gaps can arise from unanswered questions, unexplored phenomena, conflicting findings, practical challenges, or new frontiers of knowledge. They are not limited to a specific discipline or field, as gaps can exist in natural sciences, social sciences, humanities, engineering, or any other area of study.
Question: How can research gaps contribute to the research proposal?
Research gaps play a significant role in the development of research proposals. They help researchers identify a clear rationale and justification for their study. By addressing identified gaps in knowledge, researchers can demonstrate the significance and relevance of their proposed research. Research proposals often include a literature review section that highlights existing gaps and positions the proposed study as a contribution to the field. By explicitly addressing research gaps, researchers can strengthen the credibility and importance of their research proposal, as well as its potential impact on advancing knowledge and addressing critical questions or challenges.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

How Does R Discovery’s Interplatform Capability Enhance Research Accessibility

What is Convenience Sampling: Definition, Method, and Examples
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

What is a Research Gap
- 3 minute read
- 293.1K views
Table of Contents
If you are a young researcher, or even still finishing your studies, you’ll probably notice that your academic environment revolves around certain research topics, probably linked to your department or to the interest of your mentor and direct colleagues. For example, if your department is currently doing research in nanotechnology applied to medicine, it is only natural that you feel compelled to follow this line of research. Hopefully, it’s something you feel familiar with and interested in – although you might take your own twists and turns along your career.
Many scientists end up continuing their academic legacy during their professional careers, writing about their own practical experiences in the field and adapting classic methodologies to a present context. However, each and every researcher dreams about being a pioneer in a subject one day, by discovering a topic that hasn’t been approached before by any other scientist. This is a research gap.
Research gaps are particularly useful for the advance of science, in general. Finding a research gap and having the means to develop a complete and sustained study on it can be very rewarding for the scientist (or team of scientists), not to mention how its new findings can positively impact our whole society.
How to Find a Gap in Research
How many times have you felt that you have finally formulated THAT new and exciting question, only to find out later that it had been addressed before? Probably more times than you can count.
There are some steps you can take to help identify research gaps, since it is impossible to go through all the information and research available nowadays:
- Select a topic or question that motivates you: Research can take a long time and surely a large amount of physical, intellectual and emotional effort, therefore choose a topic that can keep you motivated throughout the process.
- Find keywords and related terms to your selected topic: Besides synthesizing the topic to its essential core, this will help you in the next step.
- Use the identified keywords to search literature: From your findings in the above step, identify relevant publications and cited literature in those publications.
- Look for topics or issues that are missing or not addressed within (or related to) your main topic.
- Read systematic reviews: These documents plunge deeply into scholarly literature and identify trends and paradigm shifts in fields of study. Sometimes they reveal areas or topics that need more attention from researchers and scientists.

Keeping track of all the new literature being published every day is an impossible mission. Remember that there is technology to make your daily tasks easier, and reviewing literature can be one of them. Some online databases offer up-to-date publication lists with quite effective search features:
- Elsevier’s Scope
- Google Scholar
Of course, these tools may be more or less effective depending on knowledge fields. There might be even better ones for your specific topic of research; you can learn about them from more experienced colleagues or mentors.
Find out how FINER research framework can help you formulate your research question.
Literature Gap
The expression “literature gap” is used with the same intention as “research gap.” When there is a gap in the research itself, there will also naturally be a gap in the literature. Nevertheless, it is important to stress out the importance of language or text formulations that can help identify a research/literature gap or, on the other hand, making clear that a research gap is being addressed.
When looking for research gaps across publications you may have noticed sentences like:
…has/have not been… (studied/reported/elucidated) …is required/needed… …the key question is/remains… …it is important to address…
These expressions often indicate gaps; issues or topics related to the main question that still hasn’t been subject to a scientific study. Therefore, it is important to take notice of them: who knows if one of these sentences is hiding your way to fame.
Language Editing Services by Elsevier Author Services:


Systematic Review VS Meta-Analysis

Literature Review in Research Writing
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: What is a research gap and how do I find one?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 61 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 28 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 8 Building/Facilities
- 6 Career/Job Information
- 25 Catalog/Print Books
- 25 Circulation
- 134 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 306 Databases
- 23 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 16 Online Programs
- 20 Periodicals
- 24 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 213 Research Help
- 22 University Services
Last Updated: Aug 26, 2024 Views: 491434
What is a research gap.
A research gap is a question or a problem that has not been answered by any of the existing studies or research within your field. Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn't been studied at all. Sometimes you'll find a research gap if all the existing research is outdated and in need of new/updated research (studies on Internet use in 2001, for example). Or, perhaps a specific population has not been well studied (perhaps there are plenty of studies on teenagers and video games, but not enough studies on toddlers and video games, for example). These are just a few examples, but any research gap you find is an area where more studies and more research need to be conducted. Please view this video clip from our Sage Research Methods database for more helpful information: How Do You Identify Gaps in Literature?
How do I find one?
It will take a lot of research and reading. You'll need to be very familiar with all the studies that have already been done, and what those studies contributed to the overall body of knowledge about that topic. Make a list of any questions you have about your topic and then do some research to see if those questions have already been answered satisfactorily. If they haven't, perhaps you've discovered a gap! Here are some strategies you can use to make the most of your time:
- One useful trick is to look at the “suggestions for future research” or conclusion section of existing studies on your topic. Many times, the authors will identify areas where they think a research gap exists, and what studies they think need to be done in the future.
- As you are researching, you will most likely come across citations for seminal works in your research field. These are the research studies that you see mentioned again and again in the literature. In addition to finding those and reading them, you can use a database like Web of Science to follow the research trail and discover all the other articles that have cited these. See the FAQ: I found the perfect article for my paper. How do I find other articles and books that have cited it? on how to do this. One way to quickly track down these seminal works is to use a database like SAGE Navigator, a social sciences literature review tool. It is one of the products available via our SAGE Knowledge database.
- In the PsycINFO and PsycARTICLES databases, you can select literature review, systematic review, and meta analysis under the Methodology section in the advanced search to quickly locate these. See the FAQ: Where can I find a qualitative or quantitative study? for more information on how to find the Methodology section in these two databases.
- In CINAHL , you can select Systematic review under the Publication Type field in the advanced search.
- In Web of Science , check the box beside Review under the Document Type heading in the “Refine Results” sidebar to the right of the list of search hits.
- If the database you are searching does not offer a way to filter your results by document type, publication type, or methodology in the advanced search, you can include these phrases (“literature reviews,” meta-analyses, or “systematic reviews”) in your search string. For example, “video games” AND “literature reviews” could be a possible search that you could try.
Please give these suggestions a try and contact a librarian for additional assistance.
Content authored by: GS
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 394 No 155
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs
Write Like a Scientist
A Guide to Scientific Communication
Gap Statements
A gap is something that remains to be done or learned in an area of research; it’s a gap in the knowledge of the scientists in the field of research of your study. Every research project must, in some way, address a gap–that is, attempt to fill in some piece of information missing in the scientific literature. Otherwise, it is not novel research and is therefore not contributing to the overall goals of science.
Identify the gap.
A gap statement is found in the Introduction section of a journal article or poster or in the Goals and Importance section of a research proposal and succinctly identifies for your audience the gap that you will attempt to address in your project.
A gap might be a lack of understanding about how well a particular instrument works in a certain situation. It could be introducing a new method that needs to be tested. Or it could be that you are studying a whole new organism, system, or part of a process. Your project may also address multiple gaps, in which case you should be sure to identify each of them clearly!
In a class, you might not always be studying something brand “new.” But, in most cases, you should still try to come up with something unique about your project, however small. Talk to your professor about what they expect for your gap statement if nothing seems to work.
| : “… The relationship between the four damping factors, i.e. internal friction, support loss, airflow force in free space, and squeeze force, has not yet been clarified, so it is not obvious which one is dominant in actual microsystems.” |
Here, the authors signal to us that this is a gap because they use the words “has not yet been clarified.” Other phrases that might help you identify (or form!) a gap statement are:
- …has/have not been… (studied/reported/elucidated)
- …is required/needed…
- …the key question is/remains…
- …it is important to address…
Fill the gap.
Once you identify the gap in the literature, you must tell your audience how you attempt to at least somewhat address in your project this lack of knowledge or understanding . In a journal article or poster, this is often done in a new paragraph and should be accomplished in one summary statement, such as:
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine the effects of lead on the hepatobiliary system, especially on the liver and on the gallbladder (adapted from Sipos et al. 2003 ).
You’ll often find that the first sentence of the last paragraph in a paper’s introduction will start somewhat like this, indicating the gap fill.
| Some phrases you can use to indicate your gap “fill:” |
Remember–always keep your voice professional! Colloquial phrases such as “we looked into” or “we checked if” should be avoided when introducing your gap fill.
So let’s look at this idea in context by looking at some examples from a couple of types of papers. The gap statements are underlined; the fills are italicized.
| Adapted from : Though ideally expected to be chemically very stable due to the poor reactivity of the basal aromatic plane from which SWNTs are built, the question of whether all the chemicals which are now currently proposed in the literature as purifying, suspending, or grafting agents for SWNTs actually have a limited effect on the SWNT integrity has to be addressed. Adapted from : Milly’s work recognized the importance of storage capacity of the root zone in controlling evapotranspiration and has the postential for assessing the catchment-scale response of vegetation changes. However, the practical application of this model is limited because of the complex numerical solutions required. Adapted from : A risk assessment of the potential impacts on health and environment that the production, use, and disposal of nanomaterials may engender requires information concerning both the potential for exposure to a given material and its (once exposed) potential impacts such as toxicity or mutagenicity. |
In the second and third examples, the gap may be a little less obvious–it doesn’t use any phrases to signal to you that there’s something missing, such as “has not been clarified” or “have not been reported.” But because of the way the paragraph is laid out–following the conventions of our move structures–we can see that the underlined section of text is indeed the missing information in the literature that the group sought to address in their project.
| [bg_faq_start] In the following examples, identify the gap statement. Then, identify the fill. Notice if there are any specific words or phrases used to signal either of these moves. 1. Adapted from : Paralytic shellfish poisoning occurs worldwide, and harmful algal blooms, including those responsible for PSP, appear to be increasing in frequency and intensity. PSP outbreaks in Portuguese waters have been associated with blooms of Gymnodinium caenatum in the late 1980s to early 1990s, then again after 2005. According to the national monitoring program in Portugal, G. catenatum were not reported along the Portuguese coast during the 10-year period from 1995 to 2005. The aims of this study were to fully characterize the toxin profile of G. catenatum strains isolated from the NW Portuguese coast before and after the 10-year absence of blooms to 2. Adapted from : The exchange process frequently observed in polypyrrane condensations is proposed to occur by the acid-catalyzed fragmentation of a polypyrrane into pyrrolic and azafulvene components.15 As illustrated in Scheme 2, recombination of and can form a new polypyrrane that cannot be formed by direct condensation of the dipyrromethane and aldehyde. Ultimately this process leads to the production of a scrambled mixture of porphyrins. The factors that promote the scrambling process in MacDonald-type 2 + 2 condensations are poorly understood, but suppression of scrambling is essential for preparing large quantities of pure trans-porphyrins. In this paper we describe a study of a wide range of reaction conditions for the 2 + 2 condensation that has led to refined synthetic procedures for the preparation of trans-porphyrins. 3. Adapted from : In the present paper, we focus on laser wake field acceleration in a new, highly non-linear regime. It occurs for laser pulses shorter than λ(p) but for relativistic intensities high enough to break the plasma wave after the first oscillation. In the present relativistic regime, one should notice that the plama wave fronts are curved and first break new the wave axis and for lower values than the plane-wave limit. This has been studied in 2D geometry in [14-17]. Here, we present 3D PIC simulations of two representative cases. The case (I) is just marginally above and the case (II) is far above the breaking threshold. [bg_faq_start] Good gap and fill signaling phrases are italicized.
1. “The factors that promote the scrambling process in MacDonald-type 2 + 2 condensations ….” “ a study of a wide range of reaction conditions for the 2 + 2 condensation that has led to refined synthetic procedures for the preparation of trans-porphyrins.”
2. This question is a little trickier! The authors use “In the present paper…,” then, “In the present regime…,” and finally, “Here…,” all of which sound like signaling words for filling the gap. But where is the gap? We have to look closely at what exactly is being said. It is true that the first statement appears to be somewhat of a gap fill, although they haven’t yet given us a gap statement. The authors go on to say “This has been studied in 2D geometry,” which brings us back to move 1(iii), identifying critical evidence from the literature. Thus, the is not explicit. It is a combination of stating that this concept has been studied in 2D, followed by announcement that the authors will study it in 3D. Although the first sentence (“… we focus on laser wake field acceleration…”) could also be considered part of the fill, because it comes before the gap statement and is also less descriptive, it functions more as an introduction to these moves.
3. According to the national monitoring program in Portugal, G. catenatum along the Portuguese coast during the 10-year period from 1995 to 2005.” to fully characterize the toxin profile of G. catenatum strains isolated from the NW Portuguese coast before and after the 10-year absence of blooms to
[bg_faq_end] |
| [bg_faq_start] Find 3-4 primary research articles (not reviews) from reputable journals in your field. Underline the gap statement and circle the gap fill. Remember that not all papers follow this exact move structure, so if you can’t seem to find either of these moves, you might have to look carefully at different parts of the introduction and ask yourself: [bg_faq_end] |

From research discovery to gap finding
How do you find a research gap?
The aim of all research is to add to or enhance existing knowledge. Arguably, we can only achieve this once we understand the work that has already been carried out in a given field. There are varying opinions, depending on the field of inquiry and methodological approach involved, regarding the level of familiarity a researcher should have with existing literature prior to commencing fieldwork, however it is generally accepted that research should fill gaps in the literature. It is perhaps surprising, then, that so little is written about just how to find a “research gap” in the first place.
Finding the literature
The most obvious way to find a research gap is simply to read and analyse the relevant literature. However, this is easier said than done, as the volume of published literature can be staggering. Fortunately, there are some excellent bibliographic databases, which can speed the process of searching for relevant literature. Literature analysis may then be approached either qualitatively or quantitively.
Qualitative literature analysis
A qualitative analysis may involve the development of a concept matrix (Webster & Watson, 2002) or similar.
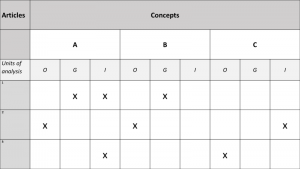
Figure 1: Example of a concept matrix (adapted from Webster & Watson, 2002)
Legend: O (organisation), G (group), I (individual)
The concept matrix assists researchers to organise the literature they have read, according to the concepts it relates to. It can be adapted, depending on the area of interest. In the example above, for instance, units of analysis are included.
Quantitive literature analysis
Quantitative analysis of literature may be carried out using a variety of tools, from systematic reviews to meta-analyses, citation analyses, and text mining (Marrone, 2017). Choice of tools may be determined to some extent by the ability of the researcher to acquire or access the technical expertise to leverage them.
Find the gap, or create one?
Reading and analysing the literature may reveal gaps which can be explored, however Alvesson & Sandberg (2011) suggest that research gaps may also be created by the researcher. By linking together work which has previously been considered separately, a researcher can uncover uncharted territory. In this way, opportunities to contribute to existing knowledge are constructed (Locke & Golden-Biddle, 1997) rather than merely identified.
What does a “research gap” look like?
Several authors have sought to characterise research gaps, describing the various forms they can take, whether considered from the perspective of objectively identifiable existing gaps in research (gap finding) or as opportunities to construct new “gaps” (gap creation). Some examples are summarised below.
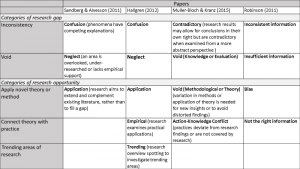
Figure 2: Characteristics of research gaps (Click to see image bigger)
Gap-finding frameworks
Step-by-step guides to finding research gaps are hard to come by, however in the field of medical epidemiology, a framework for identifying research gaps from systematic reviews of literature has been published (Robinson et al., 2011). In this field, the PICOS framework (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Setting) is commonly used to characterise a research gap. Robinson et al. (2011) suggest that an analysis of the reason for the existence of the gap can further inform the development of research questions. The reasons elucidated by Robinson et al. (2011) for the existence of research gaps are similar to the characteristics of gaps described by other authors, as shown in figure 2 (Characteristics of Research Gaps).
There are many ways to go about identifying research gaps, perhaps so many that the options may on occasion be overwhelming. A considered approach, coupled with knowledge and utilisation of the tools available to assist in research gap-finding, is likely to result in improved research design.
- Alvesson, M., & Sandberg, J. (2011). Generating research questions through problematization. Academy of Management Review. 36(2), 247-271 [doi:10.5465/AMR.2011.59330882]
- Hallgren, M. (2012) The construction of research questions in project management. International Journal of Project Management, 30(7), 804-816.
- Locke, K., & Golden-Biddle, K. (1997) Constructing opportunities for contribution: Structuring intertextual coherence and “problematizing” in organizational studies. Academy of Management Journal, 40: 1023–1062.
- Muller-Bloch, C. & Kranz, J. (2015) A framework for rigorously identifying research gaps in qualitative literature reviews. International Conference on Information Systems 2015 [available at: https://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2015/proceedings/ResearchMethods/2/]
- Marrone, M., & Hammerle, M. (2017). Relevant Research Areas in IT Service Management: An Examination of Academic and Practitioner Literatures. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 41, 517-543.
- Robinson, K. A., Saldanha, I. J. & McKoy, N. A. (2011) Development of a framework to identify research gaps from systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 64(12), 1325-1330.
- Sandberg, J., & Alvesson, M. 2011. Ways of constructing research questions: Gap-spotting or problematization? Organization, 18: 23–44.
- Webster, J., & Watson, R. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS Quarterly, 26(2), 13-23
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

What is a Research Gap? How to Identify it?
“ Choosing a topic, research or subject that has not been answered or explored yet by any other scientists is referred to as a research gap.”
Unfortunately, it’s difficult to find one!
When you start reading literature, initially you may notice that nothing is left to study! That everyone feels, even me too when I was in my initial days of PhD. But when you get enough research experience, you can find gaps in research easily.
“Every research is incomplete.”
Indeed, a research work completes when it states a gap or unexplored area with the final conclusion, so that future research will get direction.
The process of research or doctorate starts (immediately after you get admission) by initiating searching a research gap which leads to postulating a research question.
A research question is your title or statement of thesis using which you will find your thesis objectives and address a particular question. It can be stated only by finding a research or literature gap.
And as I said, it’s quite difficult for PhD students.
So in this blog post, I will explain to you what a research or literature gap is and how you can identify it.
How to appear in the PhD Interview?
What is a research or literature gap?
Firstly, a research/ knowledge gap or literature gap is though different terms but has a similar meaning. The reason is that a research problem can be addressed either by experimental research and literature review.
Definition:
A research or literature gap is a problem or unexplored/ underexplored area of the existing research.
Choosing a topic, research or subject that has not been answered or explored yet by any other scientist is referred to as a research gap.
Let us start with an example;
Take a look at the hypothetical closing sentence.
“3 common mutations IVS1-5, IVS1-1 and CD8/9 have been selected for the present to screen thalassemia patients. A common mutation IVS1-5 has been identified in 2 out of 70 unrelated thalassemia patients using the conventional PCR technique.”
Let’s say you want to do research on the Genetics of Thalassemia. Suppose this one is the closing paragraph of some research article and is a final conclusion. How can you find a research gap here?
I find many gaps, Let us find out some of them;
- The sample size is too small.
- There are 12 common mutations in beta-thalassemia which are present in almost 80% of cases. Only three are selected in the present study.
- The present study is geologically restricted.
- The author has used a single conventional PCR technique. More techniques like DNA sequencing can be used to address the same problem, which possibly provides more knowledge and can identify novel mutations as well.
- The author hasn’t clarified which type of thalassemia patients they have included in the present study.
These are some of the possible gaps in the present research. Let’s look at other closing statements for the same.
“3 common mutations IVS1-5, IVS1-1 and CD8/9 have been selected for the present to screen thalassemia patients. A common mutation IVS1-5 has been identified in 2 out of 70 unrelated thalassemia patients using the conventional PCR technique. The present study can be strengthened by increasing sample size, diversifying geological studies, increasing the number of common mutations and using other techniques for thalassemia.”
“Major limitations of the present study are small sample size, number of mutations and technique selected for the study.
All these closing statements posit the same type of research gaps. You can use these to prepare your thesis statement. Take a look at the one.
“Identifying common Beta-thalassemia mutations by DNA sequencing from south India.”

Where to find a literature gap?
Some research clearly indicates gaps in their studies whereas some don’t. And that’s why it’s difficult for students to discover one. Notedly, by looking into variables used in the study, gaps can be recognized.
- Samples- size, types, collection method, transportation conditions.
- Research technique- single, two or multiple; significance, efficiency and accuracy of the techniques used.
- Geological location and condition of the study conducted.
- Objectives selected for the study.
- Data obtained and research discussions.
You have to read tons of literature to actually determine possible gaps in the research. A research gap has been indicated in the conclusion section, final interpretation, future direction or suggestions part of a research paper.
Besides, when you came across some phrases used in the literature such as,
The present study has not been covered…..
………… excluded from the present study.
………… is important to address in future research.
…………. Techniques can be fruitful for future research.
……………. have/has not been studied/ reported/ evaluated in the present study.
Keep in mind that this indicates a gap, problem or scopes of improvement in the study.
Read more: Which factors decide a PhD Salary?
How to find a research gap?
As I said, it’s not an easy process to find a problem or gap in the research, though by following some steps that I will mention here, you can find one and can go with it.
Select a topic that you like and that motivates you:
Research interest is important because you have to do the same work for at least 4 to 5 years. Research takes a tremendous amount of physical, mental, economical and intellectual effort. Meaning you have to select a topic that likely motivates you. You should not get tired of doing that!
Find lucrative keywords to go ahead:
You can’t go through the whole topic or subject, right! you have to select one or a few. Means, make things more narrow. Take a look at the process, I have explained with an example.
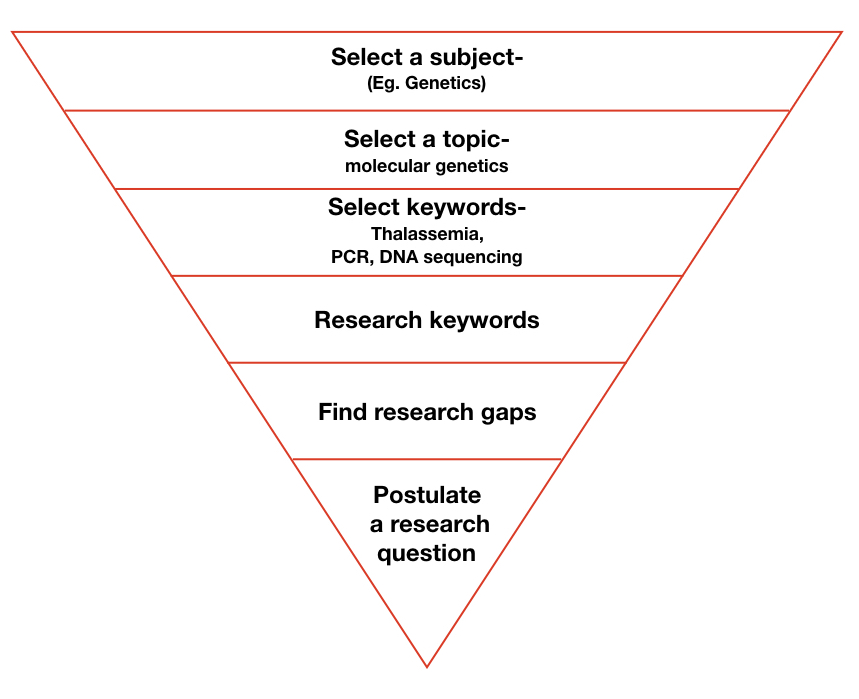
Find a keyword that is relevant to the topic you like or are interested in and go ahead with it.
Find relevant resources and literature:
Now next in the process, type your keyword or group of keywords in the Google search box and try identifying literature, reviews and research associated with it.
Find reviews, read them and try to find gaps in studies. Keep in mind that it will remain in your interest circle.
Read peer-reviewed articles and find gaps in the research:
Try to read every fresh research and review article around your topic, go through the technique and sample collection process used in each research and discover discordance or space there.
You can make a comparative analysis table as well. Take a look at the table below,
| Research study | Title and year of publication | Techniques, methods and sample collection | Outcomes of the study | The geographical location of the study conducted | What is not covered in the study | Research scope |
When you make a comparative analysis of a few studies you will get an idea about the research gap, gap in sample collection, scope to use other techniques, improvisation or new research areas to include in the study.
Choosing one from many:
When you complete the process, you may find many unanswered questions or research gaps (if you have done things in this manner) and you get stuck with many, which to choose and which to leave.
For PhD, it’s important to weightage a research work accurately; not more, not less. An imbalance will create an unnecessary burden and create problems in the future.
Henceforth, prioritizing and narrowing down the research gap is crucial.
In this case, you can take your supervisor’s help. Postulate an amazing research question that would be suitable for PhD, as per your interest, under your budget and fulfill your supervisor’s need.
Expected outcomes:
This is confusing for you surely!
You may wonder by only identifying a gap and postulating a research question, how can we expect anything as outcomes?
Expected outcomes of the research have significant value and importance in the PhD, PhD research proposal and your final report. You or your guide has to explain the possible results of the study.
It’s mandatory and will give you direction for research. Expected outcomes can be considered as a path on which you will have to walk.
Take an example of the research question we just postulated, “Identifying common Beta-thalassemia mutations by DNA sequencing from south India.”
What will be the expected results?
- You will get some common mutations.
- You will probably get some new mutations or variations.
- Or you will get nothing, which means, no mutations in any samples.
In either case, you have definite outcomes, and your final results will be around it, perhaps. You will definitely not get any information regarding the globin protein because that’s not included in the study.
Right!
You are just doing mutational analysis and want to find some common mutations in the selected population. So what research gap you will identify will surely give some expected outcomes.
Wrapping up:
Research gap/ knowledge gap or literature gap all terms leads us to the same direction and help us to propose a research question. Although as we said, expected outcomes are also an important consideration to fill the gap.
If you are new to PhD or just started this article is the best place for you to start, and will definitely assist you to find a mission piece of link in the research.
I hope you like this article. Please do visit other articles on this blog.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author

Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.
What is PhD?- History, Definition, Origin, Requirement, Fees, Duration and Process

How to write a PhD thesis?
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

Research Gap
Ai generator.

A research gap is an area within a field that lacks sufficient information or understanding, highlighting opportunities for further investigation. Identified through literature review, it guides researchers to explore new questions and develop innovative theories. Addressing these gaps advances knowledge and solves real-world problems. In areas like Marketing Gap Analysis , identifying research gaps leads to more effective strategies and improved market performance.
What is a Research Gap?
A research gap is an area within a field of study that lacks sufficient information or understanding, presenting an opportunity for further investigation. It is identified through a thorough review of existing literature and highlights areas where more research is needed. Recognizing these gaps is essential for advancing knowledge, guiding researchers to explore new questions, develop innovative theories, and improve methodologies.
Examples of Research Gap
- Healthcare : Limited studies on the long-term effects of telemedicine on patient outcomes, especially in rural areas.
- Education : Insufficient research on the impact of virtual reality in improving student engagement and learning outcomes in primary education.
- Environmental Science : Lack of comprehensive data on the effects of microplastics on marine ecosystems.
- Marketing : Few studies exploring the influence of social media influencers on consumer behavior in emerging markets.
- Technology : Sparse research on the ethical implications of artificial intelligence in workplace decision-making processes.
- Psychology : Limited understanding of the mental health impacts of prolonged social media use among teenagers.
- Economics : Insufficient analysis of the effects of cryptocurrency adoption on traditional banking systems.
- Sociology : Lack of in-depth studies on the long-term effects of remote work on family dynamics and work-life balance.
- Public Health : Few studies examining the effectiveness of community-based interventions in reducing obesity rates among children.
- Renewable Energy : Limited research on the integration of renewable energy sources into existing power grids and their economic impacts.
Different Types of Research Gaps
Research gaps are areas where knowledge is lacking or where existing research could be expanded. Identifying and addressing these gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge in any field. Here are the different types of research gaps:
1. Evidence Gap
Definition : An evidence gap occurs when there is a lack of empirical data to support conclusions or theories. This gap signifies areas where more research is needed to provide solid evidence for or against a hypothesis.
Example : Limited studies on the long-term effects of a new medication.
2. Knowledge Gap
Definition : A knowledge gap refers to a lack of understanding or awareness about a specific topic. This gap often highlights areas where research has not yet been conducted or where findings are inconsistent.
Example : Insufficient knowledge about the impact of social media on mental health among teenagers.
3. Practical-Knowledge Gap
Definition : This gap arises when there is a disconnect between theoretical research and practical application. It points to areas where findings from research have not been implemented in real-world settings or where practical challenges are not addressed by existing research.
Example : Theoretical models for disaster management that are not tested in actual disaster scenarios.
4. Methodological Gap
Definition : A methodological gap is identified when current research methods are inadequate to address certain research questions. This gap indicates the need for new or improved research methods.
Example : The need for longitudinal studies to better understand the progression of chronic diseases.
5. Policy Gap
Definition : A policy gap occurs when research does not inform policy or when there is a lack of research supporting existing policies. This gap often highlights the need for research that can influence or evaluate policy decisions.
Example : Lack of research on the effectiveness of policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
6. Population Gap
Definition : This gap is present when certain populations or demographic groups are underrepresented in research. It calls attention to the need for more inclusive research that considers diverse populations.
Example : Underrepresentation of elderly populations in clinical trials for new medications.
7. Theory Gap
Definition : A theory gap is found when there is a lack of theoretical framework to explain certain phenomena. This gap suggests the need for developing or refining theories to better understand specific issues.
Example : Incomplete theoretical explanations for the rise of extremism in modern societies.
8. Contextual Gap
Definition : A contextual gap exists when research does not take into account the context in which a phenomenon occurs. This gap highlights the need for studies that consider environmental, cultural, or situational factors.
Example : Studies on education methods that do not consider cultural differences in learning styles.
9. Perspective Gap
Definition : This gap arises when certain perspectives or viewpoints are missing from the research. It emphasizes the need for more diverse viewpoints to provide a comprehensive understanding of a topic.
Example : Limited perspectives from minority groups in research on workplace diversity.
10. Data Gap
Definition : A data gap is identified when there is a lack of available data or when existing data is insufficient to support research conclusions. This gap indicates the need for more extensive data collection and analysis.
Example : Insufficient data on climate change impacts in specific geographic regions.
How to write Research Gap
Identifying and articulating a research gap is a crucial step in academic research. It highlights the need for your study and sets the stage for your research question and objectives. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a research gap:
1. Literature Review
Conduct a thorough literature review to understand the current state of research in your field. Look for recent studies, key theories, and significant findings. Take note of any inconsistencies, unanswered questions, or areas that have not been explored.
2. Identify the Gap
After reviewing the literature, pinpoint the specific areas where research is lacking. This could be due to insufficient evidence, outdated studies, contradictory findings, or unaddressed issues.
3. Justify the Gap
Explain why this gap is important. Discuss the implications of not addressing this gap and how filling it could advance knowledge in your field or solve a practical problem.
4. Formulate Your Research Question
Based on the identified gap, formulate a clear and focused research question. This question should aim to address the gap and guide your study.
5. Contextualize the Gap
Place your research gap within the broader context of your field. Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and why it is timely and relevant.
6. Use Clear and Concise Language
When writing about the research gap, be clear and concise. Avoid jargon and ensure that your explanation is understandable to readers outside your immediate field.
How to Identify Research Gap?
Identifying a research gap is essential for developing a relevant and impactful research question. Here are the steps to effectively identify a research gap:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review
Start by thoroughly reviewing existing literature in your area of interest. Use academic databases, journals, books, and conference papers to gather information. Focus on:
- Recent studies and their findings
- Key theories and models
- Methodologies used
- Areas of consensus and disagreement
2. Analyze the Literature Critically
While reviewing the literature, critically evaluate the studies. Look for:
- Inconsistencies : Contradictory findings or conclusions
- Outdated Information : Studies that need updating due to new data or advancements
- Methodological Flaws : Weaknesses or limitations in research methods
- Unanswered Questions : Questions that previous studies have raised but not answered
3. Identify Trends and Patterns
Identify trends and patterns in the existing research. Consider:
- Common themes and topics
- Frequently used methodologies
- Populations and settings studied
- Gaps in data and analysis
4. Look for Understudied Areas
Identify topics or subtopics that have not been extensively researched. Pay attention to:
- Emerging fields or new technologies
- Neglected populations or regions
- Interdisciplinary research opportunities
5. Consult Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Review articles and meta-analyses can provide a summary of the current state of research and highlight areas where further research is needed. They often suggest future research directions and gaps.
6. Analyze Research Agendas and Funding Opportunities
Research agendas and funding calls from academic institutions, government agencies, and private organizations can highlight priority areas and identify gaps that need addressing.
7. Discuss with Experts and Peers
Engage in discussions with experts, mentors, and peers in your field. They can provide insights into current research trends and gaps that you might have overlooked.
8. Examine Conference Proceedings
Conference proceedings often contain the latest research and can indicate emerging trends and gaps. Attend conferences and review the abstracts and presentations.
9. Evaluate the Practical Relevance
Consider the practical implications of existing research. Identify areas where research findings have not been applied or where practical challenges remain unaddressed.
10. Formulate Research Questions
Based on the identified gaps, develop specific research questions. These questions should address the gaps and guide your research towards filling them.
Research Gap Uses
1. advancing knowledge.
Filling a research gap helps in advancing the overall knowledge within a field. It allows researchers to build upon existing studies and contribute new insights, theories, or methods.
2. Innovative Solutions
Addressing a research gap can lead to the development of innovative solutions to existing problems. Researchers can explore new approaches, technologies, or applications that have not been previously considered.
3. Funding and Support
Identifying a significant research gap can attract funding and support from academic institutions, government bodies, and private organizations. Funders are often interested in supporting projects that promise new discoveries and advancements.
4. Publishing Opportunities
Research that addresses a gap is often seen as valuable and original, increasing the chances of publication in reputable academic journals. This can enhance the researcher’s profile and credibility within the academic community.
5. Educational Development
For educators and students, identifying research gaps can guide the development of curricula and educational programs. It ensures that teaching materials are up-to-date and relevant to current academic and industry trends.
FAQ’s
Why is identifying a research gap important.
Identifying a research gap helps focus efforts on unexplored areas, advancing knowledge and contributing to the field.
How can I identify a research gap?
Review current literature, analyze findings, and note areas lacking comprehensive studies or conflicting results.
What are the types of research gaps?
Types include evidence gaps, knowledge gaps, practical gaps, theoretical gaps, and methodological gaps.
What is an evidence gap?
An evidence gap exists when there is a lack of empirical data supporting a particular hypothesis or theory.
How does a theoretical gap differ from a practical gap?
A theoretical gap involves missing or underdeveloped concepts, while a practical gap involves real-world issues needing solutions.
What is a methodological gap?
A methodological gap arises when certain methods have not been applied to study a specific problem.
How can conflicting results indicate a research gap?
Conflicting results suggest inconsistencies in findings, pointing to areas needing further investigation.
What is the role of a literature review in identifying research gaps?
A literature review helps identify gaps by summarizing existing studies and highlighting areas needing further research.
Can technology advancements create research gaps?
Yes, new technologies can reveal gaps by enabling studies that were previously impossible or overlooked.
What is the impact of research gaps on funding opportunities?
Identifying significant gaps can attract funding by demonstrating the need for research in unexplored areas.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
PhD Assistance
What is a research gap is there a good or poor research gap, introduction.
A research gap refers to a research question or area that has not been sufficiently addressed or answered in previous studies. It is an area where further research is needed to advance the current knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. Identifying research gaps in the literature review is important as it helps establish a study’s relevance and significance and can lead to the development of new research questions and hypotheses.
What is a research gap example?
A research gap signifies an unexplored terrain within existing knowledge, spotlighting an area lacking comprehensive investigation. Imagine, in medical research, a void in understanding the long-term effects of a newly developed treatment. This gap identification demands inquiry to bridge the chasm between current understanding and untapped insights. It’s akin to a puzzle with a missing piece, urging scholars to unravel hidden complexities. Such gaps drive scholarly exploration, fostering innovation and a deeper grasp of intricate subjects. Identifying and addressing these literature gaps in research pave the way for scientific advancement, enhancing our comprehension of the world around us.

Good research gap
A good research gap is a specific area of knowledge or a problem that has not been adequately addressed or explored in the existing literature. Here are 10 points that are typically considered mandatory in a good research gap:
- Relevance : The quantitative research gap example should be relevant to the field of study and have practical significance.
- Novelty : It should identify a new, unexplored area of research or a new angle for examining an existing research topic .
- Significance : The gap should be significant enough to warrant further investigation and have the potential to contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
- Feasibility : The research question should be feasible and realistic, taking into account factors such as time, resources, and available data.
- Clarity : The gap should be clearly defined, not too broad or too narrow.
- Specificity : The gap should be specific enough to allow for targeted research.
- Timeliness : The research question should be relevant to current issues or concerns in the field.
- Originality : The gap should be original and not simply a replication of previous research.
- Researchable : The gap should be researchable, meaning that data can be collected and analyzed to answer the research question.
- Importance : The research gap should be important enough to justify the time and resources required to conduct the research.
Poor research gap
“Poor research gap” refers to a situation where there is either no research gap identified in the existing literature or the identified research gap is not significant enough to contribute to the field of study. It means that the proposed research would not add any value to the existing knowledge base or research in the field.

Here are some examples of poor research gaps:
- “There is a lack of research on the effects of social media.”
This research gap is too broad and does not identify a specific research question or problem. It does not provide any direction for the research.
- “No one has looked at this specific topic before.”
This research gap is not valid as it is unlikely that no one has ever looked at the topic before. It is also too broad and does not provide any direction for the research.
- “The literature review is inconclusive.”
This research gap does not identify a specific problem or research question. It also does not provide any direction for the research.
- “There is no research on this topic in my country.”
This research gap is too narrow and does not consider research conducted in other countries. It also does not provide any direction for the research.
- “The existing research is outdated.”
- Check out our sample PhD Gap identification examples to see how PhD Gap identification is obtained.
Tools to Assist with Your Research Gap
Staying updated on the latest literature can be overwhelming due to the thousands of new articles published daily. Utilizing technology like PubCrawler, Feedly, Google Scholar, and PubMed updates can help keep you updated. Social media platforms like Twitter and reference managers like Mendeley can also help organize your references. Identifying the research gap in the dissertation requires a thorough literature review, but it’s important to set boundaries and not read every paper on a topic. Finding a paper you had intended to write is possible, but don’t give up. Keep reading, and you’ll find what you’re looking for. Identifying research gaps requires an extensive literature review, but don’t give up and keep reading to find what you’re looking for.
- Check out our study guide to learn more about Identifying Research Gaps to Pursue Innovative Research.
In conclusion, a research gap signifies the unexplored terrain within a field where existing literature falls short. It is the pivot for innovation and advancement, propelling scholarly inquiry forward. A research gap can be either promising or inadequate. A significant research gap opens doors to groundbreaking discoveries, generating insightful contributions. Conversely, a poor research gap might lead to redundant studies or trivial outcomes. Recognizing and addressing a research gap thoughtfully can guide researchers toward valuable inquiries, enriching the academic landscape. Ultimately, the quality of a research gap lies in its potential to ignite meaningful exploration and cultivate knowledge that shapes the trajectory of a discipline.
About PhD Assistance
At PhD Assistance , we discover research gaps not only by a broad examination of current published literature but also through a detailed study of the material by categorizing it into geographical origin settings and multi-component-based research. This segregation identifies the disparity not only in the idea but also in the demographic components of the study. This well-rounded strategy results in a more defined and concentrated research field, which adds much-needed innovation to an academic research study.
- Davis, Stephen H. “Bridging the gap between research and practice: what’s good, what’s bad, and how can one be sure?.” Phi Delta Kappan 8 (2007): 569-578. https://doi.org/10.1177/00317217070880080
- Tavernise, Sabrina. “Education gap grows between rich and poor, studies say.” The New York Times 9 (2012).
- gap identification
- literature gap in research
- quantitative research gap example
- Research gap example
- research gap example in thesis
- Research gap in Literature Review
- research gap in the dissertation
- research gap sample
- types of research gaps

Quick Contact

- Adversial Attacks
- Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ML ( Machine Learning )
- Big Data Analysis
- Business and Management
- Categories of Research methodology – PhDAssistance
- Category of Research Proposal Services
- coding & algorithm
- Computer Data Science
- Category of Machine Learning – PhDassistance
- Computer Science/Research writing/Manuscript
- Course Work Service
- Data Analytics
- Data Processing
- Deep Networks
- Dissertation Statistics
- economics dissertation
- Editing Services
- Electrical Engineering Category
- Engineering & Technology
- finance dissertation writing
- Gap Identification
- Healthcare Dissertation Writing
- Intrusion-detection-system
- journals publishing
- Life Science Dissertation writing services
- literature review service
- Machine Learning
- medical thesis writing
- Peer review
- PhD Computer Programming
- PhD Dissertation
- PhD dissertation Writing
- Phd Journal Manuscript
- Annotated Bibliography
- PhD Publication Support
- Phd thesis writing services
- Phd Topic Selection
- Categories of PhdAssistance Dissertation
- Power Safety
- problem identification
- Quantitative Analysis
- quantitative research
- Recent Trends
- Referencing and Formatting
- Research Gap
- research journals
- Research Methodology
- research paper
- Research Proposal Service
- secondary Data collection
- Statistical Consulting Services
- Uncategorized
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Academic Research and the Expert-Novice Gap: Helping Students Understand the Purpose of Research (Virtual Event)
October 3, 2024 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM Save to Calendar
Experienced researchers tend to think about research as an ongoing and iterative process in which individual researchers contribute their findings to an ongoing conversation within or across disciplines. However, as novice researchers, students may have a very different understanding of the purpose of research. The lack of a shared understanding of the goals and process of research may contribute to the frustration that students and instructors often have related to student performance on research or inquiry-based assignments.
This free virtual workshop will explore the expert-novice gap in relation to the purpose and process of academic research. Participants will learn strategies and activities that they can use to help students develop their understanding of the purpose and process of research.
For those affiliated with Ohio State, this workshop counts as credit toward the Teaching Information Literacy endorsement from the Drake Institute for Teaching and Learning.
This virtual program will include automated captioning. If you require an accommodation such as live captioning or interpretation to participate in this event, please email [email protected] as soon as possible. Requests made at least one week prior to the event will generally allow us to provide seamless access, but the university will make every effort to meet requests made after this date.
Event Organizer
Poster Samples
Looking at samples of real student posters can help you generate ideas and define your goals. As you get started, it may be helpful to look at examples of finished posters.
Below are a number of sample posters created by UT undergraduates. There is a brief discussion of each poster highlighting its greatest strengths and areas where there is room for improvement.

- More than one type of visual aid
- Logical order for sections
- Acknowledgments
Room for improvement
- Background may be distracting, or detract from content
- Sections and images are not aligned
- Too many visual components clutter poster
- White space
- Legible text and graphics
- Reports preliminary results
- All participants listed as authors, with affiliations provided
- Lacks Citations and Acknowledgements
- Labeling of images/graphics
- Inconsistent text alignment
- Color-saturated background
- Clearly defined research questions
- Effective use of visual aids
- Clear organizational structure
- Bullets break up text
- Technical language/undefined acronyms (accessible to limited audience)
- Narrow margins within text boxes
- Too many thick borders around boxes
- Uses UT seal instead of college or university wordmark

- Clear introductory material
- Use of bullet points
- Logical flow
- Color-coding in graphics
- Lacks references section
- May not be accessible to all audiences (some technical language)
- No need for borders around sections (the blue headers are sufficient)

- Compelling visual aids
- Strategic use of color
- Clear sections
- Inconsistent fonts in body text
- Abstract section mislabeled
- Bullet points are great, but only if they’re used judiciously
- Parameters of study well defined
- Clearly defined research question
- Simple color scheme
- Use of white space
- Discussion of Results
- Minor formatting misalignments
- Unauthorized use of UT seal (use wordmark instead)
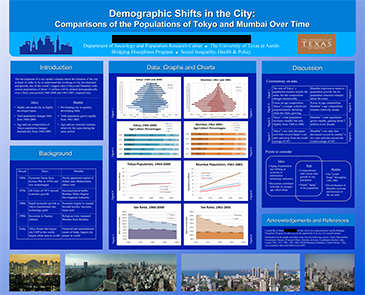
- Venn diagram in discussion
- Consistent graphics
- Multiple types of visual aids
- Light text on dark background
- Color backgrounds should be avoided, especially dark ones
- Unlabeled, non-credited photos
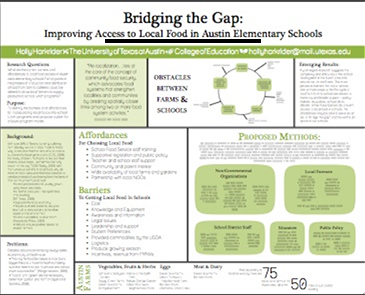
- Easy to read
- Use of shapes, figures, and bullets to break up text
- Compelling title (and title font size)
- Clean overall visual impression
- Many sections without a clear flow between them
- Lacks acknowledgements

- Use of images/graphics
- Clear title
- Accessible but professional tone
- Length/density of text blocks
- Tiny photo citations
- Connections between images and descriptive text
- Vertical boxes unnecessary
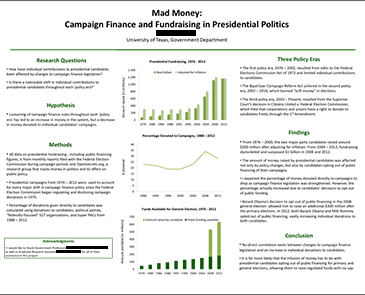
- Compelling title
- Font sizes throughout (hierarchy of text)
- Simple graphics
- Lacks clear Background section
- Relationship of Findings and Conclusion to Research questions

- Use of visual aids
- Uneven column width
- Center-justfied body text
- Lacks “Methods” section
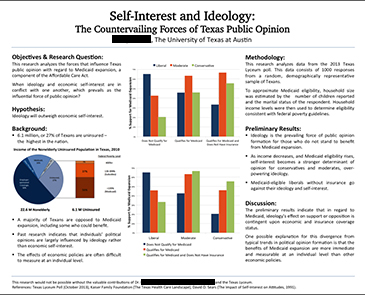
- Use of bullets
- Too many different font styles (serif and sans serif, bold and normal)
- Concise interpretation of graphics
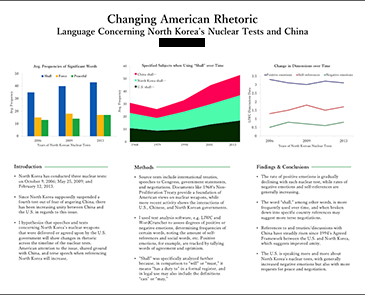
- Accessible visual structure
- Clear, simple graphics
- Fonts and font sizes
- Analysis of graphic data
- Discussion of significance
- Lacks author’s affiliation and contact information

- Balance among visuals, text and white space
- Data presented in visual format (SmartArt)
- Accesible to many audiences (simple enough for general audience, but enough methodological detail for experts)
- Some more editing needed
- When targeting an expert audience (as in the methodology section), should also report statistics ( r, p, t, F, etc.)

- Large, clear title
- Creative adaptation of sections
- Use of lists (rather than paragraphs)
- Accessible to diverse audience
- Connection between visuals (sheet music) and content

- Strategic use of color for section headers
- Labeling and citation of images
- Accessible to a broad audience
- Wide margins around poster edges
- Slightly text-heavy
- Data referenced (“Methodology”) but not discussed
What is my next step?
Begin working on the content for your poster at Create Your Message .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Times Insider
The Gender Gap Among Gen Z Voters, Explained
Claire Cain Miller spoke with eight young women supporting Harris, and eight young men backing Trump. Here’s what she learned.

By John Otis
Times Insider explains who we are and what we do and delivers behind-the-scenes insights into how our journalism comes together.
There is a significant gender gap in the political preferences of Gen Z voters in the United States, as evidenced by New York Times and Siena College polls conducted this month in six swing states.
Young women — those ages 18 to 29 — favored Vice President Kamala Harris for president by 38 points. And men the same age favored former President Donald J. Trump by 13 points. That is a whopping 51-point divide along gender lines, larger than in any other generation.
Claire Cain Miller, a Times reporter who covers gender, wanted to better understand those numbers. And she was especially curious about a specific group:
“I really wanted to hear from young men who were voting for Trump,” she said in an interview on Monday.
Ms. Miller recently published a pair of companion pieces for The Upshot, a Times section that focuses on explanatory and analytical journalism. For one of the articles, Ms. Miller talked to eight young women who said they planned to vote for Ms. Harris; for the other, she spoke with eight young men who support Mr. Trump.
Over the last few years, Ms. Miller has become increasingly interested in exploring how shifts in gender roles and societal trends have affected boys and men, some of whom feel they’ve fallen behind economically. Today more women earn college degrees than men , and are increasingly the breadwinners in their households. Over the past few decades, jobs traditionally held by men — especially those without college degrees — have dwindled.
Though Gen Z men are still somewhat more likely to identify as Democrats than Republicans, the men Ms. Miller spoke with described feeling unvalued in a shifting landscape of gender norms — and they saw Mr. Trump as a pillar of traditional masculinity.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
More From Forbes
Amd narrows the gap with nvidia in new mlperf benchmarks.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
New benchmark results from AMD, Untether AI, Google, Intel, and Nvidia demonstrate the converging AI silicon performance competition. However, system design, networking, and software make AI sing and dance. And that’s where Nvidia excels.
Finally, I can stop whining about AMD’s lack of open AI benchmarks. AMD has published excellent MLPerf inference results for their MI300 GPU, which is competitive with the Nvidia H100, although only on a single benchmark. Canadian startup Untether.ai also published new inference benchmarks showing their power efficiency. Let’s take a look.
The MLPerf Inference 4.1 Benchmark Suite
The MLCommons industry consortium, which controls and publishes the MLPerf benchmarks, has extended the twice-annual inference benchmark suite with a new one for the increasingly popular mixture-of-experts (MoE) AI models. MoE models combine multiple models to improve accuracy and lower the training costs of huge LLM models, like OpenAI’s GPT-4. AMD did not publish an MoE benchmark, but now that they have broken the benchmarking ice, an AMD spokesperson indicated we could see more shortly.
MLCommons has added a mixture of Experts model to its suite of AI benchmarks.
Its is certainly encouraging to see submissions to MLPerf for new processors. Specifically in addition to the Nvidia Blackwell and the first AMD submissions, we now have selected benchmarks for Untether.ai, AMD’s next generation Turin CPU, Google’s Trillium TPUv6e accelerator, and Intel’s Granite Rapids Xeon CPU. We will focus here on Nvidia, AMD, and Untether.ai.
AMD is roughly on par with the Nvidia H100, while the H200 is 43% faster
While AMD has previously disclosed micro benchmarks that highlight raw theoretical performance, such as that of the math performance on the MI300, these do not reflect the complex world of AI stacks. The AMD marketing claims that the MI300 is the fastest AI GPU were not validated with this new benchmark, but it is in the ballpark of the H100 when running a real AI workload. The Nvidia H200, however, beat the MI300 by some 43% on the same benchmark.
New Password Hacking Warning For Gmail, Facebook And Amazon Users
Trump vs. harris 2024 polls: harris leads by 1 point in latest post-dnc survey, today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for wednesday, august 28th.
AMD is without a doubt, now competitive with the Nvidia H100
We note that the Llama 2 70B benchmark doesn’t really allow AMD to strut its stuff with respect to having a larger HBM to support larger models. Hopefully we will see them run the new Mixtral MoE in a future MLPerf release.
Nvidia published H200 benchmarks that top AMD, but only by a little.
Nvidia also published the first Blackwell benchmarks, demonstrating about four times the performance of the H100 on medium-sized models (Llama 2 70B). Nvidia recently shared more details on Blackwell NVL72 at HotChips, in which the NVSwitch interconnected infrastructure is supposed to deliver 30 times better inference performance than H200. Can’t wait to see actual (MLPerf) benchmarks for the flagship NVL72.
Nvidia showed that the Blackwell is indeed 30X faster than the H100 for extremely large models
Nvidia did publish results for the new MoE benchmark, which shows off the the H100 and H200. Nvidia also showed a 10% to 27% performance improvement for the H200 across the MLPerf benchmark suite, which should help users as they await Blackwell’s arrival in volume.
For those worried about the delay of Blackwell volume shipments, the H100 and H200 keep getting ... [+] faster with software improvements.
Untether.ai Demonstrates Power-efficient Inferencing
We have seen before that an ASIC can provide more efficient AI inference processing, as first demonstrated with the Qualcomm Cloud AI100. The challenge is that ASICs, unlike GPUSs, are one-trick-ponies. They can perhaps perform quite efficiently on, say, Resnet-50, but not so impressively on other models.
Untether.ai thinks they can break that mold, and have submitted exceptional power efficiency on Resnet-50 thats were on-par with the Nvidia H100-NV at a fraction of the power consumption.
Untether demonstrated excellent performance at low power
Ok, so how does the Untether platform perform on LLM’s? The engineers didn’t complete their optimization on the BERT benchmark in time for the MLPerf submission deadline, but they have since completed their work and shared the results with us. As you can see below, the company seems to have avoided the traps their predecessors fell into. They are showing comparable performance as an Nvidia H100-NVL, with over 3X advantage in energy efficiency.
Untether missed the submission deadline for BERT-Large, but the results indicate the platform has ... [+] exceptional energy efficiency for language models
Conclusions
Once again, as we have seen over the years, only Nvidia published results for every benchmark, and once again Nvidia demonstrated why they are the best AI infrastructure provider due to their full stack approach of custom CPU, GPU, software, system, and networking But at the chip level, there is now legitimate competition from AMD, at least on a single benchmark. While we may enter a period of leapfrogging, similar to what we saw decades ago with RISC CPUs, these differentiators for Nvidia will be durable, and should keep Team Green in the lead for at least the next 2-3 years.
Disclosures : This article expresses the opinions of the author and is not to be taken as advice to purchase from or invest in the companies mentioned. My firm, Cambrian-AI Research, is fortunate to have many semiconductor firms as our clients, including BrainChip, Cadence, Cerebras Systems, D-Matrix, Esperanto, Groq, IBM, Intel, Micron, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, Graphcore, SImA,ai, Synopsys, Tenstorrent, Ventana Microsystems, and scores of investors. We have no investment positions in any of the companies mentioned in this article. For more information, please visit our website at https://cambrian-AI.com .

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Connected to the future, life is more meaningful: the effect of future self-continuity on the presence of meaning
- Published: 27 August 2024
Cite this article

- Lulu Xue 1 ,
- Hang Fan 2 ,
- Yun Yan 1 ,
- Liping Zhang 1 ,
- Yanna Jiang 1 &
- Lipeng Chen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0417-4935 1
Although studies have confirmed that future self-continuity impacts the presence of meaning, evidence of cross-cultural consistency remains scarce, and the underlying mechanisms between the two are unclear. To fill this research gap, we conducted two studies using a sample of Chinese college students ( N = 631). Study 1 verified the positive predictive effect of future self-continuity on the presence of meaning in the context of Eastern culture through two sub-experiments ( n = 325), thereby confirming its cross-cultural consistency. Study 2, a three-wave longitudinal study, revealed the mediating mechanisms through which future self-continuity affects the presence of meaning ( n = 306). The results suggest that future self-continuity at Time 1 can directly predict the presence of meaning at Time 3 and indirectly predict the presence of meaning at Time 3 through self-concept clarity at Time 2. Thus, self-concept clarity partially mediates the relationship between future self-continuity and the presence of meaning. These findings enrich cross-cultural research on the presence of meaning and provide new ideas and methods for enhancing the presence of meaning in individual lives.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
In the supplementary material, we report results controlling for word count and positive effect.
In the supplementary material, we test our hypothesis without control variables.
Biskas, M., Juhl, J., Wildschut, T., Sedikides, C., & Saroglou, V. (2022). Nostalgia and spirituality: The roles of self-continuity and meaning in life. Social Psychology , 53 (3), 152–162. https://doi.org/10.1027/1864-9335/a000487
Article Google Scholar
Bixter, M. T., McMichael, S. L., Bunker, C. J., Adelman, R. M., Okun, M. A., Grimm, K. J., Graudejus, O., & Kwan, V. S. Y. (2020). A test of a triadic conceptualization of future self-identification. Plos ONE , 15 (11). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242504 . Article e0242504.
Boucher, H. C., Bloch, T., & Pelletier, A. (2015). Fluid compensation following threats to self-concept clarity. Self and Identity , 15 (2), 152–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2015.1094405
Campbell, J. D., Trapnell, P. D., Heine, S. J., Katz, I. M., Ravallee, L. F., & Lehman, D. R. (1996). Self-concept clarity: Measurement, personality correlates, and cultural boundaries. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 70 (1), 141–156. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.70.1.141
Çebi, E., & Demir, A. (2022). A path model of meaning in life among university students: The roles of gratitude, self-concept clarity and self-construal. Applied Research Quality Life , 17 , 3091–3113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-022-10054-y
Chu, C., & Lowery, B. S. (2023). Perceiving a stable self-concept enables the experience of meaning in life. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin . https://doi.org/10.1177/01461672221150234
D’Argembeau, A., & Garcia Jimenez, C. (2023). Effects of past and future autobiographical thinking on the working self-concept. Memory , 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658211.2023.2269324
D’Argembeau, A., Lardi, C., & Van der Linden, M. (2012). Self-defining future projections: Exploring the identity function of thinking about the future. Memory (Hove, England) , 20 (2), 110–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658211.2011.647697
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Datu, J. A. D., & Mateo, N. J. (2015). Gratitude and life satisfaction among Filipino adolescents: The mediating role of meaning in life. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling , 37 (2), 198–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-015-9238-3
Du, X., Ye, P., Zhang, R. S., L., & Jin, S. H. (2017). Future self-continuity decreases physical pain: The mediating role of self-concept clarity. Chinese Psychological Society. (Eds.), The 20th National Psychology Conference - Psychology and National Mental Health Abstract Collection (pp.903). The 20th National Psychology Conference– Psychology and National Mental Health Abstract Collection. [In Chinese].
Du, X. P., Jiang, J., Jiang, W., Wang, J., Peng, W. Y., & Yang, K. R. (2023). Antecedents and intervention strategies of self-concept clarity: A new perspective from three facets of selfconcept structural integration. Journal of Psychological Science , 46 (1), 170–180. https://doi.org/10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20230122 . [In Chinese].
El Haj, M., & Moustafa, A. A. (2023). Who am I? Diminished sense of self in Korsakoff’s syndrome. Self and Identity , 22 (7–8), 1053–1064. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2023.2246679
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods , 39 (2), 175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193146
Geng, J., Wang, Y., Wang, P., Zeng, P., & Lei, L. (2022). Gender differences between cyberbullying victimization and meaning in life: Roles of fatalism and self-concept clarity. Journal of Interpersonal Violence , 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605211028285
Heine, S. J., Proulx, T., & Vohs, K. D. (2006). The meaning maintenance model: On the coherence of social motivations. Personality and Social Psychology Review , 10 (2), 88–110. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327957pspr1002_1
Hershfield, H. E., Garton, M. T., Ballard, K., Samanez-Larkin, G. R., & Knutson, B. (2009). Don’t stop thinking about tomorrow: Individual differences in future self-continuity account for saving. Judgment and Decision Making , 4 (4), 280–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/03071847209434499
Hershfield, H. E., Goldstein, D. G., Sharpe, W. F., Fox, J., Yeykelis, L., Carstensen, L. L., & Bailenson, J. N. (2011). Increasing saving behavior through age-progressed renderings of the future self. Journal of Marketing Research , 48 , S23–S37. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkr.48.SPL.S23
Hershfield, H. E., Cohen, T. R., & Thompson, L. (2012). Short horizons and tempting situations: Lack of continuity to our future selves leads to unethical decision making and behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , 117 (2), 298–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2011.11.002
Hicks, J. A., & King, L. A. (2009). Positive mood and social relatedness as information about meaning in life. The Journal of Positive Psychology , 4 (6), 471–482. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760903271108
Hong, E. K., Zhang, Y., & Sedikides, C. (2024). Future self-continuity promotes meaning in life through authenticity. Journal of Research in Personality , 109 , 104463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2024.104463
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cut-off criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modelling , 6 (1), 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118
Ji, L. J., Nisbett, R. E., & Su, Y. (2001). Culture, change and prediction. Psychological Science , 12 (6), 450–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.00384
Ji, L., Hong, E. K., Guo, T., Zhang, Z., Su, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Culture, psychological proximity to the past and future, and self-continuity. European Journal of Social Psychology , 49 (4), 735–747. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.2544
Ji, L. J., Imtiaz, F., Su, Y. J., Zhang, Z. Y., Bowie, A. C., & Chang, B. R. (2022). Culture, aging, self-continuity, and life satisfaction. Journal of Happiness Studies , 23 , 3843–3864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-022-00568-5
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ji, L., Wu, J., Y., & Yang, Y. Y. (2023). The breath of temporal information focus among Chinese people. Acta Psychologica Sinica , 55 (3), 421–434. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00421 . [In Chinese].
Jiang, T., Chen, Z., & Sedikides, C. (2020). Self-concept clarity lays the foundation for self-continuity: The restorative function of autobiographical memory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 119 (4), 945–959. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000259
Kanten, A. B., & Teigen, K. H. (2008). Better than average and better with time: Relative evaluations of self and others in the past, present, and future. European Journal of Social Psychology , 38 (2), 343–353. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.457
Lee-Flynn, S. C., Pomaki, G., DeLongis, A., Biesanz, J. C., & Puterman, E. (2011). Daily cognitive appraisals, daily affect, and long-term depressive symptoms: The role of self-esteem and self-concept clarity in the stress process. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 37 (2), 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167210394204
Li, F., Wang, Q. Y., Zhong, L. P., Zheng, X., & Wu, B. Y. (2019). Relationship between college students’ self-concept clarity and smart phone addiction: The mediating effect of self-esteem and social anxiety. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology , 27 (5), 900–904. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2019.05.009 . [In Chinese].
Li, B., Zhu, Q., He, R. W., Li, A. M., & Wei, H. Y. (2022). The effect of mortality salience on consumers’ preference for experiential purchases and its mechanism. Acta Psychologica Sinica , 55 (2), 301–307. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00301 . [In Chinese].
Light, A. E., & Visser, P. S. (2013). The ins and outs of the self: Contrasting role exits and role entries as predictors of self-concept clarity. Self and Identity , 12 , 291–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2012.667914
Liu, Y., Di, S., Zhang, Y., & Ma, C. (2023). Self-concept clarity and learning engagement: The sequence-mediating role of the sense of life meaning and future orientation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 20 (6), 4808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20064808
Löckenhoff, C. E., & Rutt, J. L. (2017). Age differences in self-continuity: Converging evidence and directions for future research. The Gerontologist , 57 (3), 396–408. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gnx010
Martin-Storey, A., Recchia, H. E., & Santo, J. B. (2021). Self-continuity moderates the association between sexual-minority status based discrimination and depressive symptoms. Journal of Homosexuality , 68 (12), 2075–2096. https://doi.org/10.1080/00918369.2020.1733350
Mitchell, L. L., Frazier, P. A., & Sayer, N. A. (2020). Identity disruption and its association with mental health among veterans with reintegration difficulty. Developmental Psychology , 56 (11), 2152–2166. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev000110
Napier, A. D., Slemp, G. R., & Vella-Brodrick, D. A. (2024). Life crafting and Self-Determination: An intervention to help emerging adults create an authentic and meaningful life. Emerging Adulthood . https://doi.org/10.1177/21676968241252196
Nie, H. Y., & Gan, Y. Q. (2017). The relationship among self-concept clarity, meaning in life and subjective well-being. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology , 25 (5), 923–927. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2017.05.029 . [In Chinese].
Park, J., & Baumeister, R. F. (2017). Meaning in life and adjustment to daily stressors. The Journal of Positive Psychology , 12 (4), 333–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2016.1209542
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 (5), 879–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Racy, F., & Morin, A. (2024). Relationships between self-talk, inner speech, mind wandering, mindfulness, self-concept clarity, and self-regulation in university students. Behavioral Sciences , 14 (1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14010055
Raffard, S., Michel, S., & Bayard, S. (2023). Imagining one’s personal future in women undergoing treatment for breast cancer: An exploratory study. Memory (Hove, England) . https://doi.org/10.1080/09658211.2023.2221875
Schwartz, S. J., Meca, A., & Petrova, M. (2017). Who am I and why does it matter? Linking personal identity and self-concept clarity. In Lodi-Smith, J., & DeMarree, K. (Eds.), Self-Concept Clarity . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71547-6_8
Shen, J., Wang, Y., & Zhou, C. (2022). Application of the Chinese version of the future self-continuity questionnaire in college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal , 36 (1), 73–76. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2022.01.012 . [In Chinese].
Shin, J. Y., Steger, M. F., & Henry, K. L. (2016). Self-concept clarity’s role in meaning in life among American college students: A latent growth approach. Self and Identity , 15 , 206–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2015.1111844
Slotter, E. B., & Gardner, W. L. (2014). Remind me who I am: Social interaction strategies for maintaining the threatened self-concept. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 40 (9), 1148–1161. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167214537685
Sokol, Y., & Serper, M. (2020). Development and validation of a future self-continuity questionnaire: A preliminary report. Journal of Personality Assessment , 102 (5), 677–688. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2019.1611588
Steger, M. F. (2009). Meaning in life. In S. J. Lopez, & C. R. Snyder (Eds.), Oxford handbook of positive psychology (pp. 679–687). Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Steger, M. F., Frazier, P., Oishi, S., & Kaler, M. (2006). The meaning in life questionnaire: Assessing the presence of and search for meaning in life. Journal of Counseling Psychology , 53 (1), 80–93. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.53.1.80
Szabó, Á. (2022). Envisioning positive future selves: Perceptions of the future self and psychological adaptation in recent migrants. Self and Identity , 21 (8), 877–890. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2021.2003427
Van Gelder, J. L., Hershfield, H. E., & Nordgren, L. F. (2013). Vividness of the future self predicts delinquency. Psychological Science , 24 (6), 974–980. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612465197
Van Tilburg, W. A. P., & Igou, E. R. (2019). Dreaming of a brighter future: Anticipating happiness instills meaning in life. Journal of Happiness Studies , 20 (2), 541–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-018-9960-8
Wang, L., Chen, Z. X., & He, Y. (2020). Effect of legacy motivation on individuals’ financial risk-taking: Mediating role of future self-continuity. Acta Psychologica Sinica , 52 (8), 1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.01004 . [In Chinese].
Waytz, A., Hershfield, H. E., & Tamir, D. I. (2015). Mental simulation and meaning in life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 108 (2), 336–355. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038322
Xue, L. L., Yan, Y., Fan, H., Zhang, L. P., Wang, S. Y., & Chen, L. P. (2023). Future self-continuity and depression among college students: The role of presence of meaning and perceived social support. Journal of Adolescence , 95 (7), 1463–1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12219
Yang, S., Huang, X. T., Wang, X. G., & Yin, T. Z. (2012). Neural mechanism of cultural influences on the self-construal. Advances in Psychological Science , 20 (1), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2012.00149 . [In Chinese].
Zaw, S., & Baldwin, S. (2023). Knowing who I am depends on who I’ve become: Linking self-concept clarity and temporal self-comparison. Self and Identity , 22 (6), 973–999. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2023.2244722
Zhang, C., Hirschi, A., Herrmann, A., Wei, J., & Zhang, J. (2017). The future work self and calling: The mediational role of life meaning. Journal of Happiness Studies , 18 (4), 977–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-016-9760-y
Zhang, P., Wang, P., Zhang, D., & Zhang, L. G. (2022). Effect of self-concept clarity and meaning in life on suicidal ideation in college fresh students. Chinese Mental Health Journal , 36 (7), 975–980. [In Chinese].
Zhang, F., Pi, Y., & Li, X. (2023). Photographic intervention effect on positive and negative affects during COVID-19: Mediating role of future self-continuity. Frontiers in Psychology , 13 , 1085518. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1085518
Zuo, S. J., Huang, N. W., Wang, F., & Cai, P. (2016). Meaning maintenance model: The development of theory and research challenges. Advances in Psychological Science , 24 (1), 101–110. [In Chinese].
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the young students who participated in this project.
This work was supported by the Fund for Building World-Class Universities (Disciplines) of the Renmin University of China Project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China, Beijing, China
Lulu Xue, Yun Yan, Liping Zhang, Yanna Jiang & Lipeng Chen
Research Center, Party School of China Railway Engineering Corporation, Beijing, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Lulu Xue: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing– original draft, Writing– review & editing. Hang Fan: Validation, Writing– review & editing. Yun Yan: Validation, Writing– review & editing. Liping Zhang: Validation, Writing– review & editing. Yanna Jiang: Validation, Writing– review & editing. Lipeng Chen: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing– review & editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lipeng Chen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Xue, L., Fan, H., Yan, Y. et al. Connected to the future, life is more meaningful: the effect of future self-continuity on the presence of meaning. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06521-4
Download citation
Accepted : 05 August 2024
Published : 27 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06521-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Future self-continuity
- Self-concept clarity
- Presence of meaning
- Cross-lagged
- Experimental study
- Mediating role
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Office of Research Training, Diversity, and Disparities Newsletter, August 2024

What’s New at NIDA
Changes to nida’s diversity supplement program .
ORTDD is excited to announce some changes to the NIDA Diversity Supplement Program! For more than 30 years, NIH has made available supplements to existing grants to provide research opportunities, training, and mentorship to enhance the diversity of the biomedical research workforce. NIDA is proud to participate in this NIH-wide program, and our team at the ORTDD would like to spread the word to PIs on active NIDA awards as well as to potential applicants about this opportunity. PIs are encouraged to participate, so long as an active grant mechanism is eligible, there is sufficient time remaining during the initial award period for the supplement, and the and the PI is committed to mentoring and career development for the candidate. K award grants are not eligible to have Diversity Supplements, but most other mechanisms are!
Program details: Diversity supplement scholars may be post-bacs, master’s degree holders, doctoral students, post-docs, or early career investigators who meet eligibility criteria outlined in PA-23-189 . A NIDA grantee-applicant must work closely with an eligible candidate to create a plan that will facilitate the scholar’s progression to the next career stage. The proposed research and training activities must be appropriate for the stage of the candidate, and the project must be within scope of the parent research award. Applications are administratively reviewed, that is, reviewed by NIH program staff. NIDA PIs can apply through the general NIDA Diversity Supplement Program or through a specialized program, such as the one managed by the BRAIN Initiative .
What’s new: In fiscal year 2025 (which starts on October 1, 2024), NIDA’s general Diversity Supplement Program will have multiple receipt dates. While you can submit your application at any time, the cut-off dates for NIDA’s administrative review will be August 15th, October 15th, December 15th, February 15th, and April 15th. The final receipt date to be considered for funding in the fiscal year (which ends September 30th) is April 15th. Another change to the program is that applications are limited to 6 pages regardless of the page limit for the “parent” grant mechanism , making application review equitable for all grant mechanisms. Please be certain to check your page limit!
For more information: To learn more, please see the Instructions to PI's and FAQ's , and reach out to Dr. Angela Holmes, NIDA’s Diversity Supplement Program Coordinator at ( [email protected] ).
Program Updates
A new nida funding opportunity hit the street consider applying for a “d-start”.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) has published a new notice of funding opportunity (NOFO), PAS-24-242 , entitled “Data Science Track Award for Research Transition (D-START).” Awards will support investigators to apply advanced data science techniques to address timely and challenging research questions related to substance use and substance use disorders (SUD). As defined by NIH, data science encompasses the development and use of quantitative and analytical methods to extract knowledge from large and complex data sets. Expanding expertise in data science, particularly in big data analytics and computational science, is crucial for advancing SUD research. The goal is to generate data-driven insights to inform the development and implementation of interventions for prevention, harm reduction, treatment, and recovery across diverse populations.
While the R03 mechanism is used for this award, the D-START allows for projects with budgets of up to $100,000 per year in direct costs over 2 years. NIDA plans to fund 6-7 projects per year during the 2025, 2026, and 2027 fiscal years, depending on annual institute appropriations and the receipt of meritorious applications. D-START awardees are expected to use their project findings to pursue further grant applications, such as a subsequent R01, focusing on the intersection of substance use and data science. Cross-disciplinary collaborations are strongly encouraged, and NIDA welcomes applications from individuals of diverse backgrounds, including those historically underrepresented in STEM fields. Applicants should adhere to Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable (FAIR) principles and address ethical considerations in research involving human subjects. Read more about this opportunity .
Apply for a NIDA Travel Award

Call for applications! NIDA is providing travel awards for scholars interested in attending the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco on March 12 -15, 2025 in New Orleans, LA. The deadline to apply is December 1, 2024 at 11:59pm ET.
The NIDA Travel Award Program aims to defray the costs of in-person attendance at national scientific conferences. Travel award recipients will receive an award in the amount of $1500 for meeting transportation, lodging, and/or registration. Awardees are expected to attend a NIDA “meet-and-greet” at the conference. See the NIDA Travel Award website for information about eligibility and how to apply.
Please contact Yohansa Fernández for any questions related to NIDA travel awards.
Career Development Spotlight: Dawn Bounds PhD, PMHNP-BC, FAAN

The NIDA ORTDD is excited to introduce Dr. Dawn Bounds to the research training community. Dr. Bounds is an Assistant Professor at the University of California, Irvine within the Sue & Bill Gross School of Nursing. Her research interests include marginalized youth, adolescence, risk, resilience, commercial sexual exploitation, social media, mental health, integrative health, as well as wearable and biofeedback technology. She was a 2021 NIDA Diversity Scholars Network program participant and was recently awarded a 5-year R01 grant titled “ Teaching Youth & Families Self-Regulation Skills to Disrupt the Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences: Preventing Substance Use in Adversity-Impacted Youth .” Her research focuses the impact of the Garnering Resilience in Traumatized youth and families (GRIT) program on early initiation of alcohol and cannabis use among youth. Read about her below and what aspired her to become an addiction researcher.
Please share a little about yourself and your upbringing (if you're comfortable doing so), your educational background, and research focus.
I am the oldest of two daughters who were raised by a single mom. I am also a first-generation college student who was born and raised in Chicago. I spent all of my life there including my graduate education. I graduated with a BSN from the University of Illinois at Chicago in 1999 and an MSN and PhD from Rush University in 2004 and 2015. Prior to becoming a researcher, I worked in the community as a psychiatric-mental health nurse practitioner. My experiences as a clinician working with marginalized youth on the west side of Chicago informs my research interests to this day. My program of research focuses on youth risk and resilience. More specifically, I am interested in preventing substance use initiation and disorders in adversity impacted youth.
At what point in your life did you know you wanted to become a scientist? What drew you to the STEM field and particularly substance use/addiction research?
I never knew that I wanted to become a scientist because I had little exposure to research. It is one of the reasons I am currently so committed to exposing high school and undergraduate students to research through my lab. I used to teach in a master’s program that changed to a doctoral program and I was urged to get my doctorate to continue teaching. This prompted me to get my PhD. During my program and working on a NIH funded study, I fell in love with research.
I have to admit I used to be a little resistant to working in the field of substance use/addiction due to my firsthand knowledge of what it does to families. But what I realized is that trauma and adversity (my area of interest and expertise) is inextricably linked to substance use/addiction. To continue to excel in the field of trauma and adversity, meant including substance use/addiction research.
Were there any events or individuals who inspired you throughout your professional journey?
My mother is my greatest inspiration. She always taught me to defy all odds. My own life experiences taught me persistence. I have encountered several amazing mentors and colleague along the way who have inspired me, fought and advocated for me, and supported me on my professional journey.
How did you learn about the NDSN Program? Please share about your experience as an NDSN scholar and major takeaways from participating in the program.
I tend to search out training programs and opportunities that support minoritized individuals like myself. These training programs have expanded my network and knowledge about programs like the NDSN. The NDSN provided a unique opportunity to receive a mock review of my grant which was so valuable. The biggest take away for me was to keep resubmitting my proposal. Doing so led to me finally getting funded this year.
What has been the most challenging obstacle you have had to face throughout your career journey to becoming an addiction researcher and what have you done to “push through”?
Not letting my career in academia become my sole identity has been most challenging. Academia and research can be consuming. Striking a balance between my work and the other aspects of my life has been an ongoing process. Understanding and prioritizing what’s most important to me has helped me push through with the help of my spirituality, supportive family and friends, and therapy. Building a support network that includes those who have thrived in academia is key.
Can you offer any advice to ESIs/scholars in earlier career stages who are navigating the NIH process for submitting grants and working towards the goal of being independently funded?
Persist! You belong in this space and your work is important to the field. Keep innovating, revising, and resubmitting those grants!
Is there anything else that you would like to share with the NIDA community about your inspiring journey?
I am truly grateful for being a part of the NIDA community. NIDA has supported my growth and development over the past 4 years. These initial investments through training have now led to a larger investment in my research. I’m excited to continue to collaborate with other NIDA scholars and prevent addiction and substance use disorders in adversity impacted youth.
Did You Know?
Your opinion matters check out the latest “rfi” on supporting postdoctoral scholars.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is seeking feedback from the biomedical research community through a follow-up Request for Information (RFI) as part of an overarching goal to better support the postdoctoral scholar workforce. NIH began implementing recommendations earlier this year by increasing pay levels for Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards. A Request for Information has been issued to gather community input on additional proposed actions to accelerate the career transition of postdoc scholars into thriving biomedical research careers.
Through the RFI, NIH is seeking additional specific suggestions, evidence-based strategies, and relevant data or related experiences that will help inform our potential strategies. Feedback will be accepted electronically until October 23, 2024 . Please feel free to respond and widely share the RFI with your networks! NIH is particularly interested in receiving input from:
- Trainees (e.g., graduate students, postdocs),
- Early-stage investigators,
- Biomedical faculty,
- Training directors,
- Postdoctoral and graduate student office leaders,
- Biotech/biopharma industry scientists, and research education program advocates.
NIH encourages organizations (e.g., patient advocacy groups, professional societies) to submit a single response reflective of the views of the organization or its membership. Please direct all inquiries related to this RFI to [email protected] .
Closing the Ginther Gap: Annual Update on NIH's Progress
In late July, NIH’s annual update on efforts to address the “Ginther Gap” was published Dr. Marie Bernard, the Chief Officer for Scientific Workforce Diversity (COSWD), and Dr. Mike Lauer, the NIH Deputy Director for Extramural Research. The “Ginther Gap” refers to results from a 2011 study that found a 10 percentage point difference in grant application success rates between black and white applicants, favoring white applicants. This update is a continuation of their work to examine research project grant (RPG) and R01 funding rates by race and ethnicity, as NIH has developed numerous programs to address disparities over the past decade. Drs. Bernard and Lauer report that despite some progress, disparities in funding rates by race and ethnicity persist. However, they also reveal in a recent blog that funding rates for K awards increased between 2010 and 2022. This is encouraging, as K awards often precede research project award funding.
Notable NIH initiatives to promote diversity in the scientific workforce include the Common Fund Diversity Program Consortium (DPC) and the Faculty Institutional Recruitment for Sustainable Transformation (FIRST) initiative. Along with the UNITE initiative, these programs aim to ensure that a diverse range of voices contribute to scientific innovation. The NIH remains committed to monitoring and evaluating progress towards achieving equity in funding, ensuring there are no barriers to participation. Read more about this update in the full blog post .

NIH UNITE Workshop on Structural Racism and Health Research
Have you ever wondered what is meant by “structural racism” or what structural racism has to do with health research and health outcomes? On July 18th and 19th, the NIH UNITE Initiative leadership and members convened a virtual workshop to explore these and related topics. The workshop featured researchers, clinicians, and community partners with expertise in fields such as social and natural sciences, law and criminal justice, education, public policy, and social work—as well as biomedical, behavioral, and public health. Speakers provided insights into the origins and drivers of structural racism, methodological considerations in the measurement of structural racism, and interventions to improve health outcomes through strategies that reflect an awareness of the research on structural racism. A recording of the webinar is now available using these links: July 18 Videocast | July 19 Videocast . See the workshop website for additional information about the event.
Physical Review Research
- Collections
- Editorial Team
- Open Access
Investigating the superconducting state of 2 H − NbS 2 as seen by the vortex lattice
A. alshemi, e. campillo, e. m. forgan, r. cubitt, m. abdel-hafiez, and e. blackburn, phys. rev. research 6 , 033218 – published 26 august 2024.
- No Citing Articles
- Supplemental Material
- C. Cho, J. Lyu, C. Y. Ng, J. J. He, K. T. Lo, D. Chareev, T. A. Abdel-Baset, M. Abdel-Hafiez, and R. Lortz, Evidence for the Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov in bulk NbS 2 , Nat. Commun. 12 , 3676 (2021) .
- P. Wan, O. Zheliuk, N. F. Q. Yuan, X. Peng, L. Zhang, M. Liang, U. Zeitler, S. Wiedmann, N. E. Hussey, T. T. M. Palstra, and J. Ye, Orbital Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov state in an Ising superconductor , Nature (London) 619 , 46 (2023) .
- P. Fulde and R. A. Ferrell, Superconductivity in a strong spin-exchange field , Phys. Rev. 135 , A550 (1964) .
- A. Larkin and Y. N. Ovchinnikov, Inhomogeneous state of superconductors , Sov. Phys. JETP 20 , 762 (1965).
- S. Manzeli, D. Ovchinnikov, D. Pasquier, O. V. Yazyev, and A. Kis, 2D transition metal dichalcogenides , Nat. Rev. Mater. 2 , 17033 (2017) .
- T. Knispel, J. Berges, A. Schobert, E. G. C. P. van Loon, W. Jolie, T. Wehling, T. Michely, and J. Fischer, Unconventional charge-density-wave gap in monolayer NbS 2 , Nano Lett. 24 , 1045 (2024) .
- D. Lin, S. Li, J. Wen, H. Berger, L. Forró, H. Zhou, S. Jia, T. Taniguchi, K. Watanabe, X. Xi, and M. S. Bahramy, Patterns and driving forces of dimensionality-dependent charge density waves in 2H-type transition metal dichalcogenides , Nat. Commun. 11 , 2406 (2020) .
- D. E. Moncton, J. D. Axe, and F. J. DiSalvo, Neutron scattering study of the charge-density wave transitions in 2 H − TaSe 2 and 2 H − NbSe 2 , Phys. Rev. B 16 , 801 (1977) .
- J. A. Wilson, F. J. Di Salvo, and S. Mahajan, Charge-density waves and superlattices in the metallic layered transition metal dichalcogenides , Adv. Phys. 24 , 117 (1975) .
- M. Abdel-Hafiez, X.-M. Zhao, A. A. Kordyuk, Y.-W. Fang, B. Pan, Z. He, C.-G. Duan, J. Zhao, and X.-J. Chen, Enhancement of superconductivity under pressure and the magnetic phase diagram of tantalum disulfide single crystals , Sci. Rep. 6 , 31824 (2016) .
- I. Guillamon, H. Suderow, S. Vieira, L. Cario, P. Diener, and P. Rodière, Superconducting density of states and vortex cores of 2H- NbS 2 , Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 , 166407 (2008) .
- J. Kačmarčík, Z. Pribulová, C. Marcenat, T. Klein, P. Rodière, L. Cario, and P. Samuely, Specific heat measurements of a superconducting NbS 2 single crystal in an external magnetic field: Energy gap structure , Phys. Rev. B 82 , 014518 (2010) .
- N. Kobayashi, K. Noto, and Y. Muto, Thermodynamic properties of the layered superconductor 2 H − NbSe 2 , J. Low Temp. Phys. 27 , 217 (1977) .
- A. Majumdar, D. VanGennep, J. Brisbois, D. Chareev, A. V. Sadakov, A. S. Usoltsev, M. Mito, A. V. Silhanek, T. Sarkar, A. Hassan, O. Karis, R. Ahuja, and M. Abdel-Hafiez, Interplay of charge density wave and multiband superconductivity in layered quasi-two-dimensional materials: The case of 2 H − Nb S 2 and 2 H − Nb Se 2 , Phys. Rev. Mater. 4 , 084005 (2020) .
- Y. Noat, J. A. Silva-Guillén, T. Cren, V. Cherkez, C. Brun, S. Pons, F. Debontridder, D. Roditchev, W. Sacks, L. Cario, P. Ordejón, A. García, and E. Canadell, Quasiparticle spectra of 2 H − NbSe 2 : Two-band superconductivity and the role of tunneling selectivity , Phys. Rev. B 92 , 134510 (2015) .
- M. Ichioka, V. G. Kogan, and J. Schmalian, Locking of length scales in two-band superconductors , Phys. Rev. B 95 , 064512 (2017) .
- M. Silaev and E. Babaev, Microscopic theory of type-1.5 superconductivity in multiband systems , Phys. Rev. B 84 , 094515 (2011) .
- H. F. Hess, C. A. Murray, and J. V. Waszczak, Flux lattice and vortex structure in 2 H − NbSe 2 in inclined fields , Phys. Rev. B 50 , 16528 (1994) .
- P. L. Gammel, D. A. Huse, R. N. Kleiman, B. Batlogg, C. S. Oglesby, E. Bucher, D. J. Bishop, T. E. Mason, and K. Mortensen, Small angle neutron scattering study of the magnetic flux-line lattice in single crystal 2 H − NbSe 2 , Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 , 278 (1994) .
- P. G. Kealey, D. Charalambous, E. M. Forgan, S. L. Lee, S. T. Johnson, P. Schleger, R. Cubitt, D. M. Paul, C. M. Aegerter, S. Tajima, and A. Rykov, Transverse-field components of the flux-line lattice in the anisotropic superconductor YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 − δ , Phys. Rev. B 64 , 174501 (2001) .
- C. Rastovski, C. D. Dewhurst, W. J. Gannon, D. C. Peets, H. Takatsu, Y. Maeno, M. Ichioka, K. Machida, and M. R. Eskildsen, Anisotropy of the superconducting state in Sr 2 RuO 4 , Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 , 087003 (2013) .
- S. J. Kuhn, H. Kawano-Furukawa, E. Jellyman, R. Riyat, E. M. Forgan, M. Ono, K. Kihou, C. H. Lee, F. Hardy, P. Adelmann, T. Wolf, C. Meingast, J. Gavilano, and M. R. Eskildsen, Simultaneous evidence for pauli paramagnetic effects and multiband superconductivity in KFe 2 As 2 by small-angle neutron scattering studies of the vortex lattice , Phys. Rev. B 93 , 104527 (2016) .
- P. K. Biswas, M. R. Lees, G. Balakrishnan, D. Q. Liao, D. S. Keeble, J. L. Gavilano, N. Egetenmeyer, C. D. Dewhurst, and D. M. Paul, First-order reorientation transition of the flux-line lattice in CaAlSi , Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 , 077001 (2012) .
- Chang-woo Cho, C. Y. Ng, C. H. Wong, M. Abdel-Hafiez, A. N. Vasiliev, D. A. Chareev, A. G. Lebed, and R. Lortz, Competition between orbital effects, pauli limiting, and Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov states in 2D transition metal dichalcogenide superconductors , New J. Phys. 24 , 083001 (2022) .
- L. J. Campbell, M. M. Doria, and V. G. Kogan, Vortex lattice structures in uniaxial superconductors , Phys. Rev. B 38 , 2439 (1988) .
- S. L. Thiemann, Z. Radović, and V. G. Kogan, Field structure of vortex lattices in uniaxial superconductors , Phys. Rev. B 39 , 11406 (1989) .
- K. Onabe, M. Naito, and S. Tanaka, Anisotropy of upper critical field in superconducting 2 H − NbS 2 , J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 45 , 50 (1978) .
- D. Huang, H. Nakamura, K. Küster, U. Wedig, N. B. M. Schröter, V. N. Strocov, U. Starke, and H. Takagi, Probing the interlayer coupling in 2 H − NbS 2 via soft x-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy , Phys. Rev. B 105 , 245145 (2022) .
- M. Leroux, P. Rodière, L. Cario, and T. Klein, Anisotropy and temperature dependence of the first critical field in 2 H − NbS 2 , Phys. B: Condens. Matter 407 , 1813 (2012) .
- X. Bi, Z. Li, J. Huang, F. Qin, C. Zhang, Z. Xu, L. Zhou, M. Tang, C. Qiu, P. Tang, T. Ideue, T. Nojima, Y. Iwasa, and H. Yuan, Orbital-selective two-dimensional superconductivity in 2 H − NbS 2 , Phys. Rev. Res. 4 , 013188 (2022) .
- R. Cubitt, M. R. Eskildsen, C. D. Dewhurst, J. Jun, S. M. Kazakov, and J. Karpinski, Effects of two-band superconductivity on the flux-line lattice in magnesium diboride , Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 , 047002 (2003) .
- D. K. Christen, F. Tasset, S. Spooner, and H. A. Mook, Study of the intermediate mixed state of niobium by small-angle neutron scattering , Phys. Rev. B 15 , 4506 (1977) .
- G. L. Squires, Introduction to the Theory of Thermal Neutron Scattering , 3rd ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2012).
- V. G. Kogan, London approach to anisotropic type-II superconductors , Phys. Rev. B 24 , 1572 (1981) .
- S. J. Kuhn, W. Morgenlander, E. R. Louden, C. Rastovski, W. J. Gannon, H. Takatsu, D. C. Peets, Y. Maeno, C. D. Dewhurst, J. Gavilano, and M. R. Eskildsen, Anisotropy and multiband superconductivity in Sr 2 RuO 4 determined by small-angle neutron scattering studies of the vortex lattice , Phys. Rev. B 96 , 174507 (2017) .
- A. Yaouanc, P. Dalmas de Réotier, and E. H. Brandt, Effect of the vortex core on the magnetic field in hard superconductors , Phys. Rev. B 55 , 11107 (1997) .
- E. Campillo, M. Bartkowiak, R. Riyat, E. Jellyman, A. S. Cameron, A. T. Holmes, O. Prokhnenko, W.-D. Stein, A. Erb, E. M. Forgan, and E. Blackburn, Deviations from the extended london model at high magnetic fields in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 , Phys. Rev. B 105 , 184508 (2022) .
- M. Tinkham, Introduction to Superconductivity (McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1996).
- A. Tulapurkar, A. Grover, S. Ramakrishnan, A. Niazi, and A. Rastogi, Peak effect studies in 2H- NbS 2 , Phys. B: Condens. Matter 312-313 , 118 (2002) .
- V. G. Kogan, M. A. Tanatar, and R. Prozorov, London penetration depth at zero temperature and near the superconducting transition , Phys. Rev. B 101 , 104510 (2020) .
- Y. Hamaue and R. Aoki, Effects of organic intercalation on lattice vibrations and superconducting properties of 2H- NbS 2 , J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 55 , 1327 (1986) .
- D. A. Chareev, P. Evstigneeva, D. Phuyal, G. J. Man, H. Rensmo, A. N. Vasiliev, and M. Abdel-Hafiez, Growth of transition-metal dichalcogenides by solvent evaporation technique , Cryst. Growth Des. 20 , 6930 (2020) .
- C. Witteveen, K. Gornicka, J. Chang, M. Månsson, T. Klimczuk, and F. O. von Rohr, Polytypism and superconductivity in the NbS 2 system , Dalton Trans. 50 , 3216 (2021) .
- C. D. Dewhurst, I. Grillo, D. Honecker, M. Bonnaud, M. Jacques, C. Amrouni, A. Perillo-Marcone, G. Manzin, and R. Cubitt, The small-angle neutron scattering instrument D33 at the Institut Laue–Langevin , J. Appl. Crystallogr. 49 , 1 (2016) .
- M. Marziali Bermúdez, M. R. Eskildsen, M. Bartkowiak, G. Nagy, V. Bekeris, and G. Pasquini, Dynamic reorganization of vortex matter into partially disordered lattices , Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 , 067001 (2015) .
- C. D. Dewhurst, Graphical reduction and analysis small-angle neutron scattering program: GRASP , J. Appl. Crystallogr. 56 , 1595 (2023) .
- A. Alshemi, E. Blackburn, E. Campillo, R. Cubitt, and E. Forgan, Investigation of the vortex lattice in NbS2—A potential FFLO candidate, Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL), https://doi.ill.fr/10.5291/ILL-DATA.5-42-558 , 2021.
- See Supplemental Material at http://link.aps.org/supplemental/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.033218 for experimental form factor values used in the fitting shown in Fig. 6 .
Sign up to receive regular email alerts from Physical Review Research
- Forgot your username/password?
- Create an account
Article Lookup
Paste a citation or doi, enter a citation.
- AI Resource Center
- Workforce Solutions
- Center For Cybersecurity
- Transfer Students
- Student Portal Login
Closing the Gap: Upskilling and Reskilling in an AI Era
August 26, 2024 – DeVry University released its second annual report, Closing the Gap: Upskilling and Reskilling in an AI Era . In partnership with Reputation Leaders, the research reveals that while employees are more enthusiastic about opportunities for ongoing learning, current employer upskilling and reskilling efforts are not meeting the moment with the right opportunities to reach, engage and train all employees. Read more: 2024 DeVry AI Report
Hessy Fernandez
Director, Public Relations
Email: [email protected]
Michaela Feldmann
Media Relations Specialist
Alicia McClendon
External Media & Content Specialist
Follow DeVry University
Follow Keller Graduate School of Management
About DeVry University
DeVry University strives to close society’s opportunity gap and address emerging talent needs by preparing learners to thrive in careers shaped by continuous technological change. Founded in 1931, the university offers undergraduate and graduate programs onsite and online in Business, Healthcare and Technology. DeVry University is accredited by The Higher Learning Commission (HLC, www.hlcommission.org/ ). The university’s Keller Graduate School of Management is included in this accreditation. To learn more, visit devry.edu .
Degrees & Programs
Tuition & Financial Aid
- Student Experience
About DeVry
By Degree Level
- Individual College Courses
- Undergraduate Certificates
- Graduate Certificates
- Associate Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- "> View All Undergraduate Degrees >
- "> View All Graduate Degrees >
- "> View All Degree Programs >
- Human Resource
- Sales and Marketing
- Project Management
- Master’s of Project Management (MPM)
- Master's of Business Administration (MBA)
- "> View All Business Programs >
- Health Administration
- Health Information Technology
- Health Information Management
- Medical Billing & Coding
- "> View All Health Programs >
- Artificial Intelligence
- Cyber Security
- Engineering Technology
- Media Arts and Technology
- Software and Information Systems
- Website Design Certificate
- "> View All Tech Certificates >
- "> View All Technology Programs >
Keller Graduate School of Management
- Master's of Business Administration
- Master's of Accounting and Finance
- Master's of Human Reosurces
- Master's of Information Technology
- Master's of Project Management
- "> View All Graduate Programs >
Tuition & Expenses
- Understand Tuition Costs & Fees
- Payment Plans
- Student Loans
Paying for College
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship & Grants
- State-funded Programs
- Employer Tuition Assistance
- Military Benefits
- Alumni & Family Tuition Savings
Admissions & Catalogs
- Admissions Overview
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Transfer Applicants
- Working Adult Applicants
- Academic Catalogs
Experience & Information
- Academic Calendar
- Transcript Requests
- Accountability Principles
- Title IX Information
- COVID-19 Updates and Online Resources
- About DeVry University
- Campus Locations
- Accreditation + State Authorization
- Student Testimonials
- Center for Cybersecurity
- " tabindex="0"> View All Undergraduate Degrees >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Graduate Degrees >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Degree Programs >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Business Programs >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Health Programs >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Tech Certificates >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Technology Programs >
- " tabindex="0"> View All Graduate Programs >
- Terms Of Service
- Privacy Policy
- California Employee Privacy Policy
- Careers at DeVry
- Accessibility Statement
- Student Consumer Information
- Student Complaint Procedure
- California State Disclosures
- California School Performance Fact Sheets
- DeVry University California BPPE Annual Report
- California Bureau for Private Postsecondary Education
In New York, DeVry University operates as DeVry College of New York. DeVry University is accredited by The Higher Learning Commission (HLC), www.hlcommission.org . The University’s Keller Graduate School of Management is included in this accreditation. DeVry is certified to operate by the State Council of Higher Education for Virginia. Arlington Campus: 1400 Crystal Dr., Ste. 120, Arlington, VA 22202. DeVry University is authorized for operation as a postsecondary educational institution by the Tennessee Higher Education Commission, www.tn.gov/thec . Lisle Campus: 4225 Naperville Rd, Suite 400, Lisle, IL 60532. Unresolved complaints may be reported to the Illinois Board of Higher Education through the online complaint system https://complaints.ibhe.org/ . View DeVry University’s complaint process https://www.devry.edu/compliance/student-complaint-procedure.html Program availability varies by location. In site-based programs, students will be required to take a substantial amount of coursework online to complete their program.
© DeVry Educational Development Corp. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A research gap is an unanswered question or unresolved problem in a field, which reflects a lack of existing research in that space. The four most common types of research gaps are the classic literature gap, the disagreement gap, the contextual gap and the methodological gap.
Examples of Research Gap. Here are some examples of research gaps that researchers might identify: Theoretical Gap Example: In the field of psychology, there might be a theoretical gap related to the lack of understanding of the relationship between social media use and mental health.
Simply put, a research gap is any space where there's a lack of solid, agreed-upon research regarding a specific topic, issue or phenomenon. In other words, there's a lack of established knowledge and, consequently, a need for further research. Let's look at a hypothetical example to illustrate a research gap.
These are gaps in the conceptual framework or theoretical understanding of a subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand the relationship between two concepts or to refine a theoretical framework. 3. Methodological gaps. These are gaps in the methods used to study a particular subject.
A research gap is a specific area within a field of study that remains unexplored or under-explored. Identifying a research gap involves recognizing where existing research is lacking or where there are unanswered questions that could provide opportunities for further investigation. Understanding research gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge ...
Learn what a research gap is, the different types of research gaps (including examples), and how to find a research gap for your dissertation, thesis or rese...
Identifying a research gap has many potential benefits. 1. Avoid Redundancy in Your Research. Understanding the existing literature helps researchers avoid duplication. This means you can steer clear of topics that have already been extensively studied. This ensures your work is novel and contributes something new to the field.
Research Gap Examples. Identifying research gaps is crucial for pursuing innovative research. There are various types of research gaps that can be found in existing literature. Knowledge gaps. Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn't been studied at all. For example, in the field of psychology, there ...
The following steps can help with optimizing the search process once you decide on the key research question based on your interests. -Identify key terms. -Identify relevant articles based on the keywords. -Review selected articles to identify gaps in the literature. 3.
Though there is no well-defined process to find a gap in existing knowledge, your curiosity, creativity, imagination, and judgment can help you identify it. Here are 6 tips to identify research gaps: 1. Look for inspiration in published literature. Read books and articles on the topics that you like the most.
Literature Gap. The expression "literature gap" is used with the same intention as "research gap.". When there is a gap in the research itself, there will also naturally be a gap in the literature. Nevertheless, it is important to stress out the importance of language or text formulations that can help identify a research/literature gap ...
A research gap is a question or a problem that has not been answered by any of the existing studies or research within your field. Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn't been studied at all. Sometimes you'll find a research gap if all the existing research is outdated and in need of new/updated research ...
Learn how to find an original research gap (and consequently a research topic) as quickly and efficiently as possible. In this step-by-step walkthrough, we'l...
A gap is something that remains to be done or learned in an area of research; it's a gap in the knowledge of the scientists in the field of research of your study. Every research project must, in some way, address a gap-that is, attempt to fill in some piece of information missing in the scientific literature. ... An example gap from Hosaka ...
What is a Research Gap? How to Find and Present a Research Gap - ResearchBeastThe first step of conducting and publishing a study is identifying a previously...
The most obvious way to find a research gap is simply to read and analyse the relevant literature. However, this is easier said than done, as the volume of published literature can be staggering. Fortunately, there are some excellent bibliographic databases, which can speed the process of searching for relevant literature.
A research or literature gap is a problem or unexplored/ underexplored area of the existing research. Or . Choosing a topic, research or subject that has not been answered or explored yet by any other scientist is referred to as a research gap. Let us start with an example; Take a look at the hypothetical closing sentence.
A research gap refers to an unexplored or underexplored area within a particular field of study where there is a lack of existing research or a limited understanding of a specific topic or issue…
A research gap is an area within a field that lacks sufficient information or understanding, highlighting opportunities for further investigation. Identified through literature review, it guides researchers to explore new questions and develop innovative theories. Addressing these gaps advances knowledge and solves real-world problems.
A good research gap is a specific area of knowledge or a problem that has not been adequately addressed or explored in the existing literature. Here are 10 points that are typically considered mandatory in a good research gap: Relevance: The quantitative research gap example should be relevant to the field of study and have practical significance.
The lack of a shared understanding of the goals and process of research may contribute to the frustration that students and instructors often have related to student performance on research or inquiry-based assignments. This free virtual workshop will explore the expert-novice gap in relation to the purpose and process of academic research.
Plans for a $400 million solar cell facility in Colorado have been scrapped just two months after Secretary of State Anthony Blinken highlighted the project as an example of world-leading foreign ...
Undergraduate Research Peter T. Flawn Academic Center (FAC) Room 33 2304 Whitis Ave. Austin, Texas 78712 512-471-7152. Find us on Facebook. Find us on X (formerly Twitter) ... As you get started, it may be helpful to look at examples of finished posters. Below are a number of sample posters created by UT undergraduates. There is a brief ...
The gender gap is inherently a two-sided thing. There's a larger, deeper story that I continue to cover on my beat about what is happening to boys and men in American society. As social ...
If you want to learn how to write 3+ research papers every year, watch this FREE training: https://academicenglishnow.com/3papersayear-optin?utm_source=YouTu...
New benchmark results from AMD, Untether AI, Google, Intel, and Nvidia demonstrate the converging AI silicon performance competition. However, system design, networking, and software make AI sing ...
Although studies have confirmed that future self-continuity impacts the presence of meaning, evidence of cross-cultural consistency remains scarce, and the underlying mechanisms between the two are unclear. To fill this research gap, we conducted two studies using a sample of Chinese college students (N = 631). Study 1 verified the positive predictive effect of future self-continuity on the ...
In late July, NIH's annual update on efforts to address the "Ginther Gap" was published Dr. Marie Bernard, the Chief Officer for Scientific Workforce Diversity (COSWD), and Dr. Mike Lauer, the NIH Deputy Director for Extramural Research. The "Ginther Gap" refers to results from a 2011 study that found a 10 percentage point difference ...
$2H\text{\ensuremath{-}}{\mathrm{NbS}}_{2}$ is a classic example of an anisotropic multiband superconductor, with significant recent work focusing on the interesting responses seen when high magnetic fields are applied precisely parallel to the hexagonal niobium planes. It is often contrasted with its sister compound $2H\text{\ensuremath{-}}{\mathrm{NbSe}}_{2}$ because they have similar onset ...
August 26, 2024 - DeVry University released its second annual report, Closing the Gap: Upskilling and Reskilling in an AI Era.In partnership with Reputation Leaders, the research reveals that while employees are more enthusiastic about opportunities for ongoing learning, current employer upskilling and reskilling efforts are not meeting the moment with the right opportunities to reach ...