

The 7 Types of Dissertations Explained: Which One is Right for You?
Your dissertation is a pretty big deal and likely represents years of hard slog studying your subject of expertise.
But did you know there are 7 different types of dissertation ?

The purpose of this article is to demystify the various types of dissertations you might encounter or choose to undertake during your advanced studies. Armed with this knowledge, you can select the most appropriate methodology and framework for your research interests and academic requirements.
Each type of dissertation serves a different academic purpose and requires a unique approach and structure. In this article, we’ll take a look at these differences in detail, providing clear explanations and examples from a range of academic disciplines. By the end of this article, you should have a thorough understanding of the options available for your dissertation and be better prepared to select a path that aligns with your research goals and academic ambitions.
Remember, regardless of what type of dissertation you ultimately decide to pursue, best dissertation proofreading can make all the difference between a pass and a fail.
7 Types of Dissertation
Empirical dissertations.
So, let’s dive right in with empirical dissertations—arguably the most hands-on type of dissertation out there. If you’re studying a field like psychology, biology, or social sciences, you’re probably going to become very familiar with this approach.
What exactly is an empirical dissertation?
It’s all about gathering data. You’ll be conducting your own experiments, surveys, or observations, making this type extremely engaging (and a bit daunting). Essentially, you’re collecting new data from the world or from people, rather than relying on existing data from other studies.
The structure of an empirical dissertation is pretty straightforward but involves rigorous methodology. Typically, it will include an introduction to set up your SMART research question , a literature review to justify why this question needs answering, a methodology section that details how you’ve gone about your data collection, a results chapter presenting your findings, and a discussion that ties everything back to your research question and explores the implications.
This type of dissertation not only tests your ability to conduct research and analyze data but also challenges you to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. By the end of an empirical dissertation, you should not only have answers to your original questions but also a solid chunk of real-world experience under your belt.
Best suited to: Students who are ready to roll up their sleeves and get their hands dirty.
Theoretical Dissertations
Now, shifting gears, let’s talk about theoretical dissertations. If the empirical dissertation is the hands-on, muddy boots kind of research, the theoretical dissertation is its more contemplative, indoor cousin. Perfect for those of you in fields like philosophy, literature, or certain branches of sociology and psychology, where concrete data might not be the main focus.
What’s the deal with theoretical dissertations? They revolve around developing, exploring, or expanding on existing theories. Instead of collecting new data, you invest your time and effort studying existing research and theoretical frameworks to build an argument or propose a new theory or perspective on an old one.
The structure of a theoretical dissertation generally includes a comprehensive introduction where you lay out your thesis or theory, followed by a detailed literature review that supports and provides the foundation for your thesis. After this, you’ll move into a discussion or analysis section, where you critically analyze your thesis in the light of existing theories and literature. The aim here is to offer a fresh or refined perspective that contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
This type of dissertation is a test of your analytical skills and your ability to synthesize complex ideas into a coherent argument. It’s less about creating new paths and more about mapping the ones already laid out in new ways.
Best suited to: Students who love theory and thrive on crafting arguments.
Case Study Dissertations
Next up, it’s case study dissertations. This type of dissertation is especially attractive if you’re someone who loves storytelling with a purpose or is drawn to in-depth analysis of specific events, individuals, or organizations. It’s a favorite in disciplines like business, education, psychology, and social sciences, where a single case can lead to the development of new theories and concepts.
A case study dissertation involves an intensive investigation of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. You’ll get to the nitty gritty of the specifics, examining various aspects of the case to understand its implications and applications. This method allows you to apply theoretical concepts in a real-world context, providing rich insights that aren’t always accessible through broader surveys or experiments.
The structure of a case study dissertation usually starts with an introduction to the chosen case, followed by a literature review that sets the theoretical framework. You then proceed to a detailed methodology section explaining how you collected and analyzed your data. The core of your dissertation will likely be the case analysis chapter, where you dissect the case in relation to your research question. Finally, you’ll conclude with a discussion of how the case impacts the wider field and what new understandings it brings to the fore.
Best suited to: Those who are meticulous and have a keen eye for detail, a case study dissertation allows you to explore the intricacies of a specific example while contributing to broader academic debates.
Comparative Dissertations
Next up is the comparative dissertation. This type is tailor-made for the analytically minded who love drawing connections and distinctions between different elements. It’s particularly prevalent in fields like law, education, political science, and international relations, where understanding differences and similarities across cases, laws, or educational methods can provide critical insights.
Essentially, a comparative dissertation involves systematically comparing and contrasting two or more entities. These could be policies, theories, populations, or even historical periods, depending on your study area. The goal is to identify patterns or discrepancies that reveal underlying principles or suggest new interpretations of data.
The structure of a dissertation of this nature typically includes a dissertation abstract followed by an introduction that defines the entities being compared and poses your research question. This is followed by a literature review that frames the theoretical bases for comparison. The methodology section should clearly outline the criteria and methods for comparison, ensuring transparency and replicability. The subsequent chapters will then detail the comparative analysis, discussing each entity individually before bringing them together for a comprehensive comparison. Finally, the conclusion synthesizes the findings, highlighting the significance of the differences and similarities discovered.
Best suited to: Those who can juggle multiple themes and variables without losing sight of the overarching question, a comparative dissertation challenges you to remain objective and balanced in your analysis.
Project-Based Dissertations
Project-based dissertations are more practical in nature. This type of dissertation is particularly appealing if you’re inclined towards applying your theoretical knowledge to create something tangible or solve a real-world problem. It’s a common choice in fields like engineering, computer science, and applied arts, where the end product can be a piece of software, an engineering prototype, or a design project.
What makes a project-based dissertation stand out? It centers around a project that you will plan, execute, and manage through the duration of your dissertation process. This could involve designing a new gadget, developing a software program, or creating a marketing plan for a startup. The focus is on applying the skills and knowledge you’ve acquired through your studies to produce a project that has practical and theoretical implications.
The structure of a project-based dissertation generally includes an introduction to the project, its objectives, and its relevance to your field. Following this, you’ll provide a literature review that supports the theories and methodologies you intend to use. The methodology section should detail your project plan, resources, and the processes you will follow. The main body of the dissertation will describe the project development and implementation phases in detail. Finally, the conclusion will evaluate the project’s success, its impact, and potential future developments or applications.
Best suited to: The innovative and the practical, a project-based dissertation allows you to showcase your ability to deliver a concrete outcome that demonstrates your professional capabilities.
Narrative Dissertations
If you’re drawn to writing and storytelling, a narrative dissertation might be right up your alley. This type is particularly popular in fields such as creative arts, literature, and education, where personal narratives or creative elements can be used to explore and communicate complex ideas.
What does a narrative dissertation involve? It’s about crafting a dissertation that primarily uses narrative techniques to convey research findings or explore scholarly questions. This could mean writing in a first-person perspective, incorporating fictional elements, or structuring the dissertation like a series of interconnected stories or essays.
The structure of a narrative dissertation often deviates from the traditional format. It begins with an introduction that sets the stage for the narrative journey. The literature review might be woven into the narrative itself, providing contextual background as the story unfolds. The methodology section explains how narrative methods will be used to explore the research question. The main body is where the narrative takes center stage, presenting research through personal reflections, storytelling, or hypothetical scenarios. The conclusion then ties all narrative threads together, reflecting on the insights gained and their broader implications.
Best suited to: those who think and express themselves best through stories, a narrative dissertation allows you to engage with your topic in a deeply personal and creative way.
Systematic Review Dissertations
Systematic review dissertations are perfect if you’re keen on synthesizing existing research to draw comprehensive conclusions about a specific topic. This type is particularly valuable in fields like healthcare, psychology, and social sciences, where summarizing and evaluating existing studies can provide powerful insights and inform practice and policy.
A systematic review dissertation involves a rigorous and structured approach to reviewing literature. You’ll gather all relevant data from previously published studies to answer a specific research question. The focus is on transparency and reproducibility, employing predefined methods to minimize bias and provide reliable results.
The structure of a systematic review dissertation typically begins with an introduction that outlines the research question and its significance. This is followed by a methodologically detailed section that explains the criteria for selecting studies, the search strategy used, and the methods for data extraction and synthesis. The results section then presents a detailed analysis of the studies included in the review, often using quantitative methods like meta-analysis. The discussion interprets these findings, considering their implications for the field and any limitations. The conclusion suggests areas for further research and summarizes the contributions made by the review.
Best suited to: Those with a keen eye for detail and a systematic approach to research, a systematic review dissertation can significantly impact by clarifying and summarizing existing knowledge.
Methodological Considerations
Choosing the right type of dissertation is an important decision in your academic journey, and several factors should guide your selection. This section aims to help you navigate these choices, ensuring that the methodology and framework you choose align perfectly with your research goals, available resources, and time constraints.
First, consider your discipline’s requirements and norms. Different fields favor different types of dissertations, so understanding what is expected and respected in your area of study is crucial. Next, think about your own strengths and interests. Choose a dissertation type that not only meets academic criteria but also excites you and plays to your strengths, whether they lie in empirical research, theoretical exploration, practical application, or creative expression.
Resource availability is another critical factor. Some types of dissertations, like empirical and project-based, may require access to specific equipment, software, or locations, which can be a deciding factor. Time constraints are also essential to consider; some dissertations, particularly those involving extensive data collection and analysis, may require more time than others.
Finally, discuss your ideas with your advisor or mentor. They can provide valuable insights and feedback that can help you refine your choice and ensure that you are prepared to tackle the challenges ahead. With the right preparation and understanding of what each type of dissertation entails, you can make an informed decision that sets the stage for a successful and rewarding research endeavor.
Leave a Comment
- 1-888-SNU-GRAD
- Daytime Classes

The Top 3 Types of Dissertation Research Explained

Preparing for your doctoral dissertation takes serious perseverance. You’ve endured years of studies and professional development to get to this point. After sleepless nights and labor-intensive research, you’re ready to present the culmination of all of your hard work. Even with a strong base knowledge, it can be difficult — even daunting — to decide how you will begin writing.
By taking a wide-lens view of the dissertation research process , you can best assess the work you have ahead of you and any gaps in your current research strategy. Subsequently, you’ll begin to develop a timeline so you can work efficiently and cross that finish line with your degree in hand.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a published piece of research on a novel topic in your chosen field. Students complete a dissertation as part of a doctoral or PhD program. For most students, a dissertation is the first substantive piece of academic research they will write.
Because a dissertation becomes a published piece of academic literature that other academics may cite, students must defend it in front of a board of experts consisting of peers in their field, including professors, their advisor, and other industry experts.
For many students, a dissertation is the first piece of research in a long career full of research. As such, it’s important to choose a topic that’s interesting and engaging.
Types of Dissertation Research
Dissertations can take on many forms, based on research and methods of presentation in front of a committee board of academics and experts in the field. Here, we’ll focus on the three main types of dissertation research to get you one step closer to earning your doctoral degree.
1. Qualitative
The first type of dissertation is known as a qualitative dissertation . A qualitative dissertation mirrors the qualitative research that a doctoral candidate would conduct throughout their studies. This type of research relies on non-numbers-based data collected through things like interviews, focus groups and participant observation.
The decision to model your dissertation research according to the qualitative method will depend largely on the data itself that you are collecting. For example, dissertation research in the field of education or psychology may lend itself to a qualitative approach, depending on the essence of research. Within a qualitative dissertation research model, a candidate may pursue one or more of the following:
- Case study research
- Autoethnographies
- Narrative research
- Grounded theory
Although individual approaches may vary, qualitative dissertations usually include certain foundational characteristics. For example, the type of research conducted to develop a qualitative dissertation often follows an emergent design, meaning that the content and research strategy changes over time. Candidates also rely on research paradigms to further strategize how best to collect and relay their findings. These include critical theory, constructivism and interpretivism, to name a few.
Because qualitative researchers integrate non-numerical data, their methods of collection often include unstructured interview, focus groups and participant observations. Of course, researchers still need rubrics from which to assess the quality of their findings, even though they won’t be numbers-based. To do so, they subject the data collected to the following criteria: dependability, transferability and validity.
When it comes time to present their findings, doctoral candidates who produce qualitative dissertation research have several options. Some choose to include case studies, personal findings, narratives, observations and abstracts. Their presentation focuses on theoretical insights based on relevant data points.
2. Quantitative
Quantitative dissertation research, on the other hand, focuses on the numbers. Candidates employ quantitative research methods to aggregate data that can be easily categorized and analyzed. In addition to traditional statistical analysis, quantitative research also hones specific research strategy based on the type of research questions. Quantitative candidates may also employ theory-driven research, replication-based studies and data-driven dissertations.
When conducting research, some candidates who rely on quantitative measures focus their work on testing existing theories, while others create an original approach. To refine their approach, quantitative researchers focus on positivist or post-positivist research paradigms. Quantitative research designs focus on descriptive, experimental or relationship-based designs, to name a few.
To collect the data itself, researchers focus on questionnaires and surveys, structured interviews and observations, data sets and laboratory-based methods. Then, once it’s time to assess the quality of the data, quantitative researchers measure their results against a set of criteria, including: reliability, internal/external validity and construct validity. Quantitative researchers have options when presenting their findings. Candidates convey their results using graphs, data, tables and analytical statements.

3. Mixed-Method
Many PhD candidates also use a hybrid model in which they employ both qualitative and quantitative methods of research. Mixed dissertation research models are fairly new and gaining traction. For a variety of reasons, a mixed-method approach offers candidates both versatility and credibility. It’s a more comprehensive strategy that allows for a wider capture of data with a wide range of presentation optimization.
In the most common cases, candidates will first use quantitative methods to collect and categorize their data. Then, they’ll rely on qualitative methods to analyze that data and draw meaningful conclusions to relay to their committee panel.
With a mixed-method approach, although you’re able to collect and analyze a more broad range of data, you run the risk of widening the scope of your dissertation research so much that you’re not able to reach succinct, sustainable conclusions. This is where it becomes critical to outline your research goals and strategy early on in the dissertation process so that the techniques you use to capture data have been thoroughly examined.
How to Choose a Type of Dissertation Research That’s Right for You
After this overview of application and function, you may still be wondering how to go about choosing a dissertation type that’s right for you and your research proposition. In doing so, you’ll have a couple of things to consider:
- What are your personal motivations?
- What are your academic goals?
It’s important to discern exactly what you hope to get out of your doctoral program . Of course, the presentation of your dissertation is, formally speaking, the pinnacle of your research. However, doctoral candidates must also consider:
- Which contributions they will make to the field
- Who they hope to collaborate with throughout their studies
- What they hope to take away from the experience personally, professionally and academically
Personal Considerations
To discern which type of dissertation research to choose, you have to take a closer look at your learning style, work ethic and even your personality.
Quantitative research tends to be sequential and patterned-oriented. Steps move in a logical order, so it becomes clear what the next step should be at all times. For most candidates, this makes it easier to devise a timeline and stay on track. It also keeps you from getting overwhelmed by the magnitude of research involved. You’ll be able to assess your progress and make simple adjustments to stay on target.
On the other hand, maybe you know that your research will involve many interviews and focus groups. You anticipate that you’ll have to coordinate participants’ schedules, and this will require some flexibility. Instead of creating a rigid schedule from the get-go, allowing your research to flow in a non-linear fashion may actually help you accomplish tasks more efficiently, albeit out of order. This also allows you the personal versatility of rerouting research strategy as you collect new data that leads you down other paths.
After examining the research you need to conduct, consider more broadly: What type of student and researcher are you? In other words, What motivates you to do your best work?
You’ll need to make sure that your methodology is conducive to the data you’re collecting, and you also need to make sure that it aligns with your work ethic so you set yourself up for success. If jumping from one task to another will cause you extra stress, but planning ahead puts you at ease, a quantitative research method may be best, assuming the type of research allows for this.
Professional Considerations
The skills you master while working on your dissertation will serve you well beyond the day you earn your degree. Take into account the skills you’d like to develop for your academic and professional future. In addition to the hard skills you will develop in your area of expertise, you’ll also develop soft skills that are transferable to nearly any professional or academic setting. Perhaps you want to hone your ability to strategize a timeline, gather data efficiently or draw clear conclusions about the significance of your data collection.
If you have considerable experience with quantitative analysis, but lack an extensive qualitative research portfolio, now may be your opportunity to explore — as long as you’re willing to put in the legwork to refine your skills or work closely with your mentor to develop a strategy together.
Academic Considerations
For many doctoral candidates who hope to pursue a professional career in the world of academia, writing your dissertation is a practice in developing general research strategies that can be applied to any academic project.
Candidates who are unsure which dissertation type best suits their research should consider whether they will take a philosophical or theoretical approach or come up with a thesis that addresses a specific problem or idea. Narrowing down this approach can sometimes happen even before the research begins. Other times, candidates begin to refine their methods once the data begins to tell a more concrete story.
Next Step: Structuring Your Dissertation Research Schedule
Once you’ve chosen which type of dissertation research you’ll pursue, you’ve already crossed the first hurdle. The next hurdle becomes when and where to fit dedicated research time and visits with your mentor into your schedule. The busyness of day-to-day life shouldn’t prevent you from making your academic dream a reality. In fact, search for programs that assist, not impede, your path to higher levels of academic success.
Find out more about SNU’s online and on-campus education opportunities so that no matter where you are in life, you can choose the path that’s right for you.

Want to learn more about SNU's programs?
Request more information.
Have questions about SNU, our program, or how we can help you succeed. Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will reach out to you soon!
Subscribe to the SNU blog for inspirational articles and tips to support you on your journey back to school.
Recent blog articles.

Career Advancement & Advice
Building Emotional Intelligence: Why Patience is Key to Effective Leadership

Adult Education
Climbing the Business Degree Ladder: Your Path from AAB to MBA at SNU

Emerging Trends in Healthcare Administration to Watch for in 2025

Veteran Students
Campus Spotlight: Southern Nazarene University’s VETS Center
Have questions about SNU or need help determining which program is the right fit? Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will follow-up to answer your questions!
Text With an Enrollment Counselor
Have questions, but want a faster response? Fill out the form and one of our enrollment counselors will follow-up via text shortly!
- Introduction for Types of Dissertations
- Overview of the Dissertation
- Self-Assessment Exercise
- What is a Dissertation Committee
- Different Types of Dissertations
- Introduction for Overview of the Dissertation Process
- Responsibilities: the Chair, the Team and You
- Sorting Exercise
- Stages of a Dissertation
- Managing Your Time
- Create Your Own Timeline
- Working with a Writing Partner
- Key Deadlines
- Self Assessment Exercise
- Additional Resources
- Purpose and Goals
- Read and Evaluate Chapter 1 Exemplars
- Draft an Introduction of the Study
- Outline the Background of the Problem
- Draft your Statement of the Problem
- Draft your Purpose of the Study
- Draft your Significance of the Study
- List the Possible Limitations and Delimitations
- Explicate the Definition of Terms
- Outline the Organization of the Study
- Recommended Resources and Readings
- Purpose of the Literature Review
- What is the Literature?
- Article Summary Table
- Writing a Short Literature Review
- Outline for Literature Review
- Synthesizing the Literature Review
- Purpose of the Methodology Chapter
- Topics to Include
- Preparing to Write the Methodology Chapter
- Confidentiality
- Building the Components for Chapter Three
- Preparing for Your Qualifying Exam (aka Proposal Defense)
- What is Needed for Your Proposal Defense?
- Submitting Your Best Draft
- Preparing Your Abstract for IRB
- Use of Self-Assessment
- Preparing Your PowerPoint
- During Your Proposal Defense
- After Your Proposal Defense
- Pre-observation – Issues to consider
- During Observations
- Wrapping Up
- Recommended Resources and Readings (Qualitative)
- Quantitative Data Collection
- Recommended Resources and Readings (Quantitative)
- Qualitative: Before you Start
- Qualitative: During Analysis
- Qualitative: After Analysis
- Qualitative: Recommended Resources and Readings
- Quantitative: Deciding on the Right Analysis
- Quantitative: Data Management and Cleaning
- Quantitative: Keep Track of your Analysis
- The Purpose of Chapter 4
- The Elements of Chapter 4
- Presenting Results (Quantitative)
- Presenting Findings (Qualitative)
- Chapter 4 Considerations
- The Purpose of Chapter 5
- Preparing Your Abstract for the Graduate School
- Draft the Introduction for Chapter 5
- Draft the Summary of Findings
- Draft Implications for Practice
- Draft your Recommendations for Research
- Draft your Conclusions
- What is Needed
- What Happens During the Final Defense?
- What Happens After the Final Defense?
Different Types of Dissertations Topic 1: Types of Dissertations

Dissertation
Ai generator.

Dissertations are structured documents that present findings, arguments, and conclusions in a formal manner. They demonstrate a student’s ability to conduct independent research, critically evaluate literature, and communicate complex ideas effectively.
What is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a comprehensive research project often pursued at the postgraduate level. It involves extensive study, analysis, and original contributions to a specific field. Dissertations showcase a student’s ability to conduct independent research, critically evaluate literature, and communicate complex ideas effectively.
Pronunciation of Dissertation
- American English Pronunciation : In American English, “dissertation” is pronounced as /ˌdɪs.ərˈteɪ.ʃən/.
- British English Pronunciation : In British English, the pronunciation is /ˌdɪs.əˈteɪ.ʃən/.
- Dis- : This syllable is pronounced with a short “i” sound, like in the word “this”.
- -ser- : The middle syllable is pronounced with a short “e” sound, similar to “set”.
- -tay- : This part is pronounced with a long “a” sound, as in “day”.
- -shun : The final syllable has the “shun” sound, like in “mission”.
- The stress is typically on the second syllable in both American and British English.
- It’s important to enunciate each syllable clearly for correct pronunciation.
Types of Dissertations
- Conducts original research using empirical methods.
- Involves data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Common in scientific and social science disciplines.
- Focuses on analyzing and synthesizing existing literature.
- Examines theories, concepts, or debates within a field.
- May involve a systematic review or meta-analysis.
- Integrates theoretical knowledge with practical application.
- Often found in professional fields like education , business , or healthcare.
- Includes a reflective component on real-world experiences.
- Explores and develops new theories or conceptual frameworks.
- Emphasizes conceptual analysis and argumentation.
- Common in philosophy , theoretical physics , and humanities.
- Combines qualitative and quantitative research approaches.
- Offers a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
- Utilizes both data collection methods for triangulation.
- Focuses on in-depth examination of a specific case or phenomenon.
- Provides detailed insights into real-life contexts .
- Often used in psychology , sociology, and business research.
Dissertation Format
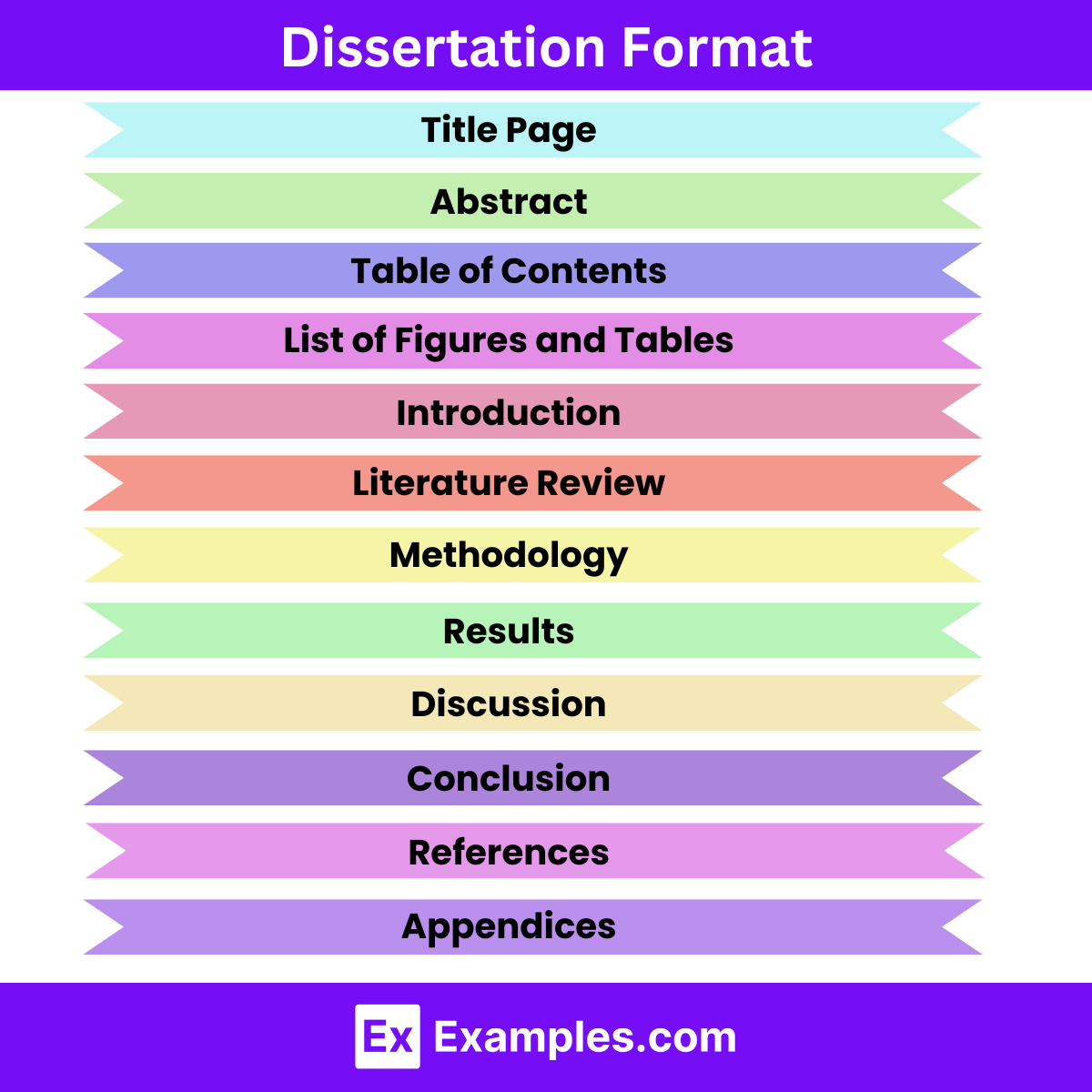
Here’s an overview of the typical format for a dissertation:
- Includes the title of the dissertation, author’s name, institution, department, degree program, date, and possibly the supervisor’s name.
- Provides a concise summary of the dissertation’s purpose, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
- Usually limited to a certain word count or character limit.
- Lists the main sections and subsections of the dissertation with corresponding page numbers.
- Enumerates all figures and tables included in the dissertation, along with their respective page numbers.
- Sets the stage for the research by introducing the topic, context, significance, objectives, and research questions.
- Provides an overview of the structure of the dissertation.
- Surveys relevant literature and theoretical frameworks related to the research topic.
- Analyzes and synthesizes existing research to establish a theoretical foundation for the study.
- Describes the research design, methods, data collection procedures, and analysis techniques used in the study.
- Justifies the chosen methodology and explains how it aligns with the research objectives.
- Presents the findings of the research in a clear and organized manner.
- Includes tables, figures, and descriptive statistics to illustrate the data.
- Interprets the results in relation to the research questions, hypotheses, and theoretical framework.
- Analyzes the implications of the findings and discusses their significance in the broader context of the field.
- Summarizes the main findings and their implications for theory, practice, or policy.
- Reflects on the limitations of the study and suggests directions for future research.
- Lists all the sources cited in the dissertation in a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Includes supplementary materials such as questionnaires, interview transcripts, or raw data.
- Provides additional details that support the main text but are not essential for understanding the dissertation.
Dissertation Topics
Here are some broad categories of dissertation topics, along with examples within each category:
- The impact of technology on student learning outcomes.
- Strategies for improving student engagement in online education.
- The effectiveness of inclusive education programs for students with disabilities.
- Assessing the role of parental involvement in children’s academic achievement.
- Investigating the relationship between teacher motivation and student performance.
- The influence of corporate social responsibility on consumer behavior.
- Strategies for managing workplace diversity and inclusion.
- Analyzing the factors affecting employee job satisfaction and retention.
- The role of leadership styles in organizational change management.
- Exploring the impact of digital marketing on consumer purchase decisions.
- Assessing the effectiveness of telemedicine in improving patient access to healthcare services.
- Investigating the psychological effects of long-term illness on patients and their families.
- Analyzing the factors influencing healthcare professionals’ adoption of electronic health records.
- Exploring the role of preventive healthcare interventions in reducing the prevalence of chronic diseases.
- Assessing the impact of healthcare policies on healthcare equity and access.
- Understanding the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- Investigating the factors influencing public perceptions of climate change and environmental policies.
- Exploring the impact of immigration policies on immigrant integration and social cohesion.
- Analyzing the effects of income inequality on social mobility and economic development.
- Assessing the effectiveness of community-based interventions in reducing crime rates.
- Investigating the adoption and diffusion of renewable energy technologies in developing countries.
- Analyzing the ethical implications of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
- Exploring the role of blockchain technology in revolutionizing supply chain management.
- Assessing the impact of smart city initiatives on urban sustainability and quality of life.
- Investigating the factors influencing consumers’ acceptance of autonomous vehicles.
Synonym & Antonyms For Dissertation
How to write a dissertation.
Writing a dissertation is a comprehensive process that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation:
- Select a topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the requirements of your academic program.
- Ensure the topic is researchable, relevant, and contributes to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
- Conduct a thorough literature review to familiarize yourself with existing research on your topic.
- Identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions that your dissertation can address.
- Develop research questions or hypotheses to guide your study.
- Outline the purpose, scope, objectives, and methodology of your dissertation in a research proposal.
- Seek feedback from your advisor or committee members and revise the proposal accordingly.
- Develop a detailed timeline or schedule for completing each stage of the dissertation writing process.
- Break down tasks into manageable chunks and set deadlines for completing each chapter or section.
- Start with the introduction, which provides background information, states the research objectives, and outlines the structure of the dissertation.
- Proceed to the literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion chapters, following the structure outlined in your proposal.
- Write each chapter systematically, using clear and concise language, and supporting your arguments with evidence from research.
- Review each draft of your dissertation carefully, focusing on clarity, coherence, and logical flow of ideas.
- Edit for grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting errors.
- Seek feedback from your advisor, peers, or academic writing support services, and incorporate suggested revisions.
- Compile all chapters, appendices, tables, figures, and references into a cohesive document.
- Ensure consistency in formatting and citation style throughout the dissertation.
- Proofread the final version to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Submit the finalized dissertation to your advisor or committee for review and approval.
- Prepare for a dissertation defense, where you’ll present your research findings and answer questions from your committee.
- Address any feedback or revisions requested by your committee and finalize the dissertation for submission.
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Examples of dissertation in education.
- Investigating the effectiveness of flipped classroom approaches in enhancing student engagement and academic performance across various subjects.
- Analyzing the correlation between emotional intelligence levels among teachers and their ability to create supportive learning environments and facilitate student success.
- Examining the benefits of parental involvement in early childhood education and identifying effective strategies for promoting collaboration between families and schools.
- Investigating disparities in access to technology resources among students from different socio-economic backgrounds and exploring interventions to bridge the digital divide.
- Assessing the effectiveness of multicultural education programs in fostering cultural competence, diversity awareness, and inclusivity among students in diverse learning environments.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of social-emotional learning (SEL) interventions in promoting mental health, resilience, and well-being among students, teachers, and school staff.
- Identifying barriers to gender equity in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education and exploring strategies to encourage girls’ participation and success in STEM fields.
- Investigating the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of teachers related to assessment and exploring professional development initiatives to improve assessment literacy and enhance student learning outcomes.
- Examining the implementation of inclusive education policies and practices for students with disabilities, including challenges faced, effective strategies, and policy implications for inclusive schooling.
- Analyzing the impact of school leadership practices on teacher professional development, instructional quality, and overall school improvement efforts.
Examples of Dissertation in Psychology
- Investigating the relationship between social media usage patterns and the prevalence of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues among adolescents.
- Examining the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating anxiety disorders and exploring the underlying mechanisms of therapeutic change.
- Assessing the long-term effects of different parenting styles (e.g., authoritarian, authoritative, permissive) on children’s emotional regulation, social skills, and overall development.
- Investigating the neurobiological mechanisms underlying addiction and exploring implications for developing more effective treatment and prevention strategies.
- Examining the factors that contribute to psychological resilience in individuals who have experienced trauma, such as childhood abuse, natural disasters, or combat exposure.
- Investigating the bidirectional relationship between sleep quality and mental health outcomes, including the impact of sleep disturbances on emotional regulation and psychological well-being.
- Comparing cultural differences in the conceptualization and assessment of personality traits, such as individualism-collectivism, and exploring implications for cross-cultural psychology.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions (e.g., mindfulness-based stress reduction, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy) in reducing stress, improving well-being, and enhancing psychological resilience.
- Examining the role of sociocultural factors (e.g., media influence, peer pressure) in shaping body image ideals and exploring interventions to prevent and treat eating disorders.
- Investigating the psychological processes underlying procrastination behavior, including motivational factors, self-regulation strategies, and interventions to promote task completion and productivity.
Examples of Dissertation in literature
- Understanding how stories from countries once colonized talk about who they are and where they fit in the world.
- Checking out how women are shown and what roles they have in old stories from the Victorian times.
- Finding out why scary stories from the past are still popular now and what they’re all about.
- Seeing how heroes are the same in stories from different places and why they’re important to us.
- Learning from stories that care about nature and how writers make us think about protecting the environment.
- Finding out why some new stories are tricky and playful with how they’re written, and what makes them special.
- Understanding how people who lived through terrible events tell their stories, and why it’s important.
- Seeing how Black artists in Harlem made cool stuff and changed how people think about Black culture.
- Exploring stories about moving to new places and how they mix different cultures together.
- Checking out how Shakespeare’s stories get turned into movies and other fun things we like today.
Examples of Dissertation in Politics
- Investigating how different types of political systems, such as democracies and autocracies, influence economic development and growth.
- Analyzing government policies and international agreements aimed at addressing climate change and their effectiveness in mitigating environmental degradation.
- Exploring the rise of populist movements and their impact on political polarization, democratic norms, and institutions.
- Examining the ethical and legal considerations surrounding humanitarian intervention and the protection of human rights in conflict zones.
- Investigating the role of nationalism and identity politics in shaping public attitudes towards immigration, multiculturalism, and social integration.
- Analyzing the effects of globalization on state sovereignty, economic policies, and the balance of power between states and multinational corporations.
- Comparing different electoral systems and their impact on political representation, party competition, and the functioning of democratic institutions.
- Examining the tension between national security concerns and civil liberties, particularly in the context of counterterrorism policies and surveillance practices.
- Assessing the barriers to women’s political participation and representation in decision-making roles, and exploring strategies for achieving gender equality in politics.
- Analyzing the role of the United Nations and other international organizations in addressing global challenges, such as conflict resolution, humanitarian crises, and sustainable development.
What exactly is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a scholarly document that presents original research on a specific topic, typically completed as part of a doctoral program. It demonstrates the candidate’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to their field of study.
How long is a Dissertation?
The length of a dissertation varies widely depending on the academic discipline, program requirements, and research topic. On average, it ranges from 80 to 200 pages, but some dissertations can be shorter or longer based on the depth and scope of the research.
What Do You Write a Dissertation For?
A dissertation is written as a culmination of doctoral studies to demonstrate a candidate’s ability to conduct independent research, contribute new knowledge to their field, and obtain a doctoral degree. It showcases expertise, critical thinking, and scholarly communication skills.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

3 Main Types of Dissertations: Differences and Similarities
We may have qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods in dissertations. This blog will elaborate on quantitative dissertations, qualitative dissertations, and mixed methods dissertations by addressing their similarities and differences.
Dissertation types
We may have qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods in dissertations. Therefore, this blog will elaborate on quantitative dissertations, qualitative dissertations, and mixed methods dissertations by addressing their similarities and differences.
Quantitative dissertations
Using the word quantitative does not mean that the dissertation must have quantitative research methods or statistical analysis techniques. Quantitative research deals with addressing research questions, hypotheses, or both. This research type relates to establishing a research strategy, concluding results, and making inferences. Classic investigations involve replication-based studies, theory-driven research, and data-driven dissertations. Nonetheless, many core characteristics pertain to quantitative dissertations regardless of the particular route you adopt on a quantitative dissertation.
They build on or test theories. These may include adopting an original or comprehensive approach with replication or modification.
They address quantitative research questions and test research hypotheses by rejecting or failure to reject the null hypothesis.
Positivist or post-positivist research paradigms affect them heavily.
They can have descriptive, experimental, quasi-experimental, or relationship-based research designs.
They resort to utilizing probability sampling techniques, generalizing from the sample to a broader population. In contrast, they may have to apply non-probability sampling techniques.
Research methods produce quantitative data (e.g., data sets, laboratory-based methods, questionnaires/surveys, structured interviews, and structured observation).
They depend on statistical analysis techniques while examining the data collected, irrespective of their descriptive or inferential structure.
They check the findings’ reliability and internal and external validity and may provide confidence intervals for the population parameters.
Statements, data, tables, and graphs are used to report their findings addressing each research question, hypothesis, or both.
Conclusions align with the findings, research questions, hypotheses, or both, and theories test or expand on extant ideas or provide insight for future approaches.
Qualitative dissertations
Qualitative dissertations involve qualitative research methods such as unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation. As they use research methods not employed in quantitative dissertations, qualitative research is beyond a choice between research methods. Qualitative research regards the research process differently by establishing research questions, developing and utilizing theory, choosing a research strategy, and presenting and discussing research findings in a substantially unique way. Thus, qualitative dissertations will have a distinct approach, relying on the specific route you adopt (for example, case study research compared to ethnographies). The traditional ways are autoethnography, case study, ethnographies, grounded theory, narrative, and phenomenological research . Nonetheless, whatever path you pursue, many broad characteristics relate to qualitative dissertations:
They are considered emergent designs, implying that the research process, and sometimes even the qualitative research questions you handle, often develop during the dissertation process.
They employ many ways to tackle the theory - sometimes capitalizing on theory to assist the research process; in other times, utilizing it to develop new theoretical insights. They sometimes use both techniques. However, the goal is seldom to test a particular theory from the outset.
Many research paradigms support them, including interpretivism, constructivism, and critical theory.
They pursue research designs that radically affect your choices during the research process and the analysis and discussion of findings. Such research designs substantially vary based on the approach taken, whether autoethnography, case study research, ethnography, grounded theory, narrative research, and phenomenological research.
They employ theoretical sampling - non-probability sampling techniques – to explore cases most fit to address their research questions.
They study people in their natural settings by using multiple research methods. This process generates qualitative data involving unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation.
They interpret the qualitative data from the researcher’s perspective and employ an inductive method to specific themes or abstractions, establishing a holistic/gestalt picture of the study.
They assess their findings’ quality concerning their dependability, confirmability, conformability, and transferability.
They elaborate on their findings primarily using personal accounts, case studies, and narratives. Moreover, they employ other means of describing themes or abstracts, processes, observations, and contradictions to address research questions.
They deliberate the theoretical mainly from the findings via the research questions and deduce tentative conclusions.
Mixed methods dissertations
Many reasons exist to include mixed methods in thesis and dissertations . Mixed methods dissertations use both qualitative and quantitative approaches in research. Although they are increasingly used with a more profound legitimacy, their components have not been adequately addressed. One can better tackle a research question by gathering qualitative and quantitative data, analyzing or interpreting them individually or in combination, and conducting multiple research phases. Thus, it is critical to perform qualitative research to investigate an issue and unearth primary themes before employing quantitative analysis to assess the relationships between them.
Mixed methods often confront challenges because qualitative and quantitative research substantially vary structure-wise. They may even be said to oppose. Hence, when having a mixed methods dissertation, you should be careful about the goals of your research and must decide whether the qualitative or quantitative components are more crucial in philosophical, theoretical, and practical terms and whether they can be combined or kept separate.
Why is editing and proofreading your dissertation or thesis critical?
Editing and proofreading your dissertation is exceedingly crucial . A professional editing and proofreading service has trained, experienced experts with PhD in their fields and will edit your work without prejudice. Their suggestions will make the dissertation or thesis more legible and practical. Another set of eyes can check your dissertation much better than you as they can readily find mistakes or areas that need fine-tuning. In academic writing, editing and proofreading ensure the credibility of the content. Many mistakes concerning grammar, punctuation, syntax, sentence construction and other minor errors are amended. An expert who will amend such mistakes will save time and ensure consistency and error-free writing for your thesis or dissertation.
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
Dissertation Submission Checklist: 5 Important Tips
How to Layout and Format a Dissertation: 10 Tips
How to Choose a Dissertation Editor in 3 Steps
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Get a free quote for dissertation editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
This brief guide elaborates on quantitative dissertations, qualitative dissertations, and mixed methods dissertations by addressing their similarities and differences. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

A good part of any research depends on the right questions asked. If you are asking wrong questions, your entire research may go off track. Therefore, understanding what questions you need to ask is essential for your research. If you are on the way to your research but don’t know how to start framing the right research questions, we have just the right information for you. This article discusses the process of formulating research questions.

One of the major struggles that English speakers and writers suffer from is the different variants of American English and British English. Mistakes regarding these variants are very common that even experts get confused at times. Therefore, if you are struggling with these differences, don’t worry — you are not alone. Now, what you can do is gradually learn more about the two English variants. We assembled a comprehensive guide that highlights the basic differences between American and British English.
Whenever you use words, facts, ideas, or explanations from other works, those sources must be cited. Academic referencing is required when you have copied texts from an essay, an article, a book, or other sources verbatim, which is called quotation. You also need referencing when you use an idea or a fact from another work even if you haven’t used their exact expression.

Choosing a topic for your dissertation or thesis at the end of your master's or doctoral study can become a daunting task. You must select a topic that you find interesting to work on. A dissertation/thesis is a crucial piece of work as it carries enormous credit points at the end of the master's study or postgraduate year. Therefore, you must choose the right and the most suitable topic. Here are some helpful tips for choosing a dissertation and thesis topic that suits you the most.

Writing a thesis can be an overwhelming task for many college and graduate students. Managing all the elements associated with a thesis while ensuring that the quality is not compromised can be challenging. However, what is even more strenuous is deciding on a thesis's layout. "How to structure a thesis" is a question that several final-year students struggle to answer. And understandably so, as all colleges and universities have their guidelines for drafting a thesis. However, there is an immutable structure that's common for every thesis. In this brief guide, we will take a look at this structure and analyze each of its components.

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Tips for Students > Dissertation Explained: A Grad Student’s Guide
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Dissertation Explained: A Grad Student’s Guide
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: March 10, 2020

Higher education is filled with milestones. When completing your PhD , you will be required to complete a dissertation. Even if you’ve heard this word thrown around before, you still may be questioning “What is a dissertation?” It’s a common question, especially for those considering to join or are already in a graduate program. As such, here’s everything you need to know about dissertations.
What is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a written document that details research. A dissertation also signifies the completion of your PhD program. It is required to earn a PhD degree, which stands for Doctor of Philosophy.
A PhD is created from knowledge acquired from:
1. Coursework:
A PhD program consists of academic courses that are usually small in size and challenging in content. Most PhD courses consist of a high amount and level of reading and writing per week. These courses will help prepare you for your dissertation as they will teach research methodology.
2. Research:
For your dissertation, it is likely that you will have the choice between performing your own research on a subject , or expanding on existing research. Likely, you will complete a mixture of the two. For those in the hard sciences, you will perform research in a lab. For those in humanities and social sciences, research may mean gathering data from surveys or existing research.
3. Analysis:
Once you have collected the data you need to prove your point, you will have to analyze and interpret the information. PhD programs will prepare you for how to conduct analysis, as well as for how to position your research into the existing body of work on the subject matter.
4. Support:
The process of writing and completing a dissertation is bigger than the work itself. It can lead to research positions within the university or outside companies. It may mean that you will teach and share your findings with current undergraduates, or even be published in academic journals. How far you plan to take your dissertation is your choice to make and will require the relevant effort to accomplish your goals.
Moving from Student to Scholar
In essence, a dissertation is what moves a doctoral student into becoming a scholar. Their research may be published, shared, and used as educational material moving forwards.
Thesis vs. Dissertation
Basic differences.
Grad students may conflate the differences between a thesis and a dissertation.
Simply put, a thesis is what you write to complete a master’s degree. It summarizes existing research and signifies that you understand the subject matter deeply.
On the other hand, a dissertation is the culmination of a doctoral program. It will likely require your own research and it can contribute an entirely new idea into your field.
Structural Differences
When it comes to the structure, a thesis and dissertation are also different. A thesis is like the research papers you complete during undergraduate studies. A thesis displays your ability to think critically and analyze information. It’s less based on research that you’ve completed yourself and more about interpreting and analyzing existing material. They are generally around 100 pages in length.
A dissertation is generally two to three times longer compared to a thesis. This is because the bulk of the information is garnered from research you’ve performed yourself. Also, if you are providing something new in your field, it means that existing information is lacking. That’s why you’ll have to provide a lot of data and research to back up your claims.
Your Guide: Structuring a Dissertation
Dissertation length.
The length of a dissertation varies between study level and country. At an undergraduate level, this is more likely referred to as a research paper, which is 10,000 to 12,000 words on average. At a master’s level, the word count may be 15,000 to 25,000, and it will likely be in the form of a thesis. For those completing their PhD, then the dissertation could be 50,000 words or more.
Photo by Louis Reed on Unsplash
Format of the dissertation.
Here are the items you must include in a dissertation. While the format may slightly vary, here’s a look at one way to format your dissertation:
1. Title page:
This is the first page which includes: title, your name, department, degree program, institution, and submission date. Your program may specify exactly how and what they want you to include on the title page.
2. Acknowledgements:
This is optional, but it is where you can express your gratitude to those who have helped you complete your dissertation (professors, research partners, etc.).
3. Abstract:
The abstract is about 150-300 words and summarizes what your research is about. You state the main topic, the methods used, the main results, and your conclusion.

4. Table of Contents
Here, you list the chapter titles and pages to serve as a wayfinding tool for your readers.
5. List of Figures and Tables:
This is like the table of contents, but for graphs and figures.
6. List of Abbreviations:
If you’ve constantly abbreviated words in your content, define them in a list at the beginning.
7. Glossary:
In highly specialized work, it’s likely that you’ve used words that most people may not understand, so a glossary is where you define these terms.
8. Introduction:
Your introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance. It’s where readers will understand what they expect to gain from your dissertation.
9. Literature Review / Theoretical Framework:
Based on the research you performed to create your own dissertation, you’ll want to summarize and address the gaps in what you researched.
10. Methodology
This is where you define how you conducted your research. It offers credibility for you as a source of information. You should give all the details as to how you’ve conducted your research, including: where and when research took place, how it was conducted, any obstacles you faced, and how you justified your findings.
11. Results:
This is where you share the results that have helped contribute to your findings.
12. Discussion:
In the discussion section, you explain what these findings mean to your research question. Were they in line with your expectations or did something jump out as surprising? You may also want to recommend ways to move forward in researching and addressing the subject matter.
13. Conclusion:
A conclusion ties it all together and summarizes the answer to the research question and leaves your reader clearly understanding your main argument.
14. Reference List:
This is the equivalent to a works cited or bibliography page, which documents all the sources you used to create your dissertation.
15. Appendices:
If you have any information that was ancillary to creating the dissertation, but doesn’t directly fit into its chapters, then you can add it in the appendix.
Drafting and Rewriting
As with any paper, especially one of this size and importance, the writing requires a process. It may begin with outlines and drafts, and even a few rewrites. It’s important to proofread your dissertation for both grammatical mistakes, but also to ensure it can be clearly understood.
It’s always useful to read your writing out loud to catch mistakes. Also, if you have people who you trust to read it over — like a peer, family member, mentor, or professor — it’s very helpful to get a second eye on your work.
How is it Different from an Essay?
There are a few main differences between a dissertation and an essay. For starters, an essay is relatively short in comparison to a dissertation, which includes your own body of research and work. Not only is an essay shorter, but you are also likely given the topic matter of an essay. When it comes to a dissertation, you have the freedom to construct your own argument, conduct your own research, and then prove your findings.
Types of Dissertations
You can choose what type of dissertation you complete. Often, this depends on the subject and doctoral degree, but the two main types are:
This relies on conducting your own research.
Non-empirical:
This relies on studying existing research to support your argument.
Photo by freddie marriage on Unsplash
More things you should know.
A dissertation is certainly no easy feat. Here’s a few more things to remember before you get started writing your own:
1. Independent by Nature:
The process of completing a dissertation is self-directed, and therefore can feel overwhelming. However, if you approach it like the new experience that it is with an open-mind and willingness to learn, you will make it through!
2. Seek Support:
There are countless people around to offer support. From professors to peers, you can always ask for help throughout the process.
3. Writing Skills:
The process of writing a dissertation will further hone your writing skills which will follow you throughout your life. These skills are highly transferable on the job, from having the ability to communicate to also developing analytical and critical thinking skills.
4. Time Management:
You can work backwards from the culmination of your program to break down this gargantuan task into smaller pieces. That way, you can manage your time to chip away at the task throughout the length of the program.
5. Topic Flexibility:
It’s okay to change subject matters and rethink the point of your dissertation. Just try as much as possible to do this early in the process so you don’t waste too much time and energy.
The Wrap Up
A dissertation marks the completion of your doctoral program and moves you from being a student to being a scholar. While the process is long and requires a lot of effort and energy, you have the power to lend an entirely new research and findings into your field of expertise.
As always, when in the thick of things, remember why you started. Completing both your dissertation and PhD is a commendable accomplishment.
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
In this article
Key Types Of Dissertation Research
- Posted on February 7, 2023
- / Under General
Are you preparing for your doctoral dissertation? Then you’ll agree that it requires serious perseverance. You spent many years on the journey of your professional development and studies. From the sleepless nights to the labor-intensive research and all of the hard work. Everything can be super difficult and daunting. Even with the most outstanding base knowledge, starting a dissertation can be really daunting.
One of the first things that you should understand is that there are different types of dissertations, and this article will focus on three of the main types of dissertations that you should know, especially for a doctoral degree.
Qualitative Dissertation
This is the first type that you should know, and it basically mirrors qualitative research that a student will help people throughout their academic journey. The research utilizes non-number-based data collection that is done through focus groups, participant observations, and interviews. Also, the data you collect is the main factor that determines whether you model your dissertation according to the qualitative method.

Another key thing to note is that there are different aspects of the qualitative dissertation, and this includes the following:
- Grounded theory
- Narrative research
- Autoethnographic
- Case study research
As mentioned earlier, a qualitative dissertation does not involve numerical data, so the method of collecting data is usually based on participant observation, focus groups, and unstructured interviews. However, the researcher will also need rubrics to help them assess the quality of their findings.
Quantitative Dissertation
This type of dissertation focuses on numbers, and it uses quantitative research methods to aggregate data so that they can be analyzed and categorized. Apart from the conventional statistical analysis, it’s important to note that quantitative research also uses key strategies that depend on the type of questions asked. This type of dissertation can also employ the use of replication-based studies, data-driven dissertations, and theory-driven research.
When performing this type of research, candidates can utilize quantitative measures that allow them to test different theories, even as they try to make their approach original. Another thing worth noting is that quantitative dissertations focus on post-positivist and positivist research paradigms. The focus is also on experimental, relationship-based, or descriptive designs.
Surveys, data sets, structured interviews and observations, questionnaire, and lab-based testing methods do data collection. In addition, qualitative researchers also measure results based on criteria like construct validity, internal validity, external validity, and reliability.
Mixed-Method Dissertation
The hybrid method is also a strategy that is commonly used by most researchers. This is a mix of both the qualitative and quantitative dissertation methods mentioned above. However, this is a relatively new option, and it’s still gaining popularity. The main benefit of this approach is that it offers more credibility and versatility. Also, it’s a more comprehensive approach that makes it possible for researchers to obtain a wider array of information and a larger range of optimization.
Most candidates prefer to collect data first with quantitative methods and categorize the data. After that, they proceed to collect data using qualitative methods and analyze the collected data. With that, they can start drawing meaningful conclusions about the collected data.
The mixed-method approach allows candidates to collect and analyze more data. With this, they can easily increase the scope of their dissertation and reach a more sustainable and succinct conclusion. If you’re using this form of dissertation, one of the most important things you’ll need to do is to make an outline of your research goals and strategy, and this should be as early as possible, especially at the beginning of the dissertation process. With that, you can easily capture only the data that you need.
- What Steps Should Take to Get My Website Ranked Higher in Search Engine Results?
- Reasons Why Search Engine Optimization Is Important For Your Site
What is Dissertation Writing? Types, Structure, and Academic Impact
If you’ve ever been on a journey through higher education, you know the massive hurdle known as dissertation writing. But really, what is dissertation? At its core, a dissertation is a comprehensive research paper…dissertation is an extended research piece submitted as part of a Ph.D., Master’s, or sometimes even undergraduate degree. It’s an opportunity to show off your research skills, critical thinking, and your ability to add to your field of study. The keyword here is “add”—a dissertation isn’t just about rehashing what others have said; it’s about contributing something new. Let’s break down the types, structure, and academic impact of dissertations to give you a clear sense of what you’re dealing with.
What Exactly is Dissertation Writing?
Dissertation writing goes beyond a typical research paper. It’s an in-depth academic work that demands a structured argument, original research, and extensive analysis. For many students, it’s the first time they dive deep into one specific area, crafting a piece of research that they can call their own. It takes time, patience, and often a lot of coffee!
The process of writing a dissertation starts with selecting a topic, followed by crafting research questions, conducting literature reviews, gathering data, and finally analyzing it all to draw conclusions. Since dissertations are often one of the last assignments before graduation, they carry significant academic weight.
Types of Dissertations
When exploring what is dissertation in various academic fields, understanding the type you’ll undertake is essential.. Different types call for different approaches and methodologies, often dependent on your field of study. Knowing the type of dissertation expected of you can help clarify your path and ensure you’re equipped with the right tools for the journey. Below are the most common types of dissertations.
1. Empirical Dissertations
When considering what is dissertation, empirical research dissertations stand out for their reliance on primary data, meaning you gather your own data through experiments, surveys, or interviews. Common in fields like psychology, sociology, and biology, this type of dissertation allows researchers to work directly with real-world data to investigate their research questions. The goal here is to apply scientific or systematic methods to produce data that you can analyze, leading to conclusions that answer specific questions. Empirical dissertations require meticulous planning around data collection, ethical considerations, and precise measurement tools. Because this method relies on direct observations or experiments, it demands time, resources, and a clear understanding of data analysis methods to ensure findings are valid and credible.
2. Non-Empirical (Theoretical) Dissertations
For students asking what is dissertation, theoretical dissertations take a different approach, relying solely on secondary data rather than primary research. Instead of conducting experiments or surveys, this type of dissertation involves analyzing existing research, theories, and frameworks. This method is often chosen in fields like literature, philosophy, and history, where the focus lies on exploring and synthesizing past research and theoretical frameworks. A non-empirical dissertation allows you to build on and challenge existing knowledge by comparing different perspectives, theories, and interpretations. However, to succeed with this approach, you must have strong critical thinking skills and a comprehensive understanding of existing literature, as it requires you to add unique interpretations or highlight overlooked connections within previous research.
3. Narrative Dissertations
A narrative dissertation is structured more like a story and often follows a chronological order. This type of dissertation is especially popular in social sciences, where researchers may document a case study or even a life story to explore certain facets of human behavior or social structures. Using storytelling techniques, narrative dissertations aim to make complex topics accessible and relatable. In these dissertations, researchers often delve into personal experiences or case histories to create a coherent narrative that not only informs but also engages readers on a deeper level. The narrativ e approach requires a strong storytelling skill, as you’ll need to keep readers’ interest while delivering insights drawn from a personal or historical context.
4. Case Study Dissertations
Case study dissertations focus on analyzing a specific instance or example to answer broader research questions. This approach is common in fields like business, education, and law, where examining a single case can offer valuable insights into a larger issue. Case study dissertations require you to choose a case that represents the phenomenon you’re studying and then thoroughly investigate it from multiple angles. By analyzing one specific example, you can gain in-depth insights, providing a focused look that reveals patterns or answers within the research. These dissertations are ideal for situations where a larger study might be impractical or unnecessary. However, the researcher must be careful in drawing general conclusions from a single case, as it may not fully represent broader trends.
5. Mixed-Methods Dissertations
Sometimes, using just one research method doesn’t suffice. Mixed-methods dissertations combine both qualitative and quantitative research approaches, aiming to provide a more comprehensive view of the research question. For example, a mixed-methods dissertation might include surveys to gather quantitative data alongside interviews to gather qualitative insights. This type of dissertation offers a balanced approach, allowing researchers to cross-validate findings and draw richer conclusions. Mixed-methods dissertations can be especially useful in complex studies where understanding both numerical data and personal experiences provides a more holistic understanding. However, this approach requires skill in managing and integrating both types of data, which can be challenging but rewarding.
Structure of a Dissertation
Now that you know the different types of dissertations, let’s talk about the essential structure. The specific format of a dissertation may vary based on university guidelines or field of study, but generally, dissertations follow a similar structure that ensures clarity and flow.
1. Title Page
The title page is the first page of your dissertation and includes the title, your name, institution, and submission date. While it may seem straightforward, the title page is significant as it sets the stage for your entire document. This page is often required to follow a specific layout and may also include details like your advisor’s name, program name, and sometimes the department. Although it’s simple, a well-organized title page signals a professional and carefully prepared document, making a good first impression.
2. Abstract
The abstract is a concise summary of your dissertation, usually between 150 and 300 words. It highlights the research question, methodology, main findings, and conclusions, giving readers an overview of your work. Despite being short, the abstract is often one of the last sections written because it’s easier to capture the essence of your work after completing it. The abstract is crucial because it provides a snapshot for readers, helping them decide if the study aligns with their interests.
3. Table of Contents
The table of contents is a roadmap for readers, listing all major sections and subsections with page numbers. It helps readers navigate the document efficiently, allowing them to locate specific chapters or topics easily. If your dissertation includes tables, figures, or appendices, these are often listed separately in the table of contents. A well-structured table of contents not only enhances readability but also gives your work a polished look, showing that you’ve organized the content thoughtfully.
4. Introduction
The introduction introduces the topic, research questions, and the significance of your study. This section sets up the context of your research, explaining why this topic matters and what you aim to achieve. It often includes background information to help readers understand the basis of your research questions. The introduction should be engaging, as it serves as the first substantial part of the dissertation where you can establish your argument and the importance of your study.
5. Literature Review
The literature review is where you analyze and summarize existing research relevant to your topic. This section demonstrates your understanding of the research landscape, showing that you’ve thoroughly explored past studies, theories, and models. By identifying gaps in existing literature, you justify your research, positioning it as a valuable contribution. The literature review is typically one of the longest sections and requires critical thinking to synthesize and evaluate different sources.
6. Methodology
The methodology section outlines the research methods you used, explaining the rationale behind them. Whether you’re using surveys, experiments, or secondary data, this section covers the techniques, tools, and processes you employed to gather data. A clear methodology allows future researchers to replicate your study, enhancing its validity and reliability. This section is critical in establishing transparency in your research, as it provides details on how your data was collected and analyzed.
The results section presents the data and findings of your research without interpretation. Here, you display your findings clearly, often using tables, graphs, or charts to make the data more accessible. This section is factual, focusing solely on what the data reveals. For complex research, results may be divided into subsections to organize information according to themes or research questions.
8. Discussion
The discussion is where you interpret the results, connecting them to your research questions and the literature review. This section is your opportunity to analyze the data, answer your research questions, and explain the broader implications of your findings. By comparing your results with existing studies, you can highlight the significance of your work and offer insights into what it means for the field. A strong discussion demonstrates the depth of your understanding and critical thinking.
9. Conclusion
The conclusion wraps up the dissertation, summarizing the key findings, discussing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. This section gives readers a final overview of your study, reinforcing your main points and highlighting the contributions your work makes to the academic field. A well-crafted conclusion leaves a lasting impression and provides closure to your argument.
10. References
The references section lists all sources cited in your dissertation, following a specific citation style. Accurate referencing is vital for academic integrity, as it acknowledges the work of other researchers and helps readers verify your sources. Some dissertations also include appendices for supplementary material, such as survey questions, additional data, or detailed calculations. By including these elements in your dissertation structure, you create a comprehensive, organized document that not only answers your research questions but also contributes meaningfully to the academic community.
Importance of Dissertation Writing in Academia
Writing a dissertation isn’t just a hoop to jump through; it has a lasting impact on your academic and professional life. Here’s why it matters:
1. Skill Development
Completing a dissertation hones several skills, including critical thinking, research abilities, time management, and writing. These skills aren’t limited to academia; they’re valuable in nearly any career path. By tackling such a complex project, you prove to yourself and future employers that you can handle challenging tasks.
2. Contribution to Knowledge
Every dissertation contributes something new to the academic field, no matter how small. Even if your findings seem modest, they add value by addressing unanswered questions or exploring new angles. In some cases, groundbreaking dissertations can even change the way people think about a topic.
3. Academic Recognition
Successfully completing a dissertation can open doors to further academic opportunities, such as publications, conferences, and networking with experts in your field. It establishes you as a knowledgeable voice, which can be especially useful if you plan on pursuing a career in academia.
Common Challenges in Dissertation Writing
Let’s not sugarcoat it—writing a dissertation is hard. But knowing the typical hurdles can help you prepare:
- Procrastination: The project is huge, and starting can feel overwhelming. Breaking it down into manageable sections can make the process less intimidating.
- Writer’s Block: Many students hit a wall during the writing process. Taking regular breaks, setting small goals, and discussing ideas with peers can help you stay motivated.
- Data Collection Issues: If you’re working with empirical research, collecting reliable data can be challenging. Planning ahead and having backup options can save time and stress.
- Time Management: Balancing a dissertation with other responsibilities is tough. A realistic schedule with milestones can keep you on track without feeling overloaded.
- Length and Depth : The required length of a dissertation can vary greatly by program and field but is often between 10,000 and 80,000 words. Knowing your target length early helps in planning your research scope and writing time. Aiming for depth without excessive length ensures your arguments remain focused, manageable, and engaging for readers.
Wrapping Up: The Road Ahead
So, what is dissertation writing? In short, it’s a rewarding but challenging academic journey that can shape your future. While each dissertation is unique, understanding the different types, structures, and academic impacts can help you approach the task with confidence. It’s a lot of work, but when done well, a dissertation can become a meaningful contribution to your field and a significant achievement in your academic life.
You may also like

Top 20 Most Famous Motivational Speakers

100+ Adjectives That Start With J

100+ Adjectives That Start With I
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Exams Know-how
What Is a Dissertation: Types & Tips on How to Write

Imagine embarking on the challenging journey of writing a dissertation – a task that marks the pinnacle of your academic pursuits. A dissertation isn't just another academic assignment; it's a substantial and original research endeavour typically undertaken at the postgraduate or doctoral level. This scholarly achievement plays several pivotal roles within academia, primarily showcasing your mastery of your chosen field. It also assesses your ability to contribute new insights to it.
Unlike shorter academic tasks, a dissertation demands an exhaustive and systematic exploration of a specific research question or topic. You'll delve into extensive literature reviews, gather and analyse data, and draw meaningful conclusions.
A dissertation is more than an academic challenge; it's a significant milestone in your academic journey, signifying your transition from a knowledge consumer to a knowledge creator. As the dissertation author, one has to delve deeply into the existing body of knowledge, identifying gaps and questions that require investigation. A dissertation proves your intellectual rigour, dedication, and contribution to the broader academic conversation. Yocket aims to guide you through this blog for an in-depth exploration of the various facets of a dissertation. Keep reading!
What is a Dissertation ?
Your dissertation represents the pinnacle of your academic journey, demonstrating your dedication, critical thinking abilities, and aptitude for conducting meaningful research. It's not just a requirement but a significant contribution to your field and the broader academic community. Let’s delve into some of the essential aspects of a dissertation and why you need it :
- Original Research: Your dissertation is centered around original research. You'll delve deeply into a specific research question or topic, often involving experiments, surveys, data analysis, or comprehensive literature reviews.
- In-Depth Analysis: Unlike shorter assignments, a dissertation requires thoroughly and systematically exploring your chosen subject. This involves an extensive examination of existing literature, meticulous data collection and analysis, and developing well-substantiated arguments.
- Structured Format: Dissertations follow a specific structure on how to write it . It typically includes chapters like an introduction, literature review, methodology, data analysis, discussion, and conclusion. Each section has a specific purpose, conveying your research process and findings.
- Contributing to Knowledge: Your dissertation should contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field. It's expected to provide new insights, theories, or perspectives that advance understanding in your study area.
- Academic Integrity: Dissertations must uphold the highest academic standards. This means adhering to rigorous research methods, ethical guidelines, and proper citation practices to avoid plagiarism.
- Independence and Initiative: While you'll receive guidance and mentorship, your dissertation primarily results from your independent work. You'll need to take the initiative in designing your research, gathering data, and writing the document.
- Evaluation and Defense: In many educational institutions, you'll defend your dissertation before a committee of experts. This oral defence lets you explain and justify your research methods, findings, and conclusions.
- Publication Potential: Exceptional dissertations can often be published in academic journals or as books, further contributing to the scholarly community.
What are the Types of a Dissertation?
There are mainly two types of dissertations. They are:
- Empirical dissertation
- Non-empirical dissertation
Let’s explore more about the types of dissertations in a detailed manner:
Empirical Dissertation
In your postgraduate degree, you’ll encounter empirical dissertations that involve collecting data, possibly requiring you to follow professional and ethical guidelines when gathering information from the public. If you’re studying natural or life sciences, your dissertation may revolve entirely around laboratory work.
This type of dissertation is known as an empirical dissertation. Such a dissertation strongly emphasises your ability to collect and systematically analyse fresh data. Your research methods might involve conducting experiments, surveys, observations, or fieldwork to gather original data.
Non-Empirical Dissertation
In the case of non-empirical dissertations, you'll be building your work upon existing data and arguments presented by others. This likely means dedicating much time to extensive reading and research.
Non-empirical dissertations, in contrast to empirical ones, do not entail the collection of new data. Instead, they thoroughly examine and evaluate pre-existing literature, theories, concepts, or case studies.
What are the Skills and Strategies Required for a Dissertation?
Irrespective of the type of dissertation you undertake and the topic you select, you will be required to demonstrate the following set of skills:
- Defining and delineating a specific research area accompanied by a well-formed research question.
- Discerning the primary issues related to your chosen subject.
- Sourcing pertinent information from various sources.
- Scrutinising the reliability and credibility of the information gathered.
- Analysing evidence from multiple perspectives within a given debate.
- Formulating a well-structured and well-argued conclusion.
- Effectively organise and present your research findings in a critical, persuasive, and articulate manner while adhering to the prescribed formatting guidelines for your paper.
What is the Word Strength for a Dissertation?
The word count for a dissertation can vary depending on your university's guidelines. Normally, for -
- For undergraduate dissertations, it ranges from 10,000 to 20,000 words.
- For master's degree holders, it is typically 20,000 to 50,000 words.
- For PhD dissertation scholars, it is 100,000 words.
Learn how you can apply for PhD in USA .
Tips and Tricks for a Good Dissertation
To perform well in your dissertation, Yocket breaks down a series of effective tips and tricks for writing a good dissertation :
- Choose a Manageable Topic - Select a focused and research-worthy topic that interests you.
- Start Early - Begin your research and writing in advance to allow for thorough planning and revisions.
- Create a Structured Plan - Develop a clear outline or plan to guide your research and writing process.
- Conduct Comprehensive Research - Review relevant literature and sources using academic databases and libraries.
- Consult Your Supervisor - Regularly communicate with your advisor for guidance and feedback.
- Maintain Clear Structure - Ensure your dissertation has a logical and well-organized structure.
- Craft a Cohesive Thesis - Develop a clear and coherent thesis statement that guides your dissertation.
- Proofread and Edit - Carefully review and edit your work for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors.
- Follow Formatting Guidelines - Consistently adhere to your institution's formatting guidelines and citation styles.
- Stay Persistent and Motivated - Maintain your motivation by setting achievable goals and persistently working toward them.
A dissertation transcends being merely a document; it stands as a symbol of the author's intellectual journey and capacity to contribute significantly to the collective knowledge of their field. It signifies the culmination of academic pursuits and marks the commencement of a new chapter as a researcher and scholar. A dissertation represents a significant intellectual endeavour and a milestone in a graduate student's academic journey. It contains months, or even years, of rigorous research, analysis, and critical thinking. The dissertation stands as a reflection of the author's intellectual curiosity, their ability to formulate research questions, and their unwavering commitment to seeking answers. The growth as a scholar is evident throughout the dissertation. So, prepare diligently for your dissertation with Yocket premium and radiate brilliance!
Frequently Asked Question about What is a Dissertation
1. What is a dissertation vs thesis?
A thesis involves the presentation of acquired knowledge, while the purpose of a dissertation is to create and defend an original concept with theoretical and practical evidence.
2. How long is a dissertation?
A dissertation is about 100-200 pages long.
3. Does a PhD do a thesis or a dissertation?
A PhD scholar does a dissertation, whereas graduate students pursuing a master's do a thesis.
4. What are the two types of a dissertation?
The two types of a dissertation are: Empirical Non-empirical

Sumeet Jain
More Topics
Top Premium Admits
Columbia University
Yocketers Admitted
Scholarships granted

Sharwari Bhosale
Cornell University

Atharva Thodge
Johns Hopkins University

Kaustubh Rai
University of Washington

Neeharika Eddula
University of Pennsylvania

John Harshith
University of Toronto

Meghamala Dash
New York University

Shravan Khunti
Duke University

Varun Bhardwaj
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor

Romil Gupta
University of California, San Diego

Harshit Timmanagoudar
University of California, Los Angeles

Prateeka Rawat
The University of Chicago

Northwestern University

The University of Edinburgh

Nandita Shekar
Articles you might like
The Indian Dream To Go For Higher Studies Abroad?
Hold all the aces before you depart for your higher studies
What After SAT / ACT Exam? | Things to do for Studies Abroad
Upcoming Events
Scholarships and Other Funding Strategies 2025
June 15th, 7:00 pm IST | 1hr
Fireside chat with Brown uni admitted student
June 21st, 3:00 pm IST | 1hr
Looking for Funding options: Scholarships, RA & TA are the way forward!
July 2nd, 5:00 pm IST | 1hr

IMAGES
COMMENTS
May 1, 2024 · This type of dissertation is particularly appealing if you’re inclined towards applying your theoretical knowledge to create something tangible or solve a real-world problem. It’s a common choice in fields like engineering, computer science, and applied arts, where the end product can be a piece of software, an engineering prototype, or a ...
Aug 23, 2021 · Learn about the three main types of dissertation research: qualitative, quantitative and mixed-method. Find out how to choose the best approach for your doctoral program based on your personal and academic goals.
Mar 26, 2016 · Even if the focus of your dissertation is on using data, don’t forget that you’re still going to need a sound theoretical basis for your work. Non-empirical dissertations. Making the choice to do a non-empirical dissertation shouldn’t be taken lightly. Sustaining an argument over the length of your whole dissertation is a distinct challenge.
The implications for you about the type of dissertation you use appear in the method you use to explore your research question and in the structure of the dissertation document, itself. While the three types vary from one another in method, the problem solving approach also varies from the other two in written format.
Aug 27, 2024 · Mixed Methods Dissertation: Combines qualitative and quantitative research approaches. Offers a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. Utilizes both data collection methods for triangulation. Case Study Dissertation: Focuses on in-depth examination of a specific case or phenomenon. Provides detailed insights into real-life contexts.
Jul 19, 2022 · Dissertation types. We may have qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods in dissertations. Therefore, this blog will elaborate on quantitative dissertations, qualitative dissertations, and mixed methods dissertations by addressing their similarities and differences. Quantitative dissertations
Mar 10, 2020 · Not only is an essay shorter, but you are also likely given the topic matter of an essay. When it comes to a dissertation, you have the freedom to construct your own argument, conduct your own research, and then prove your findings. Types of Dissertations. You can choose what type of dissertation you complete.
Feb 7, 2023 · Quantitative Dissertation . This type of dissertation focuses on numbers, and it uses quantitative research methods to aggregate data so that they can be analyzed and categorized. Apart from the conventional statistical analysis, it’s important to note that quantitative research also uses key strategies that depend on the type of questions asked.
Oct 27, 2024 · Structure of a Dissertation. Now that you know the different types of dissertations, let’s talk about the essential structure. The specific format of a dissertation may vary based on university guidelines or field of study, but generally, dissertations follow a similar structure that ensures clarity and flow.
Oct 18, 2023 · This type of dissertation is known as an empirical dissertation. Such a dissertation strongly emphasises your ability to collect and systematically analyse fresh data. Your research methods might involve conducting experiments, surveys, observations, or fieldwork to gather original data. Non-Empirical Dissertation