Economics Essay Examples


Ace Your Essay With Our Economics Essay Examples
Published on: Jun 6, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to understand economics essays and how to write your own?
It can be challenging to grasp the complexities of economic concepts without practical examples.
But don’t worry!
We’ve got the solution you've been looking for. Explore quality examples that bridge the gap between theory and real-world applications. In addition, get insightful tips for writing economics essays.
So, if you're a student aiming for academic success, this blog is your go-to resource for mastering economics essays.
Let’s dive in and get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Economics Essay?
An economics essay is a written piece that explores economic theories, concepts, and their real-world applications. It involves analyzing economic issues, presenting arguments, and providing evidence to support ideas.
The goal of an economics essay is to demonstrate an understanding of economic principles and the ability to critically evaluate economic topics.
Why Write an Economics Essay?
Writing an economics essay serves multiple purposes:
- Demonstrate Understanding: Showcasing your comprehension of economic concepts and their practical applications.
- Develop Critical Thinking: Cultivating analytical skills to evaluate economic issues from different perspectives.
- Apply Theory to Real-World Contexts: Bridging the gap between economic theory and real-life scenarios.
- Enhance Research and Analysis Skills: Improving abilities to gather and interpret economic data.
- Prepare for Academic and Professional Pursuits: Building a foundation for success in future economics-related endeavors.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
If youâre wondering, âhow do I write an economics essay?â, consulting an example essay might be a good option for you. Here are some economics essay examples:
Short Essay About Economics
Fiscal policy plays a crucial role in shaping economic conditions and promoting growth. During periods of economic downturn or recession, governments often resort to fiscal policy measures to stimulate the economy. This essay examines the significance of fiscal policy in economic stimulus, focusing on two key tools: government spending and taxation. Government spending is a powerful instrument used to boost economic activity. When the economy experiences a slowdown, increased government expenditure can create a multiplier effect, stimulating demand and investment. By investing in infrastructure projects, education, healthcare, and other sectors, governments can create jobs, generate income, and spur private sector activity. This increased spending circulates money throughout the economy, leading to higher consumption and increased business investments. However, it is important for governments to strike a balance between short-term stimulus and long-term fiscal sustainability. Taxation is another critical aspect of fiscal policy. During economic downturns, governments may employ tax cuts or incentives to encourage consumer spending and business investments. By reducing tax burdens on individuals and corporations, governments aim to increase disposable income and boost consumption. Lower taxes can also incentivize businesses to expand and invest in new ventures, leading to job creation and economic growth. However, it is essential for policymakers to consider the trade-off between short-term stimulus and long-term fiscal stability, ensuring that tax cuts are sustainable and do not result in excessive budget deficits. In conclusion, fiscal policy serves as a valuable tool in stimulating economic growth and mitigating downturns. Through government spending and taxation measures, policymakers can influence aggregate demand, promote investment, and create a favorable economic environment. However, it is crucial for governments to implement these policies judiciously, considering the long-term implications and maintaining fiscal discipline. By effectively managing fiscal policy, governments can foster sustainable economic growth and improve overall welfare. |
A Level Economics Essay Examples
Here is an essay on economics a level structure:
Globalization, characterized by the increasing interconnectedness of economies and societies worldwide, has brought about numerous benefits and challenges. One of the significant issues associated with globalization is its impact on income inequality. This essay explores the implications of globalization on income inequality, discussing both the positive and negative effects, and examining potential policy responses to address this issue. Globalization has had a profound impact on income inequality, posing challenges for policymakers. While it has facilitated economic growth and raised living standards in many countries, it has also exacerbated income disparities. By implementing effective policies that focus on education, skill development, redistribution, and inclusive growth, governments can strive to reduce income inequality and ensure that the benefits of globalization are more widely shared. It is essential to strike a balance between the opportunities offered by globalization and the need for social equity and inclusive development in an interconnected world. |
Band 6 Economics Essay Examples
Government intervention in markets is a topic of ongoing debate in economics. While free markets are often considered efficient in allocating resources, there are instances where government intervention becomes necessary to address market failures and promote overall welfare. This essay examines the impact of government intervention on market efficiency, discussing the advantages and disadvantages of such interventions and assessing their effectiveness in achieving desired outcomes. Government intervention plays a crucial role in addressing market failures and promoting market efficiency. By correcting externalities, providing public goods and services, and reducing information asymmetry, governments can enhance overall welfare and ensure efficient resource allocation. However, policymakers must exercise caution to avoid unintended consequences and market distortions. Striking a balance between market forces and government intervention is crucial to harness the benefits of both, fostering a dynamic and efficient economy that serves the interests of society as a whole. |
Here are some downloadable economics essays:
Economics essay pdf
Economics essay introduction
Economics Extended Essay Examples
In an economics extended essay, students have the opportunity to delve into a specific economic topic of interest. They are required to conduct an in-depth analysis of this topic and compile a lengthy essay.
Here are some potential economics extended essay question examples:
- How does foreign direct investment impact economic growth in developing countries?
- What are the factors influencing consumer behavior and their effects on market demand for sustainable products?
- To what extent does government intervention in the form of minimum wage policies affect employment levels and income inequality?
- What are the economic consequences of implementing a carbon tax to combat climate change?
- How does globalization influence income distribution and the wage gap in developed economies?
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
Economics Extended Essay Topic Examples
Extended Essay Research Question Examples Economics
Tips for Writing an Economics Essay
Writing an economics essay requires specific expertise and skills. So, it's important to have some tips up your sleeve to make sure your essay is of high quality:
- Start with a Clear Thesis Statement: It defines your essay's focus and argument. This statement should be concise, to the point, and present the crux of your essay.
- Conduct Research and Gather Data: Collect facts and figures from reliable sources such as academic journals, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Use this data to support your arguments and analysis and compile a literature review.
- Use Economic Theories and Models: These help you to support your arguments and provide a framework for your analysis. Make sure to clearly explain these theories and models so that the reader can follow your reasoning.
- Analyze the Micro and Macro Aspects: Consider all angles of the topic. This means examining how the issue affects individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
- Use Real-World Examples: Practical examples and case studies help to illustrate your points. This can make your arguments more relatable and understandable.
- Consider the Policy Implications: Take into account the impacts of your analysis. What are the potential solutions to the problem you're examining? How might different policies affect the outcomes you're discussing?
- Use Graphs and Charts: These help to illustrate your data and analysis. These visual aids can help make your arguments more compelling and easier to understand.
- Proofread and Edit: Make sure to proofread your essay carefully for grammar and spelling errors. In economics, precision and accuracy are essential, so errors can undermine the credibility of your analysis.
These tips can help make your essay writing journey a breeze. Tailor them to your topic to make sure you end with a well-researched and accurate economics essay.
To wrap it up , writing an economics essay requires a combination of solid research, analytical thinking, and effective communication.
You can craft a compelling piece of work by taking our examples as a guide and following the tips.
However, if you are still questioning "how do I write an economics essay?", it's time to get professional help from the best essay writing service - CollegeEssay.org.
Our economics essay writing service is always ready to help students like you. Our experienced economics essay writers are dedicated to delivering high-quality, custom-written essays that are 100% plagiarism free.
Also try out our AI essay writer and get your quality economics essay now!
Barbara P (Literature)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Good Economics Essay
Last Updated: July 16, 2024 References
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. This article has been viewed 129,400 times.
A good economics essay requires a clear argument that is well-supported by appropriately referenced evidence. Research your topic thoroughly and then carefully plan out your essay. A good structure is essential, as is sticking closely to the main essay question. Be sure to proofread your essay and try to write in formal and precise prose.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- For example a question such as “Discuss the macroeconomic consequences of rising house prices, alongside falling interest rates” could be divided into 2 parts: 1 part could be on the effects of rising prices, and 1 on the effects of falling interest rates.
- In this example you could begin by discussing each separately and then bringing the 2 together and analysing how they influence each other.
- Be sure to keep the question at the forefront of your mind and don’t veer off topic. [1] X Research source

- Be sure that you understand all the key terms that you are being asked about.
- Try to keep your reading focussed closely to the essay question.
- Don’t forget to look at any lecture or class notes you have made.
- 3 Come up with a thesis statement . A thesis statement is the main argument you will make in your essay. It should be 1-2 sentences long and respond to the essential question that’s being asked. The thesis will help you structure the body of your essay, and each point you make should relate back to the thesis.

- Once you have put together a list of key points, then try to add in some more detail that brings in elements from your research.
- When you come to write out your essay, you can develop a paragraph based on each point.

- All of the evidence and explanation will be in the main body of the essay.
- Order the key points in the body of your essay in such a way that they flow logically.
- If you are writing a longer essay, you can break the main body into different sections. [2] X Research source
- If you have a word limit, be sure to take this into account when you are planning.
- Allocate yourself a rough number of words per section.
- The introduction and conclusion can be just a paragraph each.
Writing the Essay

- What your essay is about.
- What material you will cover in the essay.
- What your argument is. [3] X Research source

- Having this stated clearly at the start can help you to stay focussed on the question as you work your way through the essay.
- Try writing out this one or two sentence statement and sticking it up in front of you as you write, so it’s stays at the forefront of your mind.

- Try to begin each paragraph with a sentence that outlines what the paragraph will cover.
- Look at the opening sentence of each paragraph and ask yourself if it is addressing the essay question. [5] X Research source

- Try to engage with arguments that run counter to yours, and use the evidence you have found to show the flaws.
- It might help to imagine someone reading the essay, and anticipating the objections that he might raise.
- Showing that you have thought about potential problems, and you can make an argument that overcomes them, is a hallmark of an excellent essay. [6] X Research source
- If there is conflicting evidence, discuss it openly and try to show where the weight of the evidence lies.
- Don’t just ignore the evidence that runs counter to your argument.

- In the conclusion you can add a few sentences that show how your essay could be developed and taken further.
- Here you can assert why the question is important and make some tentative suggestions for further analysis.
Proofreading and Making Revisions

- As you read through it, think about how closely you stick to main overarching question.
- If you notice paragraphs that drift off into other areas, you need to be tough and cut them out.
- You have a limited number of words so it’s essential to make every one count by keeping tightly focussed on the main question.

- Think about how you use the evidence too. Do you critically engage with it, or do you merely quote it to support your point?
- A good analytical essay such discuss evidence critically at all times.
- Even if the evidence supports your argument, you need to show that you have thought about the value of this particular piece of data.
- Try to avoid making any assumptions, or writing as if something were beyond dispute.

- Remember an academic essay should be written in a formal style, so avoid colloquialisms.
- Avoid contractions, such as “don’t”, or “won’t”.
- Try to avoid paragraphs that are more than ten or fifteen lines long.
- Think about how it looks on the page. [8] X Research source

- Always include a bibliography, but don’t include references to things you haven’t read or didn’t inform your argument. [9] X Research source
- Your teacher will know if you just add a load of titles into your bibliography that are not evidenced in the body of your essay.
- Always follow the bibliography format used by your department or class.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.economicshelp.org/help/tips-economic-essays/
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/planning-and-organizing/organizing
- ↑ http://carleton.ca/economics/courses/writing-preliminaries/academic-essay-writing/
- ↑ https://www.economicsnetwork.ac.uk/archive/lse_writing/page_11.htm
- ↑ https://www.royalholloway.ac.uk/economics/documents/pdf/essaywriting-departmentofeconomics.pdf
About This Article

Before you begin writing your economics essay, make sure to carefully read the prompt so that you have a clear sense of the paper's purpose and scope. Once you have read the prompt, conduct research using your textbook and relevant articles. If you cannot find research materials, ask your instructor for recommendations. After your research is done, construct a 1-2 sentence thesis statement and begin outlining your main ideas so that your essay will have a clear structure. Make sure to leave time to write a draft and revise your work before it is due. If you want to learn more, like how to cite the sources you used for your essay, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Twyla Kirkpatrick
Dec 8, 2020
Did this article help you?

Arshad Bhatti
Sep 10, 2017
Fungai Samantha Zuva
Jan 30, 2019
James Smith
Oct 2, 2016
Mallesh Itti
Jul 10, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Tips for writing economics essays
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation – primarily designed for A Level students.
1. Understand the question
Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
For example:
Q. Examine the macroeconomic implications of a significant fall in UK House prices, combined with a simultaneous loosening of Monetary Policy.
In plain English.
- Discuss the effect of falling house prices on the economy
- Discuss the effect of falling interest rates (loose monetary policy) on economy
In effect, there are two distinct parts to this question. It is a valid response, to deal with each separately, before considering both together.
It helps to keep reminding yourself of the question as you answer. Sometimes candidates start off well, but towards the end forget what the question was. Bear in mind, failure to answer the question can lead to a very low mark.
2. Write in simple sentences
For clarity of thought, it is usually best for students to write short sentences. The main thing is to avoid combining too many ideas into one sentence. If you write in short sentences, it may sound a little stilted; but it is worth remembering that there are no extra marks for a Shakespearian grasp of English. (at least in Economics Exams)
Look at this response to a question:
Q. What is the impact of higher interest rates?
Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing. As a result, those with mortgages will have lower disposable income. Also, consumers have less incentive to borrow and spend on credit cards. Therefore consumption will be lower. This fall in consumption will cause a fall in Aggregate Demand and therefore lead to lower economic growth. A fall in AD will also reduce inflation.
I could have combined 1 or 2 sentences together, but here I wanted to show that short sentences can aid clarity of thought. Nothing is wasted in the above example.
Simple sentences help you to focus on one thing at once, which is another important tip.
3. Answer the question
Quite frequently, when marking economic essays, you see a candidate who has a reasonable knowledge of economics, but unfortunately does not answer the question. Therefore, as a result, they can get zero for a question. It may seem harsh, but if you don’t answer the question, the examiner can’t give any marks.
At the end of each paragraph you can ask yourself; how does this paragraph answer the question? If necessary, you can write a one-sentence summary, which directly answers the question. Don’t wait until the end of the essay to realise you have answered a different question.
Discuss the impact of Euro membership on UK fiscal and monetary policy?
Most students will have revised a question on: “The benefits and costs of the Euro. Therefore, as soon as they see the Euro in the title, they put down all their notes on the benefits and costs of the Euro. However, this question is quite specific; it only wishes to know the impact on fiscal and monetary policy.
The “joke” goes, put 10 economists in a room and you will get 11 different answers. Why? you may ask. The nature of economics is that quite often there is no “right” answer. It is important that we always consider other points of view, and discuss various different, potential outcomes. This is what we mean by evaluation.
Macro-evaluation
- Depends on the state of the economy – full capacity or recession?
- Time lags – it may take 18 months for interest rates to have an effect
- Depends on other variables in the economy . Higher investment could be offset by fall in consumer spending.
- The significance of factors . A fall in exports to the US is only a small proportion of UK AD. However, a recession in Europe is more significant because 50% of UK exports go to EU.
- Consider the impact on all macroeconomic objectives . For example, higher interest rates may reduce inflation, but what about economic growth, unemployment, current account and balance of payments?
- Consider both the supply and demand side . For example, expansionary fiscal policy can help to reduce demand-deficient unemployment, however, it will be ineffective in solving demand-side unemployment (e.g. structural unemployment)
Example question :
The effect of raising interest rates will reduce consumer spending.
- However , if confidence is high, higher interest rates may not actually discourage consumer spending.
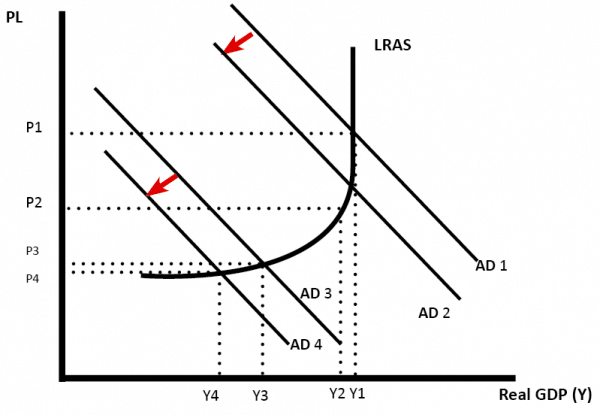
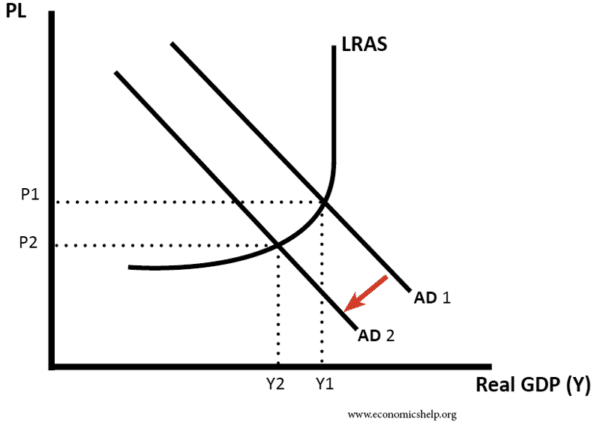
If the economy is close to full capacity a rise in interest rates may reduce inflation but not reduce growth. (AD falls from AD1 to AD2)
- However , if there is already a slowdown in the economy, rising interest rates may cause a recession. (AD3 to AD3)
Micro-evaluation
1. The impact depends on elasticity of demand
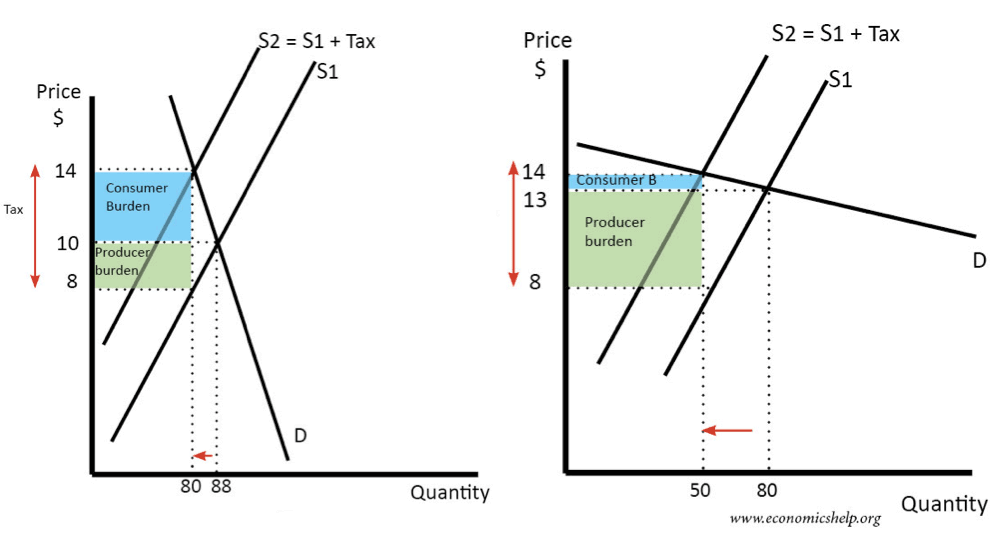
In both diagrams, we place the same tax on the good, causing supply to shift to the left.
- When demand is price inelastic, the tax causes only a small fall in demand.
- If demand is price elastic, the tax causes a bigger percentage fall in demand.
2. Time lag
In the short term, demand for petrol is likely to be price inelastic. However, over time, consumers may find alternatives, e.g. they buy electric cars. In the short-term, investment will not increase capacity, but over time, it may help to increase a firms profitability. Time lags.
3. Depends on market structure
If markets are competitive, then we can expect prices to remain low. However, if a firm has monopoly power, then we can expect higher prices.
4. Depends on business objectives
If a firm is seeking to maximise profits, we can expect prices to rise. However, if a firm is seeking to maximise market share, it may seek to cut prices – even if it means less profit.
5. Behavioural economics
In economics, we usually assume individuals are rational and seeking to maximise their utility. However, in the real world, people are subject to bias and may not meet expectations of classical economic theory. For example, the present-bias suggest consumers will give much higher weighting to present levels of happiness and ignore future costs. This may explain over-consumption of demerit goods and under-consumption of merit goods. See: behavioural economics

Exam tips for economics – Comprehensive e-book guide for just £5
9 thoughts on “Tips for writing economics essays”
I really want to know the difference between discussion questions and analysis questions and how to answer them in a correct way to get good credit in Economics
Analysis just involves one sided answers while Discussion questions involve using two points of view
This is a great lesson learnd by me
how can I actually manage my time
The evaluation points in this article are really useful! The thing I struggle with is analysis and application. I have all the knowledge and I have learnt the evaluation points like J-curve analysis and marshall learner condition, but my chains of reasoning are not good enough. I will try the shorter sentences recommended in this article.
What kind of method for costing analysis is most suitable for a craft brewery, in order to analyze the cost of production of different types of beer_
Really useful!Especially for the CIE exam papers
Does anyone know how to evaluate in those advantages/disadvantages essay questions where you would basically analyse the benefits of something and then evaluate? Struggling because wouldn’t the evaluation just be the disadvantages ?? Like how would you evaluate without just stating the disadvantage?
This is an excellent source of adbvise
Leave a comment Cancel reply
How to Write a Good Economics Essay
Governor November 28, 2019 Real World Applications 3 Comments
Many students ask “How to write an economics essay?” This Guide to Writing a Good Economics Essay is applicable to both IB economics as well as the Singapore JC A-Level H2 economics examinations. Many of the pointers here are also applicable to large-mark case study questions.
6 Steps to Writing a Good Economics Essay
Step 1: dissect the question.
Make sure you analyse and fully understand the KEYWORDS and REQUIREMENTS of the question. This is a very important skill that is taught in our economics tuition classes .
For example, “Best”, “Most Effective” are closely related but mean different things.
Paraphrase the question to make it simpler if necessary.
Take note of the command word (eg: Explain, Discuss) as it determines the approach needed for the essay, for example, whether two sides are needed or one side is sufficient. Below are some common examples found in economics essay questions:
Command Words Action Required
Account for Explain why
Analyse Break it down into step-by-step explanations
Assess For & Against. Consider other factors.
Compare Identify Similarities & Differences
Distinguish Point out differences
Discuss Explore both sides
Evaluate The Good and The Bad.
Explain Show why and how
Explain whether Cover both possibilities
Examine Look closely. How so and how not so?
To What Extent Yes…..But….Judgment
Remember to look out for the context in the question. This is usually given in the form of a country (eg: Singapore). The examples in your essay must be tailored to this particular context (for example, do not suggest interest rate policy for Singapore as that is considered infeasible in the Singapore context). If no context is given, any real-world example can be used.
Keep in mind the question throughout the essay and remember to always answer the question. Don’t go off-point!
Common Examiner’s Comment : Not Answering Question (NAQ))
Step 2: Plan Your Answer
Take some time to consider what economic framework you will use to approach the question. Scribble down your main thesis and anti-thesis points. Ensure they ANSWER THE QUESTION.
Step 3: Essay Introduction
In the introduction, include definitions of keywords in the question and spell out the economic framework you will employ for your answer as well as key definitions.
Step 4: Body of Essay
In the body , there will be several paragraphs.
The number of points/paragraphs depends on the question. It is common to require 2 main points for each 10 mark essay and similarly for 15 mark essay questions. Under each main point, there may be 1-2 sub-points.
Use one paragraph for each sub-point you are making.
However, do not be too focussed on the number of points or paragraphs. The key is to answer the question.
For each body paragraph , use TET’s PEEL(ED) structure. Include only one main idea per paragraph.
- Point – Write your point in the first sentence so that markers will know what the paragraph will be about. The topic sentence must directly answer the question!
- Explanation – Explain what you mean
- Elaboration – Provide further analysis with clear step-by-step economic reasoning. This part may be done with examples as well as diagrams.
- Link – Link your explanations back to the Point and to answer the question.
- Exemplification – Give an example to support your reasoning. It can be statistics or real-world examples (for Case Studies, evidences from the Case must be uncovered!)
- Diagram – Where possible, araw an appropriate diagram with correct labelling and refer to it in your answer. This is crucial to show economic reasoning. Diagrams are very important for economics essays!
These are of course much easier said than done! Thus, students in our economics tuition classes are regularly honed to achieve such output including with tips and tricks to spark off the correct thinking process.
Our resources including the Study Guides for A Level and IB economics also provide a very powerful and handy reference on the depth of analysis required to score the highest marks.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Mere statements and claims. No economic rigour.
Step 5: In-Body Evaluation
This applies especially to the 15 mark essays for A-Level Economics. A total of 5 marks is catered for Evaluation. Students should attempt to achieve about 2-3 in-body evaluation marks by pointing out how the thesis and anti-thesis points may not be true due to certain assumptions made that may not hold. Students may write “However,….may not necessarily happen……It would depend on whether….”. This statement can be written after the associated sub-point has been made.
Step 6: CONCLUDING SECTION
This only applies to the 15 mark essay questions.
Earn more evaluation marks by making a reasoned judgement. Deliver your verdict like a Judge!
Check back on the question before you embark on this. Ensure your judgement answers the question.
So the question now is, how does a judge arrive at and deliver a verdict? Certainly, you should not be summarising or merely paraphrasing your main points in the conclusion. Obviously, you cannot expect more marks by saying the same thing over and over again!
After a verdict and reasons have been provided, consider providing further relevant insights and/or recommendations.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Repetitive. Mere Summary.
Here are some quite common types of Concluding Sections
- Consider the relative importance of thesis and anti-thesis factors. Which factors are most important or pertinent in the given context? For example, certain policies better fit specifc types of economies.
- Consider short-term vs long-term pros and cons. Do the short-term benefits outweigh the long-term costs? Is the policy more effective in the long-term, and if so, how pressing is the problem that needs to be addressed?
- Suggest a multi-policy approach, in which each policy has strengths and weaknesses that allow them to complement each other.
There is no way to really memorise evaluation points as every question and context is different. After all, you are being tested on higher-order thinking!
There are other evaluation tips that our students will receive but the key point here is that the training of the mind to think and apply economics is essential. That is where our weekly economics lessons come into play and that is why our students are often asked questions in class and trained to think on their feet. As ex-student Xue Min from YIJC testified, Chief Tutor Mr. Kelvin Hong does not just spoon-feeds our students but mentors them in their thinking to arrive at the answers. This was different from other tutors that her classmates experienced and eventually this was the key to Xue Min’s A grade.
In your essay, write in simple and clear sentences. Everything you write should be value-adding. You do not have to spend time showing off vocabulary as no extra points are awarded for language. Focus on economic reasoning. Use succinct and effective examples which support the point you are trying to make as well as accurate diagrammatic analyses.
For samples of great economics essays, please check out our free Economics Model Essays and sample Past JC A-Level Economics Questions and Answers .
For our econs publications that are sold worldwide, please check out our A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays Publications
About The Economics Tutor
Founded by Kelvin Hong in 1998, The Economics Tutor is one of the leading economics tuition in Singapore . We provide a comprehensive program to guide students in understanding complex economic concepts and applying them through case study analyses, essay writing and discussion of real world events.
For 24 years, the way we teach JC Economics Tuition (A Level Economics Tuition) and IB Economics Tuition classes helped learners appreciate economics and everything it entails on a much larger scale. We take things step-by-step, implement effective techniques in memorising frameworks and give every student the chance to nurture their ideas.
We don’t just solely focus on helping you get stellar grades and perfect scores. We make sure that we also hone the critical thinking skills and investment / business decisions you can use outside the four walls of your classroom.
Looking for a fun, engaging and probably the best economics tutor in Singapore? Look no further—check out our extensive and high quality economics resources on the website such as our IB and A Level Economics Publications
Book your lesson today and master the nuances of economics in our next class!
its good knowledgeable post regarding ib economics commentaries. i just wanted to admin can i use your blog as reference to my students .
Go ahead. We are all for helping students learn economics well.
Thank you, A lot of info!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
See You In Our Next Econs Lesson!
5.0 stars out of 130 G o o g l e reviews
#1 Economics Tuition Singapore – Kelvin Hong - The Economics Tutor
- +65 9336 7511
- [email protected]
- JC Econs Guide
- IB Econs Guide
- Testimonials
- A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays
- Blog Resources
- Economics Videos
- Economics Notes, Infographics & Mindmaps
- Real-World Examples
- Economics Definitions
- Past A Level Economics Questions & Answers
Registration
- Register / Schedule a Class
Copyright © 2024 The Economics Tutor
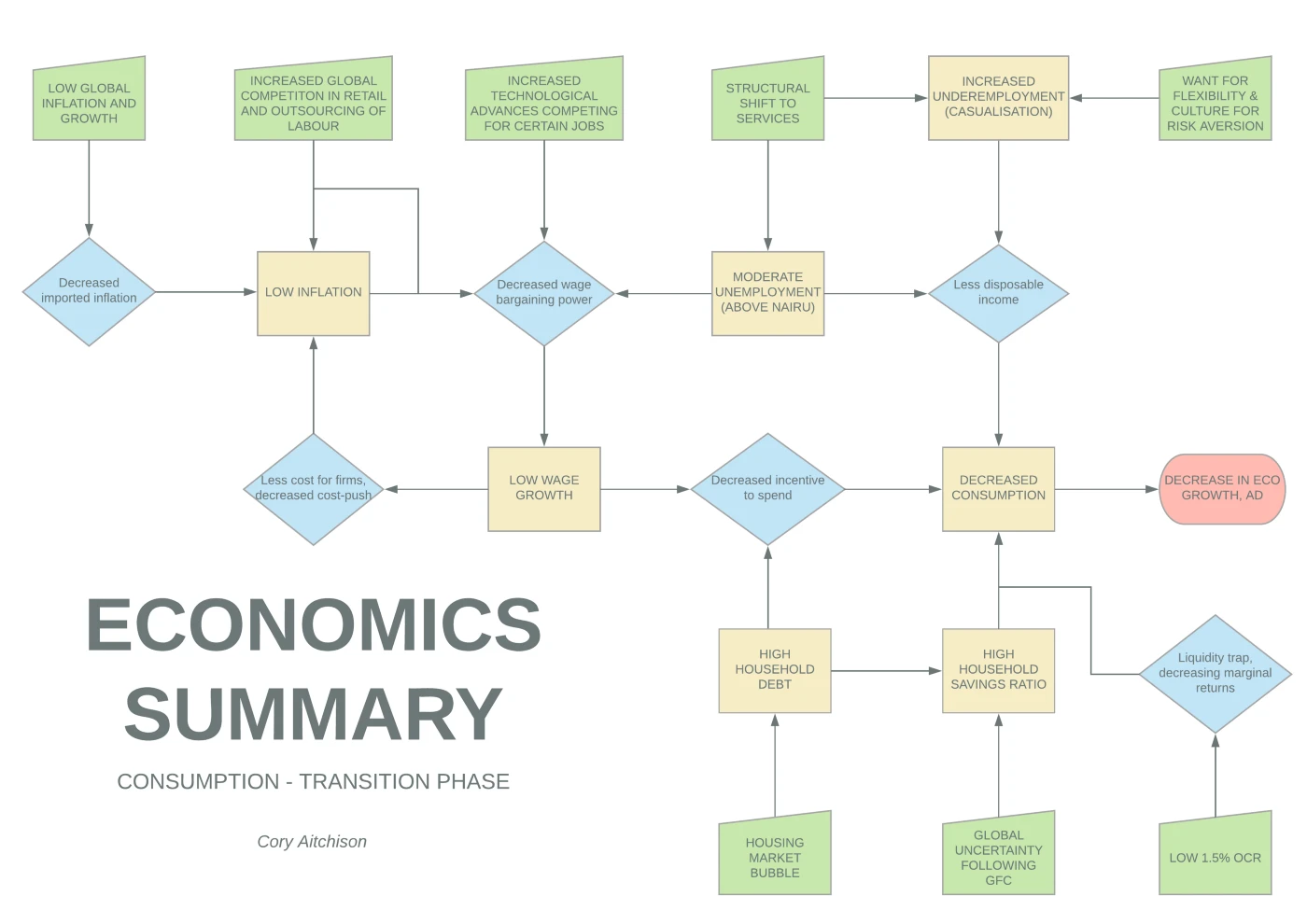
A State-Ranker’s Guide to Writing 20/20 Economics Essays
So, you want to know how to improve your preliminary and HSC economics essay...

Cory Aitchison
State Ranks (Economics and Chemistry) & 99.95 ATAR
1. Introduction to this Guide
So, you want to know how to improve your preliminary and HSC economics essay writing? Look no further! In this guide, I’ll be covering key tips to help YOU smash the structure, amaze with your analysis, conquer the contemporary, and ultimately master the mystery of maximising your marks.
My name is Cory Aitchison, currently one of the Economics tutors at Project Academy . I completed the HSC in 2018, achieving a 99.95 ATAR as well as two state ranks — 6th in economics and 12th in chemistry. Graduating from Knox Grammar School, I also topped my grade in economics and was awarded Dux of the School for STEM. Believe it or not, at the beginning of Year 11 I initially struggled with economics due to the transition in conceptual thinking required in approaching economic assessments in comparison to my other subjects such as English. However, through Year 11 and Year 12, I built up key tips and strategies — that I’ll be sharing with you in this guide — to help me not only consistently achieve top marks in my internal assessments, but to ultimately go on to achieve the results I did in the HSC.
2. The Correct Way to Write
First off, you need to understand something: HSC economics essays are NOT english essays! They aren’t scientific discussions, nor geography reports, nor historical recounts. They’re unique and often quite different from other essays that you might’ve done previously in high school. The style of writing and approach to answering questions can be confusing at first, but follow these tips and you’ll be ready in no time:
Phrasing should be understandable and concise
Unlike some subjects where sophisticated phrasing is beneficial to getting marks, HSC economics essays should emphasise getting your point across with clarity. This means don’t run your sentences on for too long, be aware of any superfluous words, and make sure you actually understand yourself what you’re trying to say in a sentence.
For example:
GOOD: “An increase in interest rates should lead to decreased economic growth.”
NOT GOOD: “As a result of a rise or increase in interest rate levels from their previous values, the general state of economic activity in the domestic economy may begin to decrease and subsequently indicate the resultant situation of a decrease in economic growth.”
“Understandable” does not mean slang or lacking in terminology
Just because you want to get a point across, doesn’t mean you should resort to slang. In fact, using economic terminology is a strong way to boost your standing in the eyes of the marker — if you use it correctly! Always make sure you use full sentences, proper English grammar, and try and incorporate correct economic terms where possible.
GOOD: “This was a detrimental outcome for the economy.”
NOT GOOD: “This was a pretty bad outcome for the economy.”
GOOD: “The Australian Dollar depreciated.”
NOT GOOD: “The Australian Dollar decreased in value.”
Analysis should be done using low modality
Modality just refers to the confidence of your language — saying something “will” happen is strong modality, whereas saying something “might” happen is considered low modality. Since a large portion of economics is about applying theory, we have to make sure that we are aware that we are doing just that — talking about the theoretical, and so we can’t say for sure that anything will happen as predicted.
Some useful words include:
May, Might, Should, Could, Can theoretically
Don’t use words like:
Must, Will, Has to, Always
3. How to use Statistics
“What’s most important is that this contemporary is used to bring meaning or context to your argument…”
Using contemporary (statistics) can often seem straightforward at first, but using it effectively is usually harder than it looks. Contemporary generally refers to applying real-world facts to your analysis to help strengthen (or weaken) the theoretical arguments. This can include many different statistics or pieces of information, including:
- Historic economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, GINI coefficients, exchange rates, or unemployment rates
- Trends or economic goals, such as long-term GDP growth rates, or the stability band for inflation
- Names of economic policies, such as examples of fiscal or microeconomic policies
- Specifics of economic policies, such as the amount spent on infrastructure in 2017

Whatever statistics you deem relevant to include in your essay, what’s most important is that this contemporary is used to bring meaning or context to your argument — just throwing around random numbers to show off your memorisation skills won’t impress the marker, and in fact might appear as if you were making them up on the spot. Rather, your use of contemporary should actively improve your analysis.
GOOD: “Following a period of growth consistently below the long-term trend-line of 3%, the depreciation of the AUD to 0.71USD in 2017 preceded an increase in economic growth to a 10-year high of 3.4% in 2018.”
NOT GOOD: “Economic growth increased by 1 percentage point in 2017 to 2018”
NOT GOOD: “GDP was $1.32403 trillion in 2017”
GOOD: “The 2017 Budget’s Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy — up 30% from 2016’s $31 billion, and 20% higher than the inflation-adjusted long-term expenditure.”
NOT GOOD: “The 2017 Budget’s Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy”
That in mind, don’t think that these statistics have to be overly specific. As long as the general ideas gets across, it’s fine. You don’t need to say “$1,505,120” — just “$1.5 million” will suffice.
Ask yourself: if I get rid of the contemporary from my paragraphs, does the essay still have enough content?
Further, don’t get roped into the “contemporary trap” — where you fall into the mindset that “if I memorise all these statistics, my essay will get good marks”. Including numbers and contemporary at the expense of having a robust theoretical explanation and analysis will definitely be detrimental in getting you top marks. Particularly in trial exams and the HSC when you’ve got all these numbers floating in your head, it can be tempting to try and include as many as you can (often just because you can!). To avoid this, always try and focus your arguments on analysis and syllabus content first, contemporary second. Ask yourself: if I get rid of the contemporary from my paragraph, does the essay still have enough content?
4. Must Have Insightful “However”s
If you really want to extend your analysis and show the marker that you know your stuff, including insightful “however”s is a strong way to do it. What I mean by this is that for each of your paragraphs, try and include a counterpoint that highlights the flexible nature of economic theory. There are broadly two kinds of “however”s:
Theoretical “However”s
These are counterpoints that are based on theory — often there will be theoretical limitations for many of the concepts you come across in economics. It’s always important to include these limitations as it reinforces your knowledge of the actual content of economics.
“Although the Budget and fiscal policy can be effective at stimulating economic growth, it is also restricted by the “implementation time lag” limitation since it is only introduced annually.”
Contemporary “However”s
These are counterpoints that are based on contemporary — highlighting how although something should happen theoretically, this isn’t usually what is observed in reality. This can be particularly powerful in that it combines your knowledge of theory with your analysis of contemporary.
“Despite the expansionary stance that the RBA adopted in 2012–2016 for monetary policy, Australia’s annual GDP growth rate has remained below the trend rate of 3% — against the theoretical expectations. This could be attributed to factors such as …”
5. How to Interpret the Question
When you first look at a question, before you even put pen to paper, you need to come up with a plan of attack — how can you ensure that you answer the question correctly, and give the markers what they want? There are three main points to look for when interpreting essay questions:
Knowing your verbs
As you may (or may not) know, NESA has a bank of words that they like to pull from when writing questions, and these words impact how they want their question answered. These verbs should help steer your analysis onto the right path. For example:
Explain: “Relate causes and effects”
To answer these questions, you have to demonstrate a thorough understanding of how theory and events impact each other and the economy. This verb particularly emphasises the idea of a process — you need to be able to make clear links as to how each step leads to the next, rather than just jumping to the outcomes.
Analyse: “Draw out and relate implications”
These questions usually wants you to investigate the connections between different aspects of economic theory. Generally this involves showing a holistic understanding of how different areas (such as micro- and macroeconomic policies) come together to make a cohesive impact on the economy. It usually helps to think back to the syllabus and how the points are introduced when figuring out which ideas to link together.
Assess/Evaluate: “Make a judgement based on value/a criteria”
These require you to not only critically analyse a topic but also come to a conclusion given the arguments you provided. This type of question usually gets you to make a judgement of the effectiveness of some economic theory — such as the ability for economic policies to achieve their goals. Make sure you actually include this judgement in your answer — for example, say things like “strong impact”, “highly influential”, “extremely detrimental”.
Discuss: “Provide points for and/or against”
Similar to assess, discuss wants you to provide arguments towards and against a particular topic. Although it doesn’t require a specific judgement to be made, it does place greater emphasis on showing a well-rounded approach to the argument — providing relatively equal weightings towards both the positive and negative sides of the discussion.
Linking to the syllabus
When trying to understand what the question wants from you, I found the best way to approach it is to consider what points in the syllabus it is referring to (To do this, you need to have a solid understanding of the syllabus in the first place). Once you’ve located it, try drawing upon other topics in the vicinity of that dot point to help you answer the question.
For example, if the question mentions “trends in Australia’s trade and financial flows”, then you know from the syllabus that you probably need to talk about value, composition and direction in order to get high marks. Further, it may also be worth it to bring in ideas from the Balance of Payments, as this is the next dot point along in the syllabus.
Digging into the source
For essay questions that provide a source for you to include in your answer, this is another goldmine from which you can discern what the marker really wants. If the source mentions microeconomic policy, it probably wasn’t on accident! Even if it may not be obvious how to link that to the question immediately, try and draw upon your knowledge and implications and see if there’s a different angle that you might be missing.
6. Putting it All together — Structuring your essay
My essays usually consisted of four main parts: an introduction, a background paragraph, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Introduction
Your introduction should not be long. I rarely wrote an introduction longer than three sentences.
First sentence: Answer the question (thesis)
Try and answer the question, while including the main key words of the question in your answer. Don’t directly restate it — instead, try and add meaning to it in a way that represents what you’re trying to get across in your essay.
For example: if the question was “Assess the impact of microeconomic policy in improving economic growth in Australia”, my first sentence might be “Microeconomic policy has had a significant impact in increasing aggregate supply and thus long-term economic growth in Australia since the 1960s”.
Next sentences: Introduce your arguments/paragraphs
In this part, it’s fine to almost list your paragraphs — there’s no need to do a whole sentence explaining each. That’s what the paragraphs themselves are for.
For example: using the same question as above, my next sentence might be “Although trade liberalisation may have been detrimental for short-term growth in manufacturing, policies such as competition policy and wage decentralisation have been highly effective in fostering economic growth in Australia”.
Background Paragraph
The aim of a background paragraph is threefold: to get across the main theory that underpins your argument; to establish the economic context for your argument; and to show the marker that you “know your stuff”.
For example, if the essay was on monetary policy, you may want to describe the process of Domestic Market Operations (how the reserve bank changes the cash rate) in your background paragraph, so that you don’t need to mention it each time you bring up changing stances. Further, it may be good to showcase the current economic climate — such as GDP growth rate and inflation — to give context to your analysis in your essay.
Some ideas for what to include in this paragraph include:
- Key theory such as DMOs or the rationale for macroeconomic policies
- Economic indicators that provide context to the time period that you’re working in, such as growth rates, inflation, unemployment rates, exchange rates, cash rates, etc.
- A brief description of the recent Budget (if talking about fiscal policy), including the stance and outcome
Bear in mind that this paragraph shouldn’t be too long — it isn’t the focus of your essay! Instead, aim for around 100–150 words at most. At this point in your essay, it may also be good to include a graph (more on this later).
Body Paragraphs
There’s no set rule for how many body paragraphs to include in your essay — I generally aim for at least 4, but there’s no real limit to how many you can (or should) write! Unlike english essays, it’s totally acceptable to just split a paragraph in two if you feel like the idea is too large to be written in one paragraph (as long as each paragraph makes sense on its own).
When writing a paragraph, I usually follow this structure:
Topic sentence
This is where you answer the question, and outline your argument or idea for this paragraph. If you are doing a discuss/assess/evaluate essay, try and make your judgement or side obvious. For example: “Trade liberalisation has been detrimental in its impact on economic growth in manufacturing industries”.
These sentences are where you bring together the theory and contemporary to build up your argument. Remember, the theory should be the focus, and contemporary a bonus. Try and weave a “story” into your analysis if you can — you should be showing the marker how everything fits together, how causes lead to effects, and ultimately bringing together relevant economic concepts to answer the question. Feel free to also include graphs here when they help strengthen your argument.
Fit in your “however” statements here. For discuss questions, this however section may take up a larger part of the paragraph if you choose to showcase two opposing arguments together.
Link your argument back to your overarching thesis, and answer the question. Following on from your “however” statement, it can often be a good idea to use linking words such as “nevertheless”, “notwithstanding”, or “despite this” to show that taking into account your arguments presented in the “however” statement, the overarching idea for the paragraph still remains.
Like the introduction, your conclusion should not be overly long. Rather, it should briefly restate the arguments made throughout your essay, and bring them all together again to reinforce how these points help answer the question.
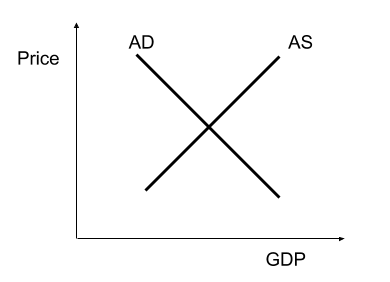
Aggregate Demand / Supply Graph
Graphs are a great way to add extra spice to your essay — not only does it help strengthen your explanations of economic theory, it also makes it look like you wrote more pages than you actually did! Graphs, such as aggregate demand graphs, business cycle graphs, and Phillips curves, can be great in reinforcing your ideas when you mention them in your essay. They usually come either in background paragraphs or body paragraphs, and it’s usually best to draw them about a quarter to a third of the page in size. It’s also good practice to label them as “Figure 1” or “Graph 1”, and refer to them as such in your actual paragraph.
Although they can be beneficial, don’t try and force them either. Not all essays have appropriate graphs, and trying to include as many as you can without regards for their relevance may come across negatively in the eyes of the marker.
8. How to Answer Source Questions
If your essay question involves a source, try and refer to it multiple times throughout your essay. For example, this can be in the background paragraph and two of your body paragraphs. Rather than just adding in an “…as seen in the source” to one of your sentences, try and actively analyse it — show the marker that you understand why they included it, and how it actually helps strengthen your arguments.
9. Plan You Essay
Don’t be afraid to use the first page of your answer booklet as a planning page. Taking a couple minutes before you answer the question to lay out your scaffold for body paragraphs is a great first step to helping ensure that you actually end up answering the question to the best of your abilities. It also serves as a great reminder to keep checking as you finish each paragraph to ensure that you actually wrote what you intended. Just make sure to make it clear to the marker that those scribbles on the page are just a plan, and not your actual essay!
10. How to Prepare for Essays in the Exam
I find it much better to prepare paragraphs and ideas that you can draw upon to help “build up” a response during the exam itself.
Don’t go into the exam with a pre-prepared essay that you are ready to regurgitate — not only are there too many possibilities to prepare for, but it’s also unlikely that you’ll actually answer the question well with a pre-prepared response.
Instead of memorising sets of essays before the exam, I find it much better to prepare paragraphs and ideas that you can draw upon to help “build up” a response during the exam itself. What I mean by this, is that in your mind you have a “bank of different paragraphs” and ideas from all the topics in the syllabus, and when you read the exam, you start drawing from different paragraphs here and there to best formulate a response that answers the question. This allows you to be flexible in answering almost any question they can throw at you.
On top of this, ensure you have a solid foundation in both the theory and contemporary — knowing what statistics or topics to include in your essay is useless knowledge unless you have the actual content to back it up.
Now that you know the basics of how to write a good HSC economics essay, it’s time to start practising! Have a go, try out different styles, and find what works best for you. Good luck!
If you would like to learn from state ranking HSC Economics tutors at Project Academy, we offer a 3 week trial for our courses. Click to learn more !
Complete Guide to HSC Biology Module 7 - Infectious Diseases
Studying HSC Biology? This one's for you. Key concepts, sample answers, and tips - all in one spot.

Beau Burrows
Biology Tutor, Band 6 in Biology

How to study for HSC: Constructing Study Habits
Learn how to construct the best study habits in to ace the HSC, written by 99+ ATAR tutors and distinguished achievers.

Riddhish Chanda
Chemistry Team at Project Academy

How I Achieved a 99.80 ATAR with 8+ Hours of Sleep Every Night
Here are 4 effective HSC study tips from the Vice Captain of Baulkham Hills!

Rishabh Jain
Head of HSC Chemistry

Complete Guide to HSC Economics – How to Ace HSC Economics
Taking my years of teaching Economics and distilling it into one post.

Aatish Budhwani
99.75 ATAR and 97 in Economics
Maximise Your Chances Of Coming First At School
Trial any Project Academy course for 3 weeks.
NSW's Top 1% Tutors
Unlimited Tutorials
NSW's Most Effective Courses
Access to Project's iPad
Access to Exclusive Resources
Access to Project's Study Space
Up: Home : Study Guidance > Effective Writing and Referencing > Writing the Economics Essay
- Writing the Economics Essay
An academic rhetoric (or organisation) is important to convince a reader that you understand the topic well – poor organisation can signal muddled thinking.
Thesis – Justification – Support
This is the rhetoric used by Bray et al.
Thesis – the main concept or idea that you are proposing
Justification – the reasons why your thesis is valid
Support – evidence that backs up your justification
Essay structure – your introduction, main body, and conclusion
Box: An example
The Thesis – Justification – Support rhetoric can be applied to an individual paragraph of an essay, or on an entire essay. For example, take the essay question:
‘The accumulation of capital is sufficient for ensuring sustainable growth in per capita living standards’. Discuss.
One possible answer would be:
Thesis: if we define capital as physical capital, the accumulation of capital will lead to diminishing returns
Justification: Demonstration of the Solow model : capital accumulation can result in higher levels of income but after a certain level not higher levels of consumption per capita (due to diminishing marginal returns).
Support: examples, such as India’s heavy investment drive in the 1950s, 1960s which was associated with low levels of ‘Hindu growth’; or econometric evidence, such as that from Mankiw, Romer and Weil (1992), which supports some of the conclusions of the Solow model (but also suggests improvements, see below).
The next section of the essay would play with the assumptions of the Solow model – for example by expanding our definition of capital to include human capital (and, if you’re really trying to impress, social capital and ‘natural’ capital as well).
You might also want to discuss if technological progress (the source of per capita income growth in the Solow model) is related to capital accumulation, for example through ‘ learning by doing ‘ (Arrow, 1962)
Previous: Effective Writing and Referencing
Next: What makes good justification?
Share this page: Email , Facebook , LinkedIn , Twitter
- Note Taking in Economics
- Effective Economics Reading
- Data Collection for Economics Assignments
- What makes good justification?
- What makes good support?
- Structuring an Essay
- Referencing
- Presentation and Group Work
- Revision for an Economics Exam
- Maths Help for Economics Students
Published by The Economics Network at the University of Bristol . All rights reserved. Feedback: [email protected] Supported by the Royal Economic Society and the Scottish Economic Society

How to Write Economics Essay: Your Ultimate Guide

Did you know that the global economic crisis of 2008, triggered by the collapse of Lehman Brothers, led to a profound reevaluation of economic policies worldwide? This crisis demonstrated the enormous influence that economics wields, and the critical role it plays in shaping our lives. Whether it's analyzing the causes and consequences of financial meltdowns, evaluating market trends, or understanding the impact of government decisions on our wallets, writing an essay on economics is the gateway to exploring these complexities.
Short Description
In this comprehensive guide, the expert team at our business essay writing service will explore the definition of an economics essay. We'll provide you with helpful tips on selecting the perfect economics essay topics to captivate your audience, and we'll delve into the essential structure required to craft a winning paper. We'll share expert insights and more to help you master the art of economic essay writing. Whether you're a student seeking academic success or a curious mind eager to explore economic concepts, join us on this enlightening journey.
Definition of an Economics Essay
So, what is economics essay all about? This type of writing is more than just an academic piece. It's a medium for you to articulate your understanding of economic theories, concepts, and real-world applications.
It's an opportunity to analyze and evaluate economic issues, providing well-researched arguments and evidence to support your perspective. Economics essays often demand critical thinking, data analysis, and the ability to communicate complex economic ideas effectively.
These essays can cover a wide range of topics, from macroeconomic policies to microeconomic market dynamics, and they serve as a platform to showcase your knowledge and insights into the world of economics.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the nuances of crafting an economics essay that not only conveys your expertise but also engages your readers.
Selecting the Right Economics Essay Topics
When it comes to choosing the ideal essay topics for economics essay, consider it a strategic decision rather than a random choice. The right topic should not only align with your academic requirements but also ignite your intellectual curiosity.
One approach is to stay informed about current economic events. For instance, exploring topics such as the economic impact of global trade tensions, the rise of e-commerce, or income inequality in the modern era can lead to engaging and relevant essays. And, if you find the task of essay writing daunting, you can always consider professional help - yes, we also offer assistance for those looking to buy essays on economics.
Alternatively, you can delve into timeless economic theories and concepts. Topics like the economic implications of the Keynesian theory, the role of the Federal Reserve in stabilizing the economy, or the economic consequences of globalization offer a wealth of essay possibilities.
Don't forget to think about your audience. Are you writing for economics enthusiasts, your professors, or a broader readership? Tailoring your topic to the interests and knowledge level of your audience is essential. Specialized readers may appreciate in-depth analyses of economic models, while a more general audience might prefer topics like the economics of sustainable agriculture or the financial challenges of college students.

Understanding the Structure of an Economics Essay
Once you've chosen your economics essay topic, the next crucial step is to master the art of structuring your essay effectively. The structure of your essay plays a pivotal role in conveying your arguments and analysis in a logical and persuasive manner.
An essay about economics typically consists of three primary sections: the introduction, the main body, and the conclusion. Let our expert finance essay writing service explore each of these elements in more detail:
1. Introduction: The introduction serves as the gateway to your essay. It's where you set the stage, introduce your topic, and present your thesis statement. Think of it as your opportunity to engage your readers' attention and lay the foundation for what follows. For instance, if your essay discusses the economic impact of renewable energy adoption, your introduction might begin with a compelling statistic or a thought-provoking question related to the subject.
2. Main Body: This is where you delve into the heart of your essay, exploring the relevant economic concepts. The main body consists of several paragraphs, each dedicated to a specific aspect of your topic. Here, you present your arguments, analyses, and evidence to support your thesis statement. In the case of the renewable energy essay, you could have separate sections discussing its environmental benefits, economic implications, and potential challenges. Make sure to use clear headings and subheadings to structure your content logically.
3. Conclusion: The conclusion provides closure to your essay. Summarize your key points, restate your thesis statement, and offer insights or implications based on your analysis. In the renewable energy essay, your conclusion might emphasize the importance of transitioning to renewable energy sources and its potential long-term benefits for both the economy and the environment.
Tips for Writing an Economics Essay
Crafting an outstanding essay economics goes beyond just presenting information. It requires a combination of research skills, critical thinking, and effective communication. Here are some essential tips from our PRO essay writer service to elevate your writing:
1. Conduct Thorough Research: Before you start writing, gather relevant data and information from reputable sources. The quality of your research will directly impact the strength of your arguments.
2. Develop a Clear and Concise Argument: Your essay should present a well-defined thesis or central argument. Ensure that your position is clear from the outset and that each section of your essay supports this argument.
3. Incorporate Real-World Examples: Economics is all about real-world applications. Include concrete examples and case studies to illustrate economic concepts and theories. Whether you're discussing supply and demand or market structures, real examples can make your essay more relatable and engaging.
4. Proper Citation and Referencing: Accurate citation and referencing are crucial. Use a recognized citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) to give credit to the sources you've used. This not only adds credibility to your essay but also avoids issues with plagiarism.
5. Address Counterarguments: Acknowledging and addressing counterarguments demonstrates a deeper understanding of the topic. It also makes your essay more well-rounded and persuasive. Consider potential objections to your thesis and provide reasoned responses.
6. Maintain Clarity and Conciseness: Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language. Ensure that your writing is clear and concise, making it accessible to a broad audience. If someone who is looking to buy essays on economics were to read your work, they should easily grasp your points.

How to Start Your Economics Essay
The beginning of your paper is your opportunity to grab your readers' attention and set the stage for the insights you'll provide. Here's how to start your essay effectively from our economics essay writing service experts:
1. Crafting an Engaging Introduction: The introduction is your chance to captivate your audience. You can start with an interesting fact or statistic related to your topic. For example, if your essay is about the economic impact of automation, you might begin with a startling statistic about job displacement due to automation in recent years.
2. Formulating a Strong Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement should be concise and crystal clear. It should convey the main argument or point you'll be making in your essay. Using the economics essay examples on automation, your thesis statement might be: 'Automation, while boosting productivity, presents significant challenges in the labor market, requiring innovative approaches to address unemployment and skill gaps.'
3. Hooking the Reader: In addition to your introduction, consider using a hook—a thought-provoking question or a compelling anecdote related to your topic. This can further engage your readers and draw them into the essay. For instance, after your initial statistic, you could pose a question like, 'But how will society adapt to this technological revolution?'
.webp)
Structuring the Main Body of Your Essay
The main body of your economics essay is where the substance of your arguments and further analysis resides. Proper structuring is essential to ensure that your points are conveyed in such a way that they flow logically and persuasively. Here's how to effectively craft the main body of your economics essay:
1. Organizing Your Ideas Logically: Ensure that the sequence of ideas in your essay flows logically. Start with the main idea, such as the most important or fundamental concepts, and then progress to more complex or detailed points. For example, if your essay discusses the impact of government taxation policies on economic growth, begin with an overview of taxation principles before delving into specific policies.
2. Using Clear Headings and Subheadings: Break down your main body into sections with clear headings and subheadings. Each section should address a distinct aspect of your topic. These headings serve as signposts for your readers, making it easier for them to navigate through your essay. In the taxation essay, you might have sections like 'Taxation Principles,' 'Historical Tax Policies,' and 'Effects on Economic Growth.'
3. Providing Evidence to Support Your Arguments: Every point you make in your essay should be supported by evidence. Use data, statistics, academic research, or real-world examples to back up your claims. For example, when discussing the effects of taxation policies on economic growth, you can include data showing the correlation between changes in tax rates and fluctuations in GDP growth.
4. Addressing Counter Arguments: Acknowledging and addressing counter arguments demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the topic. Anticipate potential objections to your thesis and provide reasoned responses. If critics argue that lower taxes always lead to higher economic growth, for instance, you can present evidence that suggests otherwise.
Writing a Compelling Conclusion
The conclusion of your economics essay serves as the final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers. A well-crafted conclusion should tie all the elements of your essay together and provide a sense of closure. Here's how to write a compelling conclusion:
1. Summarizing Key Points: Begin your conclusion by summarizing the key points and arguments you've presented in the main body of your essay. This recap reinforces the main takeaways for your readers.
2. Restating the Thesis Statement: Reiterate your thesis statement, but do so in a way that emphasizes the significance of your argument. This reinforces the central point of your essay.
3. Offering Insights or Implications: Take your essay a step further by offering insights or implications based on your analysis. Consider the broader significance of your findings. In the case of an essay on taxation policies and economic growth, you might discuss the potential policy changes that could promote economic growth while maintaining revenue.
4. Encouraging Further Thought: Conclude your essay by encouraging further thought or research on the topic. Suggest potential areas for future exploration or highlight any lingering questions. This not only demonstrates your depth of understanding but also leaves room for ongoing dialogue.
The Importance of Revision
Revision is a critical, often underestimated, phase in the process of writing a good economics essay. It's during this stage that your essay transforms from a rough draft into a polished, cohesive, and well-organized piece. Here's why revision is of paramount importance:
1. Enhancing Clarity: Revision allows you to review all your paragraphs for clarity in addressing the essay question. It's an opportunity to ensure that your ideas are expressed in a straightforward and comprehensible manner. Consider whether your arguments and explanations are easy to follow. If not, make the necessary revisions to improve clarity.
2. Polishing Grammar and Style: Revision is your chance to correct grammatical errors, typographical mistakes, and awkward sentence structures. A well-edited essay not only conveys professionalism but also ensures that your message is not overshadowed by writing issues.
3. Strengthening the Structure: During revision, you can evaluate the overall structure of your essay. Check whether your introduction effectively sets the stage, the main body logically flows from one point to the next, and your conclusion provides a satisfying resolution. Adjust the structure as needed to improve the overall flow and coherence of your essay.
4. Refining Arguments: Careful revision enables you to scrutinize your arguments and evidence. Consider whether the points you've made are adequately supported by data, examples, and analysis. If you find any gaps or areas for improvement, make the necessary adjustments.
5. Seeking Feedback: It's often beneficial to seek feedback from peers, professors, or writing tutors during the revision process. Fresh perspectives can highlight areas for improvement that you might have missed.
However, if you find the prospect of revising your work overwhelming or time-consuming, there's a convenient solution: you can simply ask for our assistance and say, ' write my essay online .' Our professional writers are here to ensure your essay is not only solid and well-structured but also error-free and ready to make a strong impact.
Final Thoughts
Mastering how to write an economics essay is a journey that demands dedication, research, and careful planning. Whether you're a student, a budding economist, or someone curious about the world of economics, embrace the challenge of essay writing with enthusiasm. Your research papers have the power to inform, inspire, and impact our understanding of this complex and ever-evolving field. So, keep writing, keep revising, and keep exploring the world of economics through the lens of your academic writing. And remember, there's support available if you ever choose to pay for essay to meet your academic goals!
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks

New posts to your inbox!
Stay in touch
How to Write an Economics Essay: Key Steps for Writing

What is Economics Essay?
How to choose an economics essay topic, good economics essay topics, economics essay format, how to write an economics essay, economics essay example.
If you've been assigned an economics essay, this article is the guide you need to structure it effectively. Start by carefully reading and analyzing the question, then follow these steps:
- Read Recommended Material : Begin with lecture notes and core textbooks and supplement with additional readings.
- Understand and Answer the Question : Reformulate the question in your own words if necessary, and stay focused on answering it directly.
- Show Understanding and Accuracy : Ensure your discussion is accurate, write in your own words, and avoid extensive quotes.
- Structure Your Essay : Include a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Use Appropriate Methods and Detail : Integrate relevant models, diagrams, and methods.
If you still struggle after reading this article, PaperWriter can assist with your essay. Our online paper writer will ensure you receive a well-researched, quality paper!
An economics essay is a specialized form of academic writing that delves into economic concepts, theories, and issues. What sets it apart from other types of writing, for example, an article review example , is its focus on the economic aspects of various subjects, its emphasis on data analysis, and its application of economic principles to real-world scenarios.
- Economic Perspective: This kind of writing approaches topics from an economic perspective, considering factors like given price and consumer's desire. It analyzes economic phenomena, such as market behaviors, price changes, production, and consumption, to provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter and its impact on total demand.
- Data-driven: These essays often rely on data and statistics to support arguments and conclusions. Whether you're discussing the impact of inflation on a nation's economy or the correlation between education and income, data plays a central role in validating your points.
- Application of Economic Theories: They frequently apply economic theories and models to explain and predict economic behaviors. Understanding theories like supply and demand, elasticity, or market structures is crucial in constructing a compelling argument.
- Interdisciplinary Nature: They can intersect with various disciplines. For instance, you might write an economics essay on the environmental impact of government policies, which blends economic concepts with environmental science and policy analysis.
- Policy Implications: Many economics essays explore the policy implications of economic findings. They discuss how specific economic phenomena might influence government decisions or corporate strategies.
- Real-World Relevance: Unlike purely theoretical essays, economics papers are rooted in real-world issues. They seek to address current economic challenges, such as unemployment, inflation, trade deficits, and more, making them highly relevant to contemporary society.
Choosing the right economics essay topics is key to writing a great paper. Here's how to pick a topic that will set you up for success:
.webp)
- Identify Your Interests - A topic you are passionate about will make the writing process more enjoyable and engaging, so think about the areas of economics that fascinate you.
- Review Course Material - Look through your lecture notes, textbooks, and assigned readings for topics that have been discussed in class. This way, you'll find a relevant and manageable topic.
- Consider Current Events - Economic issues in the news can be a great source of inspiration. Look for recent developments or ongoing debates that you can analyze.
- Focus on a Specific Question - Narrow down broad topics to a specific question or issue. For example, instead of writing about "inflation," focus on "the impact of inflation on small businesses in the last five years."
- Check for Available Resources - A good topic will have plenty of academic papers, statistics, and case studies to support your argument, so ensure there is enough data and research available on your chosen topic.
- Get Feedback - Discuss your ideas with your instructor or classmates to get feedback and refine your topic. This can help you choose a topic that is both interesting and feasible.
Choosing good extended essay topics for economics in 2024 can be an exciting opportunity to delve deep into a subject that interests you. Here are some intriguing ones from our nursing paper writing service :
The Impact of Digital Currencies on Traditional Banking: Analyze the rise of cryptocurrencies and their potential to disrupt traditional banking systems, considering factors affecting demand and market equilibrium.
Economic Consequences of Climate Change Policies: Investigate the economic effects of government policies aimed at combating climate change, including carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes, and their impact on market demand and equilibrium price.
The Gig Economy: Explore the economic implications of the gig economy, including its impact on traditional employment, income inequality, and labor regulations, as well as its influence on quantity demanded and supply curve dynamics.
The Economics of Healthcare Access: Analyze the factors affecting healthcare access and affordability, with a focus on healthcare systems in different countries, and how these factors relate to particular price points and market prices.
Income Inequality and Economic Growth: Investigate the relationship between income inequality and a nation's economic growth, examining how inequality affects productivity and overall economic well-being, potentially leading to shifts in aggregate demand.
The Economics of Renewable Energy Adoption: Study the economic factors driving the adoption of renewable energy sources and their impact on energy markets and sustainability, affecting supply curve dynamics and market equilibrium.
Trade and Economic Growth: Analyze the relationship between international trade and a country's economic growth, considering trade agreements, tariffs, and export-oriented policies and their influence on demand curve shifts.
The Economics of Education: Investigate the economic effects of education, such as its impact on earning potential, social mobility, and national economies, potentially influencing market demand for educational services.
Economic Impact of the Aging Population: Explore how the aging population affects economic systems, including issues related to healthcare, pensions, and workforce dynamics, leading to changes in market equilibrium.
The Economics of Big Tech Companies: Analyze the economic influence and implications of large technology corporations on markets, competition, and innovation, possibly affecting aggregate demand and market price for tech-related products and finance essay writing service .
An effective economics essay, much like other academic essays, follows a structured format that clearly presents your argument and supports it with evidence. Here's a detailed guide to formatting your paper:
| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| Title Page | Clearly state the topic of your essay. Include your full name. Add the course name and code. Indicate the submission date. |
| Abstract | Provide a brief summary of your essay, including the main argument and key findings (150-200 words). |
| Introduction | Explain why the question is important in the real world or for the field of economics. Present your main argument or answer to the question. Summarize the main points you will discuss in the essay, matching the order of your paragraphs. |
| Literature Review | Summarize existing research and theories related to your topic. Identify gaps in the current literature that your essay will address. Explain how your essay contributes to the existing body of knowledge. |
| Methodology | Describe the methods you used to gather data and conduct your analysis. List the sources of your data, such as surveys, databases, or case studies. Mention any models, diagrams, or statistical tools you used. |
| Main Body | Organize your paragraphs in a logical order, such as by importance, chronology, or causation. Start each paragraph with a sentence that clearly addresses the essay question. Follow the topic sentence with detailed reasoning and evidence. Use specific examples, data, and case studies. |
| Discussion | Discuss the significance of your findings and how they relate to your thesis. Explain the broader implications of your findings for the field of economics or real-world applications. Acknowledge any limitations in your research and suggest areas for future study. |
| Conclusion | Recap your main arguments and findings. Reaffirm your thesis statement in light of the evidence presented. Highlight the importance of your conclusions for the real world or the discipline of economics. Suggest possible directions for future research on the topic. |
| References | List all the sources you cited in your essay in the appropriate format (typically APA or MLA). Optionally, include a list of additional readings that are relevant to your topic. |
| Appendices | Include any additional material, such as charts, graphs, or detailed data tables, that support your analysis but are too lengthy to include in the main body. |
Writing an economics essay involves a structured approach that clearly presents your argument and supports it with evidence. To write a clear essay, follow this economics essay structure:
.webp)
Introduction
Your economics essay introduction should set the context and present your main argument. Here's how to structure it:
- Context Statement : Explain why the question is important. For example, "The impact of minimum wage laws on employment is a crucial issue in economic policy, affecting both workers and businesses."
- Answer the Question : Provide your main argument. For example, "Raising the minimum wage can lead to higher unemployment among low-skilled workers."
- Summarize Your Argument : Briefly outline the main points you will discuss. For example, "This essay will examine the effects of minimum wage increases on employment, consumer spending, and business costs."
The main body should logically develop your argument. Here's how to organize it:
- Paragraph Structure : Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence that addresses the question.
- Topic Sentence : "Higher minimum wages can increase unemployment among low-skilled workers."
- Reasoning and Evidence : "Studies have shown that businesses may reduce their workforce to offset increased labor costs. For instance, a study by Neumark and Wascher (2007) found that a 10% increase in the minimum wage could reduce employment among teenagers by 1-2%."
Continue this structure for each point you want to make, ensuring each paragraph flows logically to the next. Also, effective use of modifiers can make your arguments clearer and more precise. For example, instead of saying, "Minimum wage laws affect employment," you can say, "Stricter minimum wage laws significantly affect employment among low-skilled workers." You can find out more on how to use modifiers in our dedicated article.
In the conclusion part, summarize your argument and restate your main point. Highlight the significance of your findings.
- Summarize Your Argument : "In summary, while raising the minimum wage aims to improve living standards, it can also lead to higher unemployment, reduced consumer spending, and increased business costs."
- Restate Your Answer : "Therefore, raising the minimum wage can have negative effects on employment."
- Significance : "Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers to balance the benefits and drawbacks of minimum wage increases."
Stressed About Your Economics Essay Deadline?
Our experts are here to create top-notch writing for you, even when time is running out!

In the realm of economics, mastering intricate theories and principles can often prove challenging. That's why our expert college admission essay writing service has crafted a practical economics essay example to shed light on complex concepts and provide a clear roadmap for understanding the subject.
Title: The Impact of Minimum Wage on Income Inequality
Income inequality has become a pressing concern in modern economies. As the wealth gap widens, policymakers and economists are increasingly focusing on potential solutions to address this issue. One such solution is the adjustment of minimum wage rates. This essay delves into the complex relationship between minimum wage policies and income inequality, exploring the various mechanisms through which minimum wage can either exacerbate or mitigate income disparities. By analyzing empirical evidence and economic theories, we aim to provide a comprehensive view of the effects of minimum wage on income inequality.
Minimum Wage and Low-Income Workers
Minimum wage policies have a direct impact on low-income workers. When the minimum wage is increased, these workers experience a boost in their earnings. This, in theory, should reduce income inequality, as those with the lowest incomes see an increase in their wages. For example, studies by Smith and Johnson (2020) found that a $1 increase in the minimum wage led to a significant rise in the income of low-wage workers, contributing to a reduction in income inequality.
Effects on Employment and Income Inequality
However, the relationship between minimum wage and income inequality is more intricate. Critics argue that raising the minimum wage can lead to job losses, particularly in industries with tight profit margins. This raises concerns about unemployment among low-skilled workers. For instance, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projected that a $15 minimum wage, if implemented, could lead to the loss of 1.3 million jobs by 2024.
Regional Disparities
Another aspect to consider is regional disparities in the cost of living. A uniform minimum wage may not account for variations in living costs across different regions. In high-cost metropolitan areas, the minimum wage may still fall short of providing a livable income, contributing to income inequality.
Income Substitution
Some argue that the impact of minimum wage on income inequality is offset by a phenomenon known as 'income substitution.' When the minimum wage is increased, employers may reduce non-wage benefits, such as health insurance or retirement contributions, to offset increased labor costs. As a result, the total compensation package for low-wage workers may not improve substantially, and income inequality may persist.
Counter Arguments
It's essential to acknowledge counter arguments as well. Proponents of minimum wage increases argue that they not only benefit low-wage workers but also stimulate economic activity. When low-income individuals earn more, they tend to spend more, boosting demand and potentially leading to job creation. Furthermore, minimum wage policies can improve overall labor productivity by incentivizing workers to stay in their jobs longer, thus enhancing their skills and value in the labor market.
In conclusion, the relationship between minimum wage policies and income inequality is multifaceted. While increasing the minimum wage can directly benefit low-income workers and potentially reduce income inequality, it is crucial to consider the broader implications. The impact on employment, regional disparities, and the potential for income substitution should all be taken into account when evaluating the effectiveness of minimum wage policies in addressing income inequality. Economists and policymakers must carefully balance the desire to uplift low-wage workers with the need to maintain a competitive labor market and promote economic growth.
- Smith, A., & Johnson, B. (2020). The Impact of Minimum Wage on Income Inequality. Journal of Economic Research, 45(3), 311-328.
- Congressional Budget Office (CBO). (2021). The Effects of a Minimum-Wage Increase on Employment and Family Income. https://www.cbo.gov/publication/56193
As we wrap up this article, let's quickly recap the main steps for writing an economics essay:
- Choose a topic that interests you and aligns with your course.
- Read recommended materials thoroughly.
- Reformulate the essay question in your own words.
- Structure your essay with a clear outline.
- Use models, diagrams, and data to support your arguments effectively.
Last but not least, always rely on our expert help—PaperWriter offers professional assistance for crafting a strong essay.
How Do You Start an Economic Essay?
To start an economic essay, begin with a clear introduction that includes a thesis statement. Briefly outline the main points you will discuss in your essay. Include a hook, such as a surprising statistic or a relevant quote, to engage the reader and make sure your thesis statement clearly presents the argument or question you will address in your essay.
How Do I Write an Economics Essay?
To write an economics essay, follow these steps:
- Research : Gather relevant data and sources.
- Outline : Plan the structure of your essay.
- Introduction : State your thesis and main points.
- Body : Develop each point with evidence and analysis.
- Conclusion : Summarize your findings and restate your thesis.
Is an Economics Essay in APA or MLA?
Economics essays are typically written in APA format. This format includes in-text citations and a reference list at the end. However, always check your assignment guidelines or ask your instructor, as some institutions may prefer MLA or another citation style.
- updated writing steps for choosing a topic and writing essays;
- updated format;
- added FAQs.
- Essay Writing in Economics -Useful Advice . (n.d.). https://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/assets/university/schools/school-of-economics-and-finance/documents/advice-essay-writing.pdf
- How to Structure Your Economics Essay . (n.d.). https://www.ibmastery.com/blog/how-to-structure-your-economics-essay
How to Write a Nursing Essay: The Definitive Guide

How to Write a French Revolution Essay Guide
.webp)
Best AI Essay Writer Tools

How to Write a Reflective Essay?

How to Write a Persuasive Essay that Spurs Action - Expert Tips

How to Write an Illustration Essay?

How to Write an Essay: Advice From Professionals

Good Persuasive Speech Topics That Spark Intrigue

Business Essay Topics to Help Students Stay Ahead

How to write economics essays
All Economics exam papers at A-Level will have a 25-mark essay-style question, which requires evaluation .
There are different approaches that can be taken in dealing with essay questions, and there is not one essay writing 'template' or 'wizard' that can deal will all questions. However, a commonly used method is to use the first half of your essay to complete the analysis and the second half to evaluate - this is an easy approach to master, and can be used to answer most microeconomic and macroeconomic essays. More on this later.
What the mark scheme tells us
The mark-scheme for a 25-mark question is typically based on the ' levels ' method, with marks allocated in the following way:
4 marks for correctly demonstrating knowledge and understanding of economic concepts and models
4 marks for applying your knowledge and understanding to the 'context' put before you - this case a chocolate manufacturer
8 marks for providing an analysis of the decision (in this case, to raise price) - i.e. what are the expected effects, consequences and results
9 marks for evaluating a decision (question, issue, policy, or problem) based on your judgment , with reference to the problems or risks associated with the decision (policy, problem etc.)
Points to note
- Exam boards often state that, in a 25-mark question, definitions are not specifically required , but it is good practice to define key economic terms that are specific to economics, and to the question.
- Application does not happen in one section of your answer, but should run throughout your answer . In other words, answers that are purely theoretical and detached from the context will not earn high marks.
- For analysis and evaluation, developing a chain of reasoning is essential - ( read more on chains of reasoning ) you have to show exactly how you arrived at a point, judgment or conclusion. A carefully chosen, well draw, accurately explained and fully integrated diagram is essential for effective analysis. This is only possible if you start out by making your assumptions clear.
- For evaluation, it is essential that you provide an alternative approach , (alternative decision, policy etc.) and that your conclusion is not just a summary but a 'weighted' judgment .
- While you only have 30 minutes to write, it is essential you plan your route through your answer - 4-5 minutes planning is worth its weight in gold!
So, lets have a look at a couple of ways to deal with a 25-mark question. Both have similar openings and conclusions, but start out with different assumptions.
' Evaluate the decision by a chocolate manufacturer to raise the price of its 'luxury' box of chocolates .'
There are several factors a chocolate manufacturer will take into account when making a decision about its price. Factors affecting this decision depend on the market structure it operates in, the level of competition it faces, its size and ownership structure. These will affect its main business objective, which in turn will affect its decision regarding price and non-price factors.
We will assume that the chocolate manufacturer's objective is to maximise profits and that it is a price maker and facing a downward sloping demand curve. This means that it is not operating in a highly competitive market, and can raise price without suffering a complete collapse in sales. Profit maximisation arises at the output where MC=MR, which in the diagram is quantity Q. At profit maximisation, the area of supernormal profits (SNP) is area p a b c.
At this quantity, marginal revenue equals marginal cost, which means that any change in price or quantity produced will move it away from profit maximisation. For example, if the chocolate manufacturer increases price to P1, demand will contract along the demand (AR) curve, from 'a' to 'v', resulting in equilibrium quantity falling to Q1. At Q1, MR is greater than MC, which means there is an opportunity cost because the firm could reduce price and produce more, which would lead to an increase its supernormal profits. So, reducung price and producing extra marginal units of output will add to SNP until MC=MR is reached. Hence, in terms of achieving its profit maximising objective, an increase in price above 'P' is clearly counter-productive. This is supported by the probability that demand for 'luxury' chocolates is price elastic, and the producer is operating in the elastic range of the AR curve. As a result, any increase in price will reduce total revenue, and also reduce SNP, which falls to area P1 v w x.
However, there are issues with this analysis. Are the assumptions about the chocolate producer and its market valid? Is the chocolate producer targeting profits, or attempting to achieve a different objective? Will there be negative, and even unexpected consequences of the price rise?
The assumptions regarding the market structure certainly might not hold - in a less competitive market, with fewer firms, the price rise may have a much smaller effect because consumers have less choice. Demand may be more inelastic than predicted, especially if there is loyalty to the brand of chocolate - even though it is a luxury product.
Also, the chocolate producer may have previously been a revenue or sales maximiser and may have decided to change its strategy from revenue or sales maximising to profit maximising. As a revenue or sales maximiser price will be set at a lower level, to stimulate sales or gain more revenue. Management salaries or bonuses may be connected with sales, hence a low price will help the firm achieve this objective. The price increase will move it towards profit maximisation rather than away from it, and help it achieve its new objective. Alternatively, the producer may be a 'profit satisficer' looking to increase its profits but not maximising them. In any of these cases, the price rise might be a rational decision.
It is not known whether rivals will keep their prices on hold, reduce them or raise them to match the firm's price increase. If the firm has a few close competitors, then these firms may be interdependent, meaning it may be more beneficial to keep prices on hold to reduce uncertainty.
Furthermore, the price rise could encourage unwanted new entrants, attracted by the opportunity presented. Raising price could also send a signal to existing producers to launch their own 'luxury' version of the product.
Of course, there may be alternative decisions to consider to help it achieve its objectives, such as changing its non-price activities. So, the price rise could be justified if an effective marketing campaign could help increase demand (AR) and, diagrammatically, shift the AR (and MR) curve to the right, as shown.
In this case, profits are maintained, or even increased, as shown, with lower supernormal profits at area P1 k r m.
Taking a wider view, price rises reduce consumer surplus, and if personal incomes remain constant, consumer will have less income to spend on other goods and services, and the price rise will cause a negative income effect. Of course, a rise in the price of chocolate would not have the same effect as a rise in interest rates or house prices, so the income effect is very small.
In conclusion, the decision to raise prices cannot be judged without understanding the nature of the market, the level of competition and the firm's current objectives, and compared with alternatives. There is also the wider economic context to consider, such as whether the economy is in a recession, with pressure on disposable income, or whether the economy is growing, with consumers feeling confident. There are clearly risks associated with an increase in price, and it might be less risky not to raise price, and put more effort into non-price strategies. However, if the assumptions that the firm is already a profit maximiser, that there are no other changes to its non-price activity, and that the behaviour of other chocolate producers does not change, then a price rise seems unjustifiable as it would fail to achieve its dominant objective - to maximise profits - and raising price would, in this case, be an irrational decision.
Answer two - the alternative answer
We will assume that the chocolate manufacturer's objective is to maximise profits and that it is a price maker and facing a downward sloping demand curve. We will also assume that it currently is not profit maximising, but producing at an output greater than profit maximisation, at output Q, and a lower price, at P in the following diagram. Profit maximisation arises at the output where MC=MR, which in the diagram is quantity Q1, and price P1.
At the quantity Q, while marginal revenue is negative at 'f' and below marginal cost at 's', the chocolate manufacturer still makes a supernormal profit, shown as the area SNP (area Pvwx). Also, at the current price of P, price elasticity of demand is inelastic because, in the diagram quantity demanded, Q at price P is to the right of the mid-point of the demand (AR) curve. Given that, at the mid-point, PED equals (-) 1.0, which is where MR=0, at its current output, PED must be inelastic.
Given these assumptions, a decision to increase price above P will help the manufacturer achieve profit maximisation. Because the firm operates in the inelastic portion of its demand (AR) curve, the planned price rise reduces the quantity demanded, to Q1, but increases total revenue - at least up to the output where MR=0. The reduction in output that follows means that the variable costs of production fall, which means that marginal costs fall (from 's' to 't'), while at the same time marginal revenue increases from 'f' to 't'. Assuming profit maximisation is still the dominant objective, the price rise is clearly beneficial, as it leads to increased profits (area P1a b c) resulting from the lower marginal cost and the higher marginal revenue.
However, there issues with this analysis. Firstly, are the assumptions about the chocolate producer valid, secondly, is the chocolate producer wishing to increase profits, and thirdly, will there be any negative, and even unexpected consequences of the price rise?
The assumptions regarding the market structure certainly might not hold - the market could be much more competitive, and approach perfect competition. This would result in a very different outcome for the producer, especially in terms of a price elasticity of demand, which rises with increased competition. In a more competitive market, there are more choices for the consumer, and any price rise by one firm may result in falling revenue. Demand may be more elastic than predicted, especially because the price rise is for the 'luxury' version of the box of chocolates, where demand is likely to be more elastic.
Also, the chocolate producer may not be a profit maximiser, but may instead be a revenue or sales maximiser, in which case the price rise could move it away from maximising sales or revenue points. If the firm is a large producer where there is a separation of ownership and control, it is more likely that other 'managerial' objectives dominate decision making. If, for example, the firm is looking to maximise sales volume, perhaps because management salaries or bonuses are connected with sales, then a price rise would not be beneficial.
It is not known whether rivals will keep their prices on hold, reduce them or raise them to match the firm's price increase. If the firm has a few close competitors, then the fact that these firms may be interdependent means that it may be more beneficial to keep prices on hold and reduce uncertainty.
Of course, there may be alternative decisions to consider to help it achieve its objectives, such as changing its non-price policy. So, if there is also a successful marketing campaign designed to increase sales, or build a brand, price increases could be postponed until the brand is well established.
In conclusion, the decision to raise prices cannot be judged without understanding the nature of the market and competition and the firm's current objectives, and compared with alternatives. There is also the wider economic context to consider, such as whether the economy is in a recession, with pressure on disposable income, or whether the economy is growing, with consumers feeling confident. There are clearly risks associated with an increase in price, and it might be less risky not to raise price, and put more effort into non-price strategies. However, if all the assumptions listed above are fully met, then a price rise seems justifiable in that the firm can achieve its dominant objective - to maximise profits.
These are two answers which use a similar structure, and common introduction and conclusion - but start with different assumptions, and therefore have a different analysis, and evaluation.
There are other several possible approaches to this question, and other evaluative points that could have been included. For example, there could have been more emphasis on what rivals might do, and there could be more robust questioning about exactly how much the price is being increased by, and whether this is just a temporary strategy. The essay could also have raised the question of the possible external effects arising from less output and consumption (namely fewer negative consumption and production externalities). However, with the time constraint in the examination room, it is not possible to cover every 'blade of grass' and some good points may have to be sacrificed.
Finally, the 'starting point' and assumptions could have been different, which would have led to a different analysis.
Conclusion and key takeaways
Having a structure to help you tackle an essay-style question is very important.
Both essays use the same four-part structure :
- Part 1, the analysis - making assumptions, and using the correct diagram to show how a decision or policy will work to achieve an objective.
- Part 2, the evaluation begins with ' the bridge ' of the essay - assumptions are questioned and probably changed.
- Part 3 the full evaluation , where an alternative or alternatives are explained based on the change of assumptions.
- Part 4, the conclusion , where the evidence or strength of argument is assessed, and the decision, policy or assertion is 'accepted in full', 'accepted in part' or 'rejected' in favour of the alternative(s).
Finally, it is clear how important diagrams are in analysis and evaluation, and helping develop a logical chain of reasoning - so ensure that you have undertaken enough practice in constructing, applying and integrating diagrams to a wide range of past questions.
Other tips:
How to study economics
How to write the perfect conclusion
How to answer data response questions
How to include chains of reasoning
Writing for Economics
Up: Economics Network > Writing for Economics

Essay writing
The idea of setting essays is to offer you the chance to make a longer, more complex argument. Nonetheless, in the model we recommend, the fundamentals remain the same. In each paragraph, a flow of main idea (thesis) — explanation / reasoning (justification) — evidence / example (support) is an excellent structure to use. If you read through academic writing, you will find this structure over and over. The same is true for professional writing. There are of course other structures, however this one always works and makes you sound concise and clear.
An essay has conventional sections that it is wise to follow. These are an introduction, main body and a conclusion. The 'LSE' essay structure can be described as 'say what you're going to say (intro), say it in detail (main body), say what you've said (conclusion)'. Although this may appear repetitive, it offers the reader great clarity. Also, if you think about the executive summary, background, analysis and conclusions / recommendations sections of a business report, you can see that a similar structure holds.
In your essay, try to follow this structure for your essay sections.
Statement about the context of the question — explain why the question in important (either in the 'real' world or for the discipline of economics)
Give your answer to the question
Summarise your argument in support of this answer — this summary should match the order of your paragraphs
Decide on the most logical order of your paragraphs — this might be importance, chronology or causation, but the basic flow should be simple and clear
Start each paragraph with a sentence that clearly addresses the question itself — this will be your thesis for the paragraph and if a reader only read these opening sentences, they should make sense one after the other and provide a summary of your argument Follow the opening 'topic' sentence with your reasoning and evidence for why this opening statement is valid. Be specific, not general. The more detail you can bring in, the more expert you will sound and the more persuasive your argument will be
Conclusion Summarise your argument again — as you did in the intro (different words though!)
Restate your answer to the essay question
So what? — say what the significance of your answer is either in the 'real' world or to the discipline of economics
Bibliography
List the books / articles you read while researching your answer
Below you'll find two essays written by students last year. Bearing the above in mind, decide which one makes the clearer argument and which, therefore, got the higher mark.
In the year 2000, there were auctions of spectrum rights for third generation mobile telephones in several European countries. These auctions generated very different amount of revenue in different countries. How can this be explained?
Auction theory as a very useful brunch of game theory is of the great interest of modern economists. Among other reasons of its popularity stands direct importance of its ideas to modern businesses and governments. Nowadays any business sector is more or less competitive, which requires all it's participants to be dynamic and creative. Modernization and expansion is a vital part of modern business world. Governments, as owners of resources that allow businesses to expand and modernize, are always ready to sell those resources as it will eventually help businesses and certainly bring revenues.
The best way for government to sell available resources is to declare an auction. That's where auction theory comes into play. Modern auction theory is a very powerful tool for designing auctions of very profitable kind. Proper auction design will rise maximum amount of money for the government and provide companies with resources they need. However actions that maximize profits for the government have a direct influence also on the life of the citizens, as Dixit puts it: "...because of significant contributions the budget, auctions affect important macroeconomic magnitudes, such as interest rates".
So, auctions held by government, and to be more specific properly designed actions directly influence the life of modern country. In this essay I would like to make a kind of short review of auctions of spectrum rights for third generation mobile phones held in Europe in year 2000. The peculiarity of these auctions lies in the fact that revenues that were generated by European governments are different as a result of differently designed actions they held. This fact allows as to trace features of the auctions that were successful and resulted in relatively high revenues for the government.
There were 6 European countries to held spectrum right auctions in 2000. They were: United Kingdom, Austria, Germany, Italy, Netherlands and Switzerland. Let's start with United Kingdom as it was the first country to hold such kind of auctions.
Strategy that United Kingdom had chosen was selling 5 licenses during classical ascending auction. Auction resulted in huge revenues: 650 euros per capita. Firstly it should be said that auctions as any normal business activity should be competitive in order to be effective. UK spectrum auction was relatively competitive attracting 13 participants. There are several reasons why this action attracted so many participants. Firstly, UK was the first country in the world to hold spectrum rights auction. Participants were not completely aware of the usefulness of 3G cell phones, but were eager to get competitive advantage in the new generation mobile communication technology. Secondly, UK sold 5 licenses to the market with 4 major phone operators. This fact attracted new entrants, since at least one of the licenses can be potentially won by new entrants to the market. Both this facts generated highly competitive auction environment and limited possible collusions. Result of the auction was a huge success for UK government.
The next country to run spectrum rights auction in 2000 was Netherlands. This auction raised 170 euros per capita. Reason of such flop, comparing to the British result was lack of competition. When auction were run there were 5 major phone operators for 5 licenses to be sold. Few entrants decided to participate in the auction, since everybody was sure that 5 licenses will be distributed among market leaders. Another factor that made things even worse was the fact that that was an ascending auction. In this case with few participants there is a risk of collusion among market leaders. Netherlands would have generated much more money if they would some how encourage competition and change the action design in such a way that it would be possible for participants other than market leaders to place bids independently of each other to reduce collusion (sealed bid).
Italy generated 240 euros per capita and attracted 6 participants. Italy intentionally reduced amount of participants by imposing a requirements that participant of the auction must satisfy. Such situation combined with the fact that Italian auction was ascending could result in possible collusions among competitors. As a result wrong auction design resulted in low revenues.
Swiss auction was a real flop. They generated only 20 euros per capita. Here amount of participants was also artificially limited by allowing participants to join into the groups. And the price that government accepts was also reduced for some reason. Number of participants was sufficient to run profitable auction, but combination of officially permitted collusions and low reserve price resulted in absolutely insufficient revenues.
German and Austrian auctions were similar. Number of participants in both countries' auctions was low, which means that there were risks of collusion. Both countries sold licenses in blocks, allowing "number of winners be determined by bidders". Additionally Austrian government set a very low reserve price. Germany and Austria generated 615 and 100 euros per capita in revenue respectively. Germany designed auction in such a way that bids of two main market players were rationalized in a way that it resulted in high revenues.
Generally, the main difference in revenues generated from spectrum rights auctions can be explained by the difference in chosen auction design. Different auction design results in different amounts of money in revenues. Countries that tried to facilitate competitive bidding and limited the possibilities of collusion enjoyed high revenues.
Klemperer say that what really matters in auction design is "robustness against collusion and attractiveness to entry". Exactly the combination or lack of one of this factors resulted in the difference in the revenues generated by European countries. Any country that wants to increase revenues from auction must try to facilitate the competition among bidders by trying to make participation in auction as attractive as possible and eliminating any barriers for participation. There should be no cooperation between participants, as it will result in lower bids and as a consequence in low revenues. Countries should not choose auction design that facilitates collusion, as ascending auction in our case.
Of course there are several other reasons for difference in revenues, among them there is a fact that UK as a country that run the first spectrum rights auction in the world, might have enjoyed high revenues simply because participants were new to the licenses and had no idea of their true value. Overall economic situations in the counties as well as political might also result in differences in revenues. But the main reason for difference in profitability of the spectrum licenses auctions is difference in auction designs which were effective in some countries and not in the others.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
A.K. Dixit and S. Skeath, Games of Strategy , 2nd edition, Norton, 2004
Paul Klemperer, Auctions: Theory and Practice Electronic version of book on http://www.paulklemperer.org/index.htm
In the year 2000, European auctions of 3G mobile telecommunication licenses raised over 100 billion euros in government revenues. The countries that participated were United Kingdom, Netherlands, Italy, Switzerland, Germany and Austria. There was a big differential between revenues raised in each country with United Kingdom leading at 650 euros per capita and Switzerland coming in last at 20 euros per capita. The reasons for this big discrepancy in revenues is likely due to poor auction designs and the sequence in which the auctions took place.
When it comes to auction design, the two crucial components are attracting entry and preventing collusion. Ascending auctions encourage bidders to act collusively and deter weaker potential bidders as they know that the stronger bidder will always out bid him. On the other hand, (first-price) sealed-bid auctions act in the opposite direction from ascending auctions. It does not give bidders a chance to collude and encourages weaker bidders to participate. However, the disadvantage of using a sealed-bid auction is that it is more likely to lead to inefficient results than an ascending auction. The reason for this is that sometimes bidders with a lower value may beat opponents with a higher value. Hence, there is no perfect auction design and they must be customized to suit different environments and targets.
United Kingdom was the first to hold the auctions and they are a good example of how a well-planned auction design and good marketing strategies can lead to a favourable outcome. As there were five licenses and 4 incumbents, they had an ascending auction. To prevent collusion, each license could not be shared and each bidder was allowed no more than one license. Also, the fact that at least one license was available to new entrants lead to fierce competition from nine new entrants. To top it all off, UK had a solid marketing strategy which was planned over three years (1997 - 2000). All this helped contribute to UK raising 39 billion euros and being the most successful out of all the countries that took part in the 3G auctions.
Netherlands, Italy and Switzerland made the mistake of following UK and carrying out an ascending auction when a sealed-bid auction would have served them better. This resulted in revenues less than that achieved by UK.
In the case of Netherlands, they had five licenses and five incumbents. This deterred new entrants as well as facilitated collusion. For example, Deutsche Telekom colluded with local incumbents to bid for a 3G license. A sealed-bid would have worked better as this would have discouraged joint bidding, raise higher revenues as well as give new entrants a glimmer of hope.
Italy had their auction next but failed to learn from Netherlands and UK. Their auction design was not robust and failed to adapt to the environment in Italy. They adopted the UK design but had the additional rule that if bidders did not exceed licenses, the number of licenses would be reduced. They did not realize that having one more bidder than license does not assure that the outcome will be competitive. Also, Italy had failed to anticipate that firms would react differently to those in Netherlands and UK as they now had more information. Hence, weaker bidders were discouraged by previous auctions and did not bother to participate and since the participation rate was low, it made it easier for the strong bidders to collude. A bad auction design that was not tailored to the Italian environment and a low reserve price resulted in Italy only earning less than 25 billion euros.
Switzerland was the most unsuccessful amongst all the countries that held the auctions. It raised only 20 euros per capita in its ascending auction and this can be attributed to an unfeasible auction design, badly formulated rules and an absurdly low reserve price. Since the beginning, weaker bidders were deterred by the auction form. They felt that they did not stand a chance against the strong bidders and hence did not bother participating. This resulted in little competition. Furthermore, The Swiss government committed auction suicide when they permitted last-minute joint-bidding! This resulted in nine bidders colluding to become just four. The last mistake that the Swiss government made was to set a reserve price that was way too low. Since there were four licenses and four bidders, bidders ended up paying only the reserve price.
Germany and Austria chose a more complicated auction design.
Germany's auction design was an ascending auction of twelve blocks of spectrum from which bidders could create four three-block licenses or six two-block licenses. Germany's auction design was very susceptible to collusion and deterring new entrants but they were lucky and managed to earn high revenues.
Austria, on the other hand, adopted Germany's auction design but was not so lucky and only earned 100 euros per capita. The reason for this was that there were 6 bidders competing for 12 blocks of spectrum and a very low reserve price (one-eight of the reserve price in Germany). So instead of trying to get three blocks of spectrum, the bidders divided the 12 blocks of spectrum equally and paid the reserve price. This reason lead to Austria earning less per capita revenue than UK and Germany.
The other factor that affected the amount of revenue earned by each country was the sequence in which the auctions took place. Looking at the results of the 3G auctions held in 2000, it can be seen that the most successful auctions were the first of their type (United Kingdom and Germany). The reason for this is that between auctions, bidders learnt from previous auctions, came up with new strategies and learnt more about their rivals. However, the auction designs remained almost the same and were unable to keep up with the new ideas the bidders had come up with. This resulted in the later auctions not being as successful as the first.
In conclusion, the reason for the different revenues earned amongst the countries that took part in the 3G auctions is due to the auction designs and the sequence in which they took place. Revenues depend on how well the auction design is able to attract entry and prevent collusion. Also, it has to be able to adapt to new environments. For example, a good auction design takes into account the information bidders have and the knowledge they have gained from previous auctions. A sensible reserve price is of high importance as well and should not be overlooked like in the case of Switzerland and Germany. Lastly, auction design is not "one size fits all" and the failure of the government to design an auction that suited the country's environment lead to different revenues being earned.
References:
A.K. Dixit and S.Skeath, Games of Strategy, 2 nd edition, Norton, 2004
Professor Kenneth Binmore, "Economic Theory Sometimes Works"
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on October 30, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 13, 2023.
- Restate the problem statement addressed in the paper
- Summarize your overall arguments or findings
- Suggest the key takeaways from your paper
The content of the conclusion varies depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument through engagement with sources .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: restate the problem, step 2: sum up the paper, step 3: discuss the implications, research paper conclusion examples, frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem . You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture.
While you are restating a problem you’ve already introduced, you should avoid phrasing it identically to how it appeared in the introduction . Ideally, you’ll find a novel way to circle back to the problem from the more detailed ideas discussed in the body.
For example, an argumentative paper advocating new measures to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture might restate its problem as follows:
Meanwhile, an empirical paper studying the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues might present its problem like this:
“In conclusion …”
Avoid starting your conclusion with phrases like “In conclusion” or “To conclude,” as this can come across as too obvious and make your writing seem unsophisticated. The content and placement of your conclusion should make its function clear without the need for additional signposting.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Having zoomed back in on the problem, it’s time to summarize how the body of the paper went about addressing it, and what conclusions this approach led to.
Depending on the nature of your research paper, this might mean restating your thesis and arguments, or summarizing your overall findings.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
In an argumentative paper, you will have presented a thesis statement in your introduction, expressing the overall claim your paper argues for. In the conclusion, you should restate the thesis and show how it has been developed through the body of the paper.
Briefly summarize the key arguments made in the body, showing how each of them contributes to proving your thesis. You may also mention any counterarguments you addressed, emphasizing why your thesis holds up against them, particularly if your argument is a controversial one.
Don’t go into the details of your evidence or present new ideas; focus on outlining in broad strokes the argument you have made.
Empirical paper: Summarize your findings
In an empirical paper, this is the time to summarize your key findings. Don’t go into great detail here (you will have presented your in-depth results and discussion already), but do clearly express the answers to the research questions you investigated.
Describe your main findings, even if they weren’t necessarily the ones you expected or hoped for, and explain the overall conclusion they led you to.
Having summed up your key arguments or findings, the conclusion ends by considering the broader implications of your research. This means expressing the key takeaways, practical or theoretical, from your paper—often in the form of a call for action or suggestions for future research.
Argumentative paper: Strong closing statement
An argumentative paper generally ends with a strong closing statement. In the case of a practical argument, make a call for action: What actions do you think should be taken by the people or organizations concerned in response to your argument?
If your topic is more theoretical and unsuitable for a call for action, your closing statement should express the significance of your argument—for example, in proposing a new understanding of a topic or laying the groundwork for future research.
Empirical paper: Future research directions
In a more empirical paper, you can close by either making recommendations for practice (for example, in clinical or policy papers), or suggesting directions for future research.
Whatever the scope of your own research, there will always be room for further investigation of related topics, and you’ll often discover new questions and problems during the research process .
Finish your paper on a forward-looking note by suggesting how you or other researchers might build on this topic in the future and address any limitations of the current paper.
Full examples of research paper conclusions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
While the role of cattle in climate change is by now common knowledge, countries like the Netherlands continually fail to confront this issue with the urgency it deserves. The evidence is clear: To create a truly futureproof agricultural sector, Dutch farmers must be incentivized to transition from livestock farming to sustainable vegetable farming. As well as dramatically lowering emissions, plant-based agriculture, if approached in the right way, can produce more food with less land, providing opportunities for nature regeneration areas that will themselves contribute to climate targets. Although this approach would have economic ramifications, from a long-term perspective, it would represent a significant step towards a more sustainable and resilient national economy. Transitioning to sustainable vegetable farming will make the Netherlands greener and healthier, setting an example for other European governments. Farmers, policymakers, and consumers must focus on the future, not just on their own short-term interests, and work to implement this transition now.
As social media becomes increasingly central to young people’s everyday lives, it is important to understand how different platforms affect their developing self-conception. By testing the effect of daily Instagram use among teenage girls, this study established that highly visual social media does indeed have a significant effect on body image concerns, with a strong correlation between the amount of time spent on the platform and participants’ self-reported dissatisfaction with their appearance. However, the strength of this effect was moderated by pre-test self-esteem ratings: Participants with higher self-esteem were less likely to experience an increase in body image concerns after using Instagram. This suggests that, while Instagram does impact body image, it is also important to consider the wider social and psychological context in which this usage occurs: Teenagers who are already predisposed to self-esteem issues may be at greater risk of experiencing negative effects. Future research into Instagram and other highly visual social media should focus on establishing a clearer picture of how self-esteem and related constructs influence young people’s experiences of these platforms. Furthermore, while this experiment measured Instagram usage in terms of time spent on the platform, observational studies are required to gain more insight into different patterns of usage—to investigate, for instance, whether active posting is associated with different effects than passive consumption of social media content.
If you’re unsure about the conclusion, it can be helpful to ask a friend or fellow student to read your conclusion and summarize the main takeaways.
- Do they understand from your conclusion what your research was about?
- Are they able to summarize the implications of your findings?
- Can they answer your research question based on your conclusion?
You can also get an expert to proofread and feedback your paper with a paper editing service .
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, April 13). Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved September 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-conclusion/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing a research paper introduction | step-by-step guide, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, checklist: writing a great research paper, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Essay Editor
How to End a College Essay: Strategies and Examples

Writing a college essay takes skill, but making a strong college essay conclusion is often the most important part. A great ending can make a big impact on your readers and bring your main ideas together. This guide will walk you through four strategies that will help you create impactful conclusions that resonate with your audience.
1. Writing a Memorable College Essay Conclusion
The conclusion of your essay is your last chance to strengthen your main points and leave a lasting impression. A well-written ending can make your whole essay better and more memorable.
Successful Essay Ending Examples
Here are some great ways to end an essay:
- Share a thoughtful idea that connects to your main point, giving a sense of closure and understanding.
- Quickly go over your main points, showing them in a new way.
- Discuss why your topic matters beyond just your essay.
- Link back to your introduction, making your writing feel complete.
Example:
"When I started looking into how music affects the brain, I didn't know I'd find a connection to my grandmother's struggle with Alzheimer's. I learned that songs people know well can often bring back memories for patients, even when they have trouble talking. This discovery changed how I see music's power and gave me a new way to connect with my grandmother. When we hum her favorite songs together, I see hints of recognition in her eyes, reminding me that sometimes, big scientific ideas can have very personal effects."
Common Mistakes in Ending an Essay
Avoid these problems when writing your college essay conclusion:
- Adding new ideas: Your conclusion should bring together existing points, not introduce new information.
- Just repeating your main point: While it's important to remind readers of your main idea, simply saying it again word-for-word doesn't work well.
- Using overused phrases: Don't use expressions like "In conclusion" or "To sum up."
- Stopping too suddenly: Make sure your conclusion gives a feeling of completion and doesn't leave readers hanging.
Aithor's advanced language model can help you write compelling conclusions that avoid these common mistakes and enhance the overall impact of your essay.
2. Thought-Provoking Questions: A Powerful Way to End an Essay
Ending an essay with a question that makes people think can get your readers interested and encourage them to keep thinking about your topic. This approach leaves a strong impression and can make your essay more memorable.
"After looking at how social media changes how we see ourselves, we're left with an important question: Can we find a way to share our lives online while still living them fully offline? Maybe the answer isn't choosing between the online and real worlds, but learning how to connect well in both."
When using this method, make sure your question is:
- Related to your essay's main topic
- Open-ended, encouraging deeper thought
- Not easy to answer with just "yes" or "no"
3. How to End Your College Essay with a Call to Action
A call to action (CTA) in your conclusion can encourage your readers to do something based on the ideas you've talked about. This works well for essays about social issues, environmental problems, or personal growth topics.
"In this essay, we've looked at the problem of plastic in our oceans. Now, it's time to help fix it. Start by replacing one single-use plastic item you use every day with something you can use again. It could be as simple as using a reusable water bottle or bringing your own bags to the store. Tell your friends and family what you're doing. By taking these small steps, we're not just making less waste; we're starting a chain reaction that can lead to cleaner oceans and a healthier planet."
When writing a CTA for your college essay conclusion, make sure it's:
- Clear and easy to write
- Directly related to your essay's main points
- Something your readers can actually do
Aithor can assist you in writing perfect calls to action that connect with your readers and fit well with your essay's content.
4. Personal Anecdotes: An Engaging Essay Ending
Ending an essay with a personal story can help your readers feel connected to you and strengthen your main message. This approach makes your writing more relatable and human.
"Last summer, I helped at a local animal shelter. One day, they brought in an older, scruffy dog named Max. For weeks, people passed him by, always choosing younger, cuter puppies instead. I started spending extra time with Max, and slowly, his playful side came out. When a family finally took him home, the happiness on their faces – and Max's wagging tail – showed me how important it is to give every living thing a chance. This taught me more about patience, unfair judgments, and the power of second chances than any book ever could."
When using a personal story to end your college essay:
- Make sure it relates to your main topic
- Keep it short and powerful
- Use clear language to paint a picture for your readers
Tips on How to End a College Essay
To write a strong conclusion, think about these extra tips on how to end a college essay:
- Wrap up your main points clearly while suggesting how they might apply to other things or future ideas to keep your readers thinking.
- Make sure your conclusion sounds like the rest of your essay for a smooth, polished finish.
- Don't weaken your arguments by sounding unsure in your conclusion.
- Be extra careful with grammar and punctuation in your conclusion, as it's the last thing your readers will remember.
- Write your conclusion to connect with your specific readers, whether they're college admissions staff, teachers, or other students.
- Write a short and powerful conclusion that drives your main points home without repeating too much or using too many words.
Remember, your conclusion is your last chance to make a strong impression. Take your time to write it carefully, making sure it ties together your main points and shows why your essay matters.
For those wondering how to end a reflection paper, Aithor can help you improve your college essay conclusion, making sure it's polished, powerful, and fits your specific needs. This top writing tool can help you refine your essay ending examples and give you guidance on how to end a reflection paper or any other type of school writing.
Related articles
Top 10 use cases for ai writers.
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
Can Plagiarism Be Detected on PDF?
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism: Do They Really Differ?
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Economics news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Economics Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
- Exam Support
Essay on Oligopoly and Collusion
Last updated 3 Feb 2019
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Here is what I feel is a superbly clear and well-structured essay answer to a question on the economic and social effects of collusion within an oligopoly.
Evaluate the view that collusion between firms in an oligopoly always works against consumer and society’s interests. Use game theory in your answer.
An oligopoly is where the industry or market is dominated by a few producers/firms with a high level of market concentration, where the component firms have a high level of interdependent decision making. Collusion can be tacit and/or explicit, and the aim of which is to achieve higher supernormal profits, with the firms as a whole achieving joint profit maximisation. Collusion between firms is harmful to consumers. This is because firms collude to raise prices, as mentioned earlier, resulting in the price level seen below. This reduces the consumer surplus available, reducing the welfare of individuals. This can often be highly regressive, if the impact of increased prices, such as with the Big Six Gas Suppliers, has a disproportionate impact on the less well off. Furthermore, because firms are working together, with internal quotas to divide up sales, there is less need to compete, resulting in less dynamic efficiency. This results in less innovation, and thus little improvement in the quality of products available to individuals. Indeed, the UK Competition and Markets Authority supports this claim, arguing that collusion can result in “reductions of output, efficiency, innovation and choice, all of which are harmful to consumers.” An example of this can be seen with Apple, who were sued by consumers for price-fixing with publishers to force consumers to over pay for e-books.
However, collusion between firms can often derive benefits for consumers. For instance, tacit collusion includes firms who monitor what other firms sell to ensure that they are matching the cheapest price in a geographical area, or who market that consumers are “never knowingly undersold” such as John Lewis. This is a case in which firms are technically engaging in tacit collusion, but which may also result in driving down of prices as firms seek to match improvements in cost efficiencies made by other firms. This is also true with products such as mobile phone contracts where it is easy to compare prices.
Collusion in an oligopoly can hugely benefit firms, which can have beneficial consequences for society. For instance, collusion between coffee growers allows small firms to push for fairer prices against more dominant monopsonistic corporations such as Starbucks. Furthermore, because these producer cooperatives like Fairtrade are often based overwhelmingly in less developed regions, this can also be useful in helping to alleviate extreme poverty. Furthermore, collusion allows for firms to lower the costs of competition, that can then be passed onto consumers. Because oligopolies exist in highly concentrated markets dominated by a few firms, there is often a huge degree of branding and differentiation that needs to take place in order for firms to stand out, e.g. with the UK retail banking industry with firms such as Barclays and HSBC. If all firms engage in marketing wars, there is no net societal benefit. However, if firms collude, they can reduce the need to fund these marketing wars, that can allow for cost savings to be passed onto consumers. Additionally, collusion allows for agreed upon industry standards, for instance with procedures in testing on humans in pharmaceutical research, which benefits both consumers and firms.
However, the extent to which this occurs depends on a few factors. Firstly, the vast majority of collusion that takes place isn’t that of poor farmers working together - oligopolies are more concentrated industries with very high barriers to entry, such as the Big Four Accountancy Firms, and pharmaceutical companies. Furthermore, the benefits that accrue from firms working together are dependent on those firms passing those cost savings onto consumers - however, if they are all explicitly colluding, they may decide to spend that money on share buy-back schemes and dividends, which may not benefit society at large. Indeed, in 2017, US firms spent more money on share buy-backs than they did on research and development. Lastly, the benefits from firms agreeing upon industry standards are likely to be very marginal given the government and regulatory bodies, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) tend to set industry standards centrally.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the extent of the impact on consumers and firms depends fundamentally on how long the oligopoly is able to carry on collusion - we can analyse this through game theory. Assuming the following pay offs in a cartel such as OPEC, where states agree to collude to reduce production levels and benefit from a higher price:
If all firms cooperate, they will achieve £4bn revenue. However, if one firm decides to defect and to increase production while still gaining from higher prices, they will gain £5bn. The socially optimal equilibrium in this model (for firms) is to cooperate, because the total utility is greater than any other option. However, this is an unstable equilibrium: no matter what the other firm does, each agent is better off by defecting, resulting in a Nash equilibrium of Defect, Defect. Indeed, this model can be shown by how in October 2018, Iran accused Saudi Arabia and Russia of breaking OPEC’s agreement on cutting output. Thus, the effects of collusion are very much dependent on how long it is able to last.
Author: Cary Godsal (February 2019)
More resources available here on the topic of oligopoly
- Tacit Collusion
- Overt collusion
- Game Theory
- Nash Equilibrium
You might also like
Oligopoly - kinked demand curve.
Study Notes

John Nash celebrated on More or Less
30th May 2015
Three-O2 Merger Plans Under Scrutiny
5th February 2016
Efficiency in Market Structures
Topic Videos
British Gas hikes electricity prices by 12.5%
2nd August 2017
Co-op joins the price war in the funeral industry
10th September 2018
Government Failure - Selection of Revision MCQs
Practice Exam Questions
Tesco Raises Prices for Meal Deals
22nd October 2022
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

How to Write a Band 6 HSC Economics Essay
Writing a Band 6 HSC Economics essay can be difficult because the essay questions can vary from addressing a specific section of the syllabus to having a broad focus and therefore requiring synthesis of entire topics.
Furthermore, there are two HSC Economics essays in the HSC exam, which make up 40 marks of the whole exam!
Section III – is a stimulus based economic essay response where you MUST make reference to the stimulus provided and integrate it into your response. Section IV – a free response economic essay.
This article aims to therefore streamline the writing process and provide a sustained, logical and cohesive approach that is backed by findings from experienced HSC Economics markers: the ones who mark hundreds of essays year in year out.
Ready to learn how to ace your HSC Economics Essay? Let’s jump in!
Here is the example question we’re going to use throughout this article to demonstrate what to do to get that Band 6 in your HSC Economics Essay ( Question 27 of the 2016 HSC ).
Editor’s Note: Although this post was made in 2018, any sample responses will be written as if they were written in 2016, reflecting the current state of the economy at the time.

Step 1: Plan Your Response Step 2: Finish Your Introduction Strong Step 3: The Writing Process Step 4: Practise Writing HSC Economics Essay Plans
Step 1: Plan Your Response
Use the first page of your writing booklet to sketch a plan of your response.
In fact, this was often what I would do first upon beginning an Economics exam. I’d develop a plan for my essays and then go back to the Multiple Choice section.
This achieved two things:
It warmed up my mind so that I was ready to engage with Section I and Section II More importantly, this ensured I would not forget my essay plans throughout the exam and I could readily return to my plan to jog my thought process.
This is critical because the Economics essay emphasises a logical progression of ideas.
Therefore, in many ways, an essay plan allows you to visualise your thought process and reduce the chance of you forgetting your train of thought or worse, going on a tangent and including irrelevant details.
This helps keep your response sustained, which is a key component of the A range marking criteria. Your essay must continually drive towards developing your thesis – the actual answer to the essay question itself.
In saying so, before we plan, we must understand the NESA directive verbs. This will determine the level of depth and the approach the markers are looking for.
If you’re unsure about your directive verbs, check out NESA’s glossary of key directive verbs !
How to Plan for an HSC Economics Essay:
The most important thing about any essay is the answer to the question itself with your thesis. All points, arguments and statistics are simply used to support it.
As a result, begin the plan by writing a direct answer to the question. In your thesis you want to:
Provide context for the question – include definitions of key terms such as monetary policy or economic objectives. Then use qualifiers or intensifiers (to some extent, significantly, is ineffective) to answer the essay question.
For our example, the thesis would look like:
Expansionary monetary policy conducted by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) involves deliberate actions to theoretically increase the supply of funds and reduce the cash rate, the cost of borrowing, in an effort to achieve economic objectives. However in practice, the RBA’s aggressively expansionary monetary policy, exemplified by its low 1.50% cash rate, has only had a limited impact on the economy.
Next, organise your ideas into dot points which you can will write your paragraphs on.
Also note down any sub points or arguments you think of underneath. This can include theory, links to the stimulus if this is a Section III essay, relevant statistics or graphs.
As this is the planning stage, it isn’t essential to get it all down perfectly, even just a word or key term to retain your train of thought is fine.
Below is an IDEAL plan using our example question. I have used more words than I normally would to help you read along (in reality, one word dot points are fine, as long as you can understand what you’ve written).

If there are natural links and connections between paragraphs this can also be useful in transitioning in between different paragraphs to maintain the cohesiveness of the essay, i.e. making it flow better.
Still feeling overwhelmed with writing your HSC Economics Essay for your upcoming Economics assessment? Get additional help writing your HSC Economics essays with our HSC Economics Tutoring Sydney .
Step 2: Finish Your Introduction Strong
Now you have already written a strong thesis and have provided context for the essay.
All that is left is to connect your paragraph points to answering the thesis. This is in lieu of simply stating which objectives you will be looking at, which is not as effective and thesis-driven. Compare the pair:
Rather than saying:
Economic growth, inflation, unemployment and external stability are economic objectives which monetary policy have failed to address.
The transmission mechanism’s failure to boost consumption and business investment has lead to poor economic growth, and combined with below target inflation, unemployment that exceeds the NAIRU (non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment), and an increasing current account deficit (CAD) driven by a widening trade deficit, monetary policy has failed to achieve a positive impact on the Australian economy and its objectives.
It is much more impressive to the marker if you are able to show a direct link between your points and the thesis you are addressing, as it shows a logical approach.
Are you taking Business Studies too? Master the HSC Business Studies report with our guide !
Step 3: The Writing Process
The other general criteria in HSC Economics essays is the related to the way you write and use language , including economic terms, concepts, relationships and theories.
This of course means you must know your content well and be able to connect different parts of the syllabus together and understand their relationships.
Once you have mastered your content, the criteria then asks for a ‘sustained, logical and cohesive’ response. In order to achieve this, it is best to use a clear structure (which we have planned for in Step 1) as it forces you to retain a logical and cohesive structure.
Here’s how to do it:
Use DPEEL (writing structure)
To provide a basic structure, follow DPEEL which will ensure you are using economic terms, concepts, relationships and theories consistently in your essay.

Definition – assume the marker is a layperson (has limited knowledge of the course) and ensure you are defining the economic term or concept to reflect your understanding. Can be integrated into the response and does not need its own sentence. Point – Attack the question and pinpoint what your overall answer will be, akin to a mini thesis. Explain – Provide further details that elaborate on your point. Depending on which directive verb you are asked, this is also where you can start to show relationships (analyse), provide additional economic theories that demonstrate a cause and effect (explain) or make a judgement (assess). Evidence – Integrate elements from the stimulus if it is a Section III Economics essay. Further, it reflects more in depth synthesis if you refer to specific statistics or quotes from the stimulus rather than simply stating a vague, ‘as seen in Source 1.’ If it is a Section IV Economics essay, this is where relevant statistics, graphs or economic theory will further elaborate and support your argument. However make sure you also explain graphs and their effects, rather than simply referring to them as ‘Figure 1,’ as failure to do so severely limits their effectiveness. Link – Conclude your paragraph by linking your points back to your original thesis.
Use transition signals
The ‘sustained’ element of the marking criteria means the markers want the essay to flow uninterrupted . No additional details or sidetracks.
The best way to achieve this is through the use of transition signals.
Transition signals include words such as furthermore, hence, as a result, this leads to, but, however. These are ‘linking’ words which along with the DPEEL structure FORCE you to stay on track and sustain your attack on the thesis, as each sentence must relate to the previous. Hence this makes it extremely difficult for you to stray off topic, allowing you to create a sustained response!
Prepare a table of key statistics and economic developments
Just like with English, Economics is also a subject with high demands on memory. Not only must you remember course content, you must also remember relevant statistics and graphs. An efficient way to facilitate this process is a simple table that allows you to organise your information. For example:
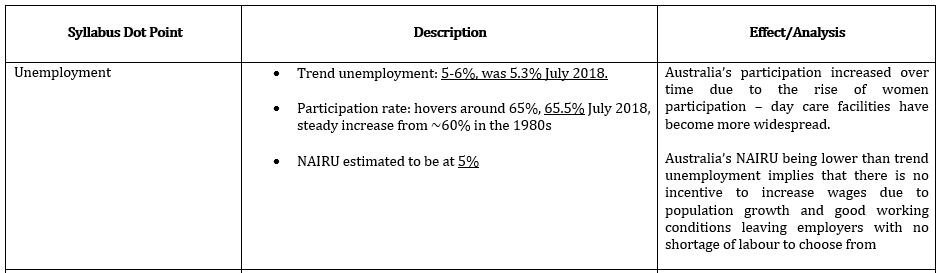
This will increase your mind’s ability to chunk the information without feeling overwhelmed.
Write a Strong Conclusion
HSC Economics essay conclusions are quite straightforward.
They need to:
Reaffirm your position and perspectives by restating your thesis — your answer to the question. Tie up your points and summarise how those ideas have supported your thesis. Provide a final statement that ‘ zooms out ‘ and provides a broad perspective of the question. This could be through providing an insight into future trends, expectations or areas for discussion.
Make sure you don’t overdo the conclusion. Three to four sentences is more than enough and the last thing a marker wants to see is a conclusion that has overstayed its welcome!
Step 4: Practise Writing HSC Economics Essay Plans
The final and most important tip is to practise this approach using different styles and topics of essay questions. It is also important that you plan the essays as you would in an exam to give you practice for planning for unseen questions.
We’ve done the hard work for you and you can find a collection of HSC Economics Essay Questions !
Apply these steps to build your consistency in writing logically and systematically.
That is the only way you will improve and better appreciate the amazingly pragmatic text type that is the HSC Economics essay. If you need more essay questions you can use past HSC exams, your textbook, or ask your teacher.
HSC Economics Tutoring Sydney can help you write strong Economics Essays, and make sure you get valuable feedback!
On the hunt for more HSC Economics resources?
Check out some of our other articles and guides below:
- HSC Economics Past Papers Master List
How to Write Effective HSC Economics Study Notes
The ultimate guide to getting a band 6 in hsc economics, are you looking for some extra help with your hsc economics essay writing, we pride ourselves on our inspirational hsc economics coaches and mentors.
We offer tutoring and mentoring for Years K-12 in a large variety of subjects, with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or at one of our state of the art campuses in Hornsby or the Hills!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor get in touch today!
Give us a ring on 1300 267 888, email us at [email protected] or check us out on TikTok !
Terry Huang completed his Bachelor of Secondary Education with a Bachelor of Commerce at the University of New South Wales. A strong believer that lessons should be engaging, relevant, and effective, his hustle and teaching approach have led to his recognition on the UNSW Faculty of Social Sciences Dean’s List for Academic Excellence, the NSW Teachers Federation Future Teacher scholarship, and the New Colombo Plan program. Terry enjoys listening to Kanye West, learning about cryptocurrency and memorising scenes from The Office .
- Topics: 🏦 Economics , 📚 Study
Related Articles
Hsc economics past papers – master list, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for Economics Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in
New south wales, queensland and victoria.
2024 Theses Doctoral
Essays in Financial Economics
Fischer, Lukas Felix
This dissertation studies three topics related to different types of network effects in financial economics. The first chapter, "Of Coupons and Cargo - International Debt, Production, and Trade," quantifies the relationship between firms' supply chain networks and financing decisions. Most multinational corporations raise a significant amount of debt capital outside their home country. In contrast to prevailing evidence, access to deeper financial markets cannot explain this phenomenon in its entirety, as international debt issues carry higher spreads than securities concurrently issued domestically. Novel data on the universe of fixed income securities, subsidiary locations, and shipment-level trade flows from seventeen countries, is used to understand the drivers of international debt issuance. On the extensive margin firms raise debt in exactly those markets which play a key role in their supply chain (through subsidiaries, suppliers, or customers). Tests on the intensive margin indicate that firms adjust the face value of debt outstanding in a given country following exogenous changes in their operating exposure. These results are consistent with firms using international capital markets to hedge their exposure to fluctuations in exchange rates. The second chapter, "Did You Catch the Game Last Night? - Peer Group Effects in Sell-Side Analyst Forecasts," assesses the reaction of sell-side equity analysts to sentiment shocks, as well as how such non-financial information permeates through social networks. We identify a source of peer group influence that is plausibly orthogonal to information provision, yet nonetheless affects economic decision-making: the shock to an equity analyst of their undergraduate college football team winning the NCAA Championship Game. We find that analysts' forecasts respond positively to their undergraduate school's football team winning the NCAA final. We then show that the shock of 'winning' spreads within an analyst's brokerage, positively influencing the forecasts of their colleagues. Brokerages where the degree of this diffusion is greater have lower female representation in their analyst teams, as well as lower ESG scores. The third chapter, "Sharing is Caring? - Knowledge Diffusion in Researcher Networks," focuses on the effects of social networks in innovation. Social interactions are at the core of many economic processes, including research and development. Yet their contribution to innovation is not well understood. A novel dataset on more than 19,000 economists linked to more than one million unique research projects and fifty million tweets (#EconTwitter) is used as laboratory to explore the relationship between different social interactions and research outcomes. Results suggest that interactions play a dominant role in the idea generation phase of research and a lesser one in the context of ongoing projects. They seem to matter little for completed research projects. More socially active scholars are more productive, as measured by the number of papers written, and their working papers are more visible (i.e., downloaded more frequently). A working paper being endorsed leads to an increase in downloads by 20%. However, indicative of a trade-off in spending their valuable time, these projects are less impactful based on citation measures.
- Finance--Econometric models
- Economics--Sociological aspects
- Social networks
- Business logistics
- Economics--Decision making
- College sports--Economic aspects
- National Collegiate Athletic Association
- NCAA football

More About This Work
- DOI Copy DOI to clipboard

Plain woven khadi cloth, c 1867. Courtesy the V&A Museum, London
Citizens and spinning wheels
For indians to be truly free, gandhi argued they must take up traditional crafts. was it a quixotic hope or inspired solution.
by Benjamin Studebaker + BIO
Political theorists often argue that citizens need to have certain capabilities for their political projects to be successful. Ancient and medieval political theorists, like Plato or Aquinas, often demand that people receive advanced spiritual and civic education as a prerequisite for participating in rule. This training is intricate. It takes time, and it can be expensive. Pre-industrial economic systems do not generate a very big surplus. In highly stratified ancient republics, citizenship was often reserved for the rich and powerful.
Modern liberals, like Adam Smith or Benjamin Constant, tend to take a different approach – they argue that most people already have the qualities that are necessary for citizenship. If they don’t have them, they can gain them by participating in markets and in civil society organisations, without need for careful planning. It helps that modern liberals envision a more limited role for their citizens – they need enough civic education to be able to vote for representatives, but they are not expected to make important everyday political decisions.
Gandhi was a different sort of thinker. He wanted ordinary people to make difficult moral and political judgments themselves. Instead of lowering the bar for citizenship or excluding the poor and the weak from citizenship, Gandhi argues that it is possible to dramatically improve the capabilities of ordinary people.

Gandhi spinning yarn in the late 1940s. Photo Wikipedia
To do this, he called for the reconstruction of the varna system, in which young people adopt the professions of their parents. In its original form, the system consists of four varnas. There are the Brahmins, who serve as scholars, priests or teachers. There are the Kshatriyas, who serve as rulers, administrators or warriors. There are the Vaishyas, who serve as farmers or merchants. Finally, there are the Shudras, who serve as artisans, labourers or servants. The members of all four varnas are householders, in the sense that it is permissible for people occupying any of the four varnas to produce children. One’s varna is determined by one’s parents’ varna.
T he varnas are often ranked so that the Brahmins enjoy the highest status, followed by the Kshatriyas, the Vaishyas and the Shudras. But Gandhi rejected ranking the varnas in this way. For him, the varna system becomes a caste system when the varnas become hierarchical status markers. In his view, all four varnas are meant to be equal, and people in all four varnas are meant to be able to engage in spiritual development – not just the Brahmins.
There are some Indians outside the varna system. The Dalits – or untouchables – are considered to be without a varna. For Gandhi, the category of Dalit is itself an offence against the varna system, insofar as it is a category that presupposes a hierarchical ranking and excludes some people from spiritual realisation. There are also some Indians who are not householders, but have instead committed themselves to ascetic lifestyles. After some number of lifetimes at the householder level, a Hindu practitioner is said to advance into a new ashrama or stage of life. While Brahmins serve as spiritual teachers, they remain householders, and so have not yet transitioned to asceticism. A person who wishes to become an ascetic must not have any dependents. This does not necessarily mean that the ascetic can never have had a spouse or children, provided that when the ascetic embraces asceticism, appropriate provisions have been made. Once asceticism is embraced, commitments to celibacy and childlessness necessarily follow, lest any new dependents be acquired. Taken together, the whole varna system is called varnashrama , referring together both to the four kinds of householders and the four stages of life.
He believed the system could and should raise everyone to the same level of spiritual and political education
Why would Gandhi wish to revive this system, a system that – by his own admission – develops very easily in an undemocratic direction, into a system of hierarchical caste ? When childhood is about preparing to compete in the job market and adulthood is consumed with worry about money, there’s no time for spiritual growth. But if children learn how to make a living at home, from their parents, Gandhi argues, they ‘need not even go to a school to learn it’. This leaves the mind ‘free for spiritual pursuits’. It allows the education system to focus on character development, on art and philosophy. By freeing Indians from the need to find their own way to earn a living, Gandhi hoped to give them the time necessary to become great souls.
Gandhi’s envisioned reform of the varna system faced obstacles. For one, the varna system and the caste system are often confused, even by Indians. Many people think that some professions are higher status than others. If profession is hereditary and different professions become associated with different levels of social status, this can result in a system of status hierarchy, in which some families occupy higher positions and others are subordinated. For Gandhi, caste hierarchy was a corruption of the varna system. Gandhi was a committed egalitarian – he believed the system could and should be used to raise everyone to the same level of spiritual and political education. However, caste perverted varna in the opposite direction, creating rigid, impenetrable social and political barriers between families.
T he varna system was plagued by caste hierarchy, but that was just the beginning of its problems. By the early 20th century, many of the traditional professions were no longer performed. Gandhi, for instance, had given up the profession of his parents to become a lawyer. When he made the decision to go to England for a legal education, he was kicked out of Sabarmati Ashram. Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first prime minister, was born a Brahmin. But Nehru took no interest in reading spiritual works. Instead, he went to law school.
Gandhi became convinced that it was a great evil for Indians to abandon the hereditary professions. Indians must not go to law school. If they do, this would give rise to a class of trained professionals, a group of bureaucrats, who would dominate India. These bureaucrats would run India the same way the British had run India, and under them ordinary Indians would remain incapable of participating in political decision-making.
In 1915, when Gandhi returned to India from South Africa, he argued that Indians who had adopted the Western professions – like law, medicine and engineering – should give them up. They should instead take up traditional Indian crafts. Gandhi himself gave up the law and took up the spinning wheel, making khadi – a kind of traditional Indian cloth. In the caste system, the manual crafts occupied the lowest position. High-caste Indians were prohibited from engaging in manual work on pain of expulsion from their caste. By encouraging Indians to take up the manual crafts, Gandhi subverted the caste system. But he also hoped to lay the groundwork for recovering varna.
If all Indians could learn the traditional crafts – and if all Indians consistently refrained from purchasing industrially produced goods – the crafts would ensure the livelihoods of all Indians. Future generations could simply learn the traditional crafts at home, from their parents, allowing them to pursue spiritual growth and participate directly in politics.
The manual crafts weren’t just a protest against the British but key to universal self-realisation in India
So, at first, the schools would need to teach the crafts – to ensure they were known to everyone, and to violate caste prohibitions on manual labour. But once the crafts were widely known and the caste prohibitions were no more, the crafts could be learned at home, and the schools could be turned to their true purpose – preparing young people to rule themselves. Gandhi called this self-rule ‘swaraj’.
Why the emphasis on crafts? For Gandhi, only the traditional crafts were universally available to Indians, even under British rule. Training Indians as farmers would not work as long as ownership of farmland remained concentrated. Indian farmworkers would be made to work long hours as agricultural labourers unless and until the land could be redistributed, and that could happen only after the departure of the British. Gandhi believed it was necessary to prepare for swaraj immediately, and the crafts presented themselves with practical and political appeal.
It would be possible to revive the crafts only if Indians made a point to exclusively purchase products made by traditional methods. For the crafts to survive in the long term, Indians would have to continue the anticolonial protest against manufactured goods even after independence. For Gandhi, the manual crafts weren’t just a protest against the British – they remained central to producing conditions for universal self-realisation in India.
As the Second World War drew to a close, Gandhi grew concerned that Indian independence would come too early, before this was properly grasped by the other independence leaders. His friend Nehru disagreed with him about the traditional crafts. In a letter to Nehru, Gandhi argued that by performing a ‘quota’ of manual labour, the people could ‘rest content’ with their ‘real needs’, freeing them up for spiritual learning. Nehru countered that traditional villages were ‘backward intellectually and culturally’, and that an economy based on primitive technology would be isolated and uncompetitive.

Gandhi Day paraders in Delhi, July 1922. Photo by Topical Press Agency/Getty
For Gandhi, Nehru had missed the point. As long as Indians could produce all the necessaries of life through the traditional crafts and they refrained from purchasing industrial goods, there was no need to make the economy competitive. What good is it to make the economy competitive, if that means that most people will have to spend all their time struggling to earn a living? What kind of life is that? How are people who live that way meant to find the time for politics and spirituality? Such a country would be riven with violence and exploitation. From Gandhi’s point of view, it would be hardly any different from British India.
After this exchange of letters in 1945, Gandhi became increasingly focused on preserving the traditional crafts, especially spinning cloth on the traditional spinning wheel. He emphasised the spinning wheel ever more heavily, so much so that, even to this day, the wheel lies at the centre of the Indian flag.
A fter the Second World War ended in 1945, independence was imminent. With very little time left to win the argument, Gandhi became suspicious of the other Indian independence leaders. In late 1945, Gandhi accused them of wanting ‘to destroy khadi’. In 1946, he emphasised that the introduction of the industrial spinning mill is so corrosive to his political project that if a ‘tyrant wants to destroy the spinning-wheel itself … we should ourselves perish with the spinning-wheel and not live to witness its destruction.’ He insists that spinning is the only way ‘to achieve swaraj for the poorest of the poor and the weakest of the weak’.
In Gandhi’s final years, he grew more and more focused on khadi. His writings in 1946 and 1947 refer to this cloth hundreds of times. He worries about uncertified khadi dealers, its commercialisation, the use of fabrics and materials to circumvent khadi rules. He argues that it is necessary to create a ‘yarn bank’ to ensure that khadi workers always have access to the materials. Spinning will work as a vehicle for swaraj only if the spinners understand the role it plays. He writes: ‘[I]f workers themselves lack faith then the claim for khadi will fall to the ground.’
The workers are to desist from adopting the mill because they know it is the thin end of the wedge, that to abandon the wheel for the mill is to start the process of colonialism all over again. If the workers do not understand that, then they will allow the wheel to be taken from them. Without the wheel, the varna system cannot be recovered, and any swaraj the workers obtain will be empty. In July 1946, a critic accuses Gandhi of forcing the villagers to spin. Gandhi replies that Indian villagers ‘gave up khadi because they were tempted by mill-cloth’. He compares mill-cloth to a poisonous drug, suggesting he is freeing the villagers from a kind of addiction. He denies that he is violating their rights – if mill-cloth is not available and the villagers do not make their own cloth, they ‘have the right to shiver in the cold and remain naked’.
Commit to this new education, and Gandhi was confident that ‘in five years India will be a leading country in Asia’
In July 1946, Gandhi writes that towns existed before the arrival of the British. Things were ‘bad enough then’ but now ‘they are much worse’ because the towns have become cities devoted to enriching both ‘Indian millionaires’ and ‘British masters’. Khadi is to ‘undo the great mischief’. That mischief is not just the British, but the spiritual situation that, for Gandhi, allowed the British to colonise India. This is a view Gandhi maintained throughout his life. In 1908, he argued that the British were able to establish themselves in India only because the Indians assisted them. He writes that ‘in order to become rich all at once’ the Indians welcomed the British ‘with open arms’.
In the autumn of 1946, Gandhi was still hoping that Nehru understood – or could be made to understand – the importance of khadi. Gandhi says: ‘We shall have full freedom only when our uncrowned king Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru and his colleagues in the Interim Government devote themselves to the service of the poor as people expect them to do.’ He quotes Nehru as having called khadi the ‘livery of our freedom’.
In May 1947, Gandhi pleads for government workers to ‘forget their quarrels and disputes over ideologies and start learning and teaching spinning, khadi work and village industries’. If they commit to this new kind of education, Gandhi expresses confidence that ‘in five years India will be a leading country in Asia’.
But, over the course of 1947, it became increasingly clear that Gandhi was not going to win the argument. In June, he bemoaned the situation, calling the other independence leaders ‘selfish’. In November, Gandhi writes that if the village industries are neglected in an independent India, ‘we will be acting like a man who remembers God in sorrow and forgets Him when He showers [us in] happiness.’ Later that month, he confesses that ‘talk of khadi and village industries does not interest people any more.’ ‘I know that khadi and all allied activities have slackened because we have achieved swaraj,’ Gandhi writes, ‘India will get what is ordained for her. What can we do?’
I n the days and weeks leading up to his death in January 1948, Gandhi began suggesting a new political system designed to empower the villages – the Panchayati Raj. Representative democracy could not be relied upon to integrate the economy and religion into a system that unites the need to survive with the need to spiritually thrive. But, before his alternative political system could be elaborated, much less implemented, Gandhi was assassinated. Just a few weeks earlier, in December 1947, Gandhi had lamented that ‘the main implication of khadi’ was not grasped by the independence movement. He said he had ‘no doubt’ that khadi is ‘more important than ever if we are to have freedom’ for ‘the masses of the villagers of India’. ‘Through khadi,’ Gandhi struggled ‘to establish supremacy of man’ over machine. He strove for equality of all men and women, and he strove ‘to attain subservience of capital under labour in place of the insolent triumph of capital over labour’.
So, Gandhi saw varna as the way to discipline capital so that it served life. But his vision for the role of the varna system was always quixotic. Indians, including Nehru, embraced economic modernisation. As Nehru put it, he felt there was ‘no reason’ why millions of Indians should not have ‘comfortable up-to-date homes where they can lead a cultured existence’. This was to be achieved with electricity, trade, modern transportation and heavy industry, not with a return to traditional village crafts. Gandhi left open the possibility that, if Indians felt it good and necessary, then they could add new professions beyond the traditional crafts. He recognised that political decision-making is difficult and requires capacities and specialties that are not easily cultivated in people. Even deeply religious people who are sincerely committed to the truth often disagree with one another, and for Gandhi this was baked into the human condition.
In 1930, Gandhi had written that, while all faiths ‘constitute a revelation of Truth’, they are all ‘imperfect and liable to error’. He suggested that this stems from the fact that, while ‘the soul is one’, the ‘bodies which she animates are many’. Since we cannot ‘reduce the number of bodies’, faith in the unity will ‘partake of human imperfection’. Embodied human beings will put their faith ‘into such language as they can command’, and their words are interpreted by other imperfect beings. Everyone will think themselves right, but ‘it is not impossible that everyone is wrong’. This produces a need for tolerance – not an ‘indifference towards one’s own faith’, but a ‘purer love for it’.
Gandhi tasks the poor with preventing the varna system from ossifying into one of caste
In the spirit of this view, Gandhi often described himself as one who ‘experiments’ with truth. Satyagraha , nonviolent civil resistance , rests on the idea that all of us, even those with spiritual education, can be mistaken. Other people should confront us in those situations – carefully, and nonviolently.
For Indians to have true swaraj, they must have the education necessary not merely to understand the reasoning behind Gandhi’s economic model, but to participate themselves in reforming that model based on their own understanding of truth. They must be able to think for themselves about whether all Indians should perform the manual crafts. They must be able to develop views about which professions are necessary and which are unnecessary. Gandhi’s desire to empower Indian citizens to rule themselves led him to allow India’s citizens freedom to work in additional professions, provided they practise them out of love rather than greed.
That proposal came with risks of its own. If one varna contains both those who depend exclusively on the traditional crafts and those who perform additional professions, this could lead to hierarchy within it. This is especially likely if those who perform additional professions are able to derive additional income from those professions. At points, Gandhi suggests that those who earn additional income from additional professions could serve as ‘trustees’, retaining some control over the wealth they gain from their additional professions, provided that they use this wealth to benefit others. This would leave some economic and political inequalities intact. Over time, it could lead to the reemergence of caste.
Gandhi ultimately tasks the poor with preventing the varna system from ossifying into one of caste. To perform this role, they must acquire the advanced civic education necessary to engage in satyagraha, and that in turn is possible only insofar as they are able to earn a living through the crafts. This was an enormous responsibility to place upon the shoulders of ordinary workers. The varna system can resist lapsing into a system of caste only when it is possible for the workers to consistently become spiritually learned and to remain spiritually learned across time. For Gandhi, it is only when the poor gain knowledge that they ‘become strong’ and ‘learn how to free themselves’. Nothing less will do, because the varna system is too fragile to maintain itself by lesser means.
Those who view Gandhi merely as a critic of violence, hierarchical caste and untouchability miss what is meant here by freedom and equality. This is about securing for every Indian the economic prerequisites for spiritual growth. For Gandhi, it is only in a world where everyone practices the crafts – and everyone can learn them at home from their parents – that there will be time enough for every person to develop their own spiritual praxis. In such a system, there is clearly observance of hereditary occupation, and therefore of varna.
Gandhi failed to establish this system, and no alternative system has arisen to perform the same function. The poor are still compelled to trade away their time in the struggle for survival, while the rich waste the time they take from the poor. But Gandhi tried to solve this problem, and many of us do not even try.
This piece contains excerpts from ‘The Varna System in Gandhi’s Theory of Civic Education’, first published in the journal Economic and Political Weekly in May 2024.

Political philosophy
C L R James and America
The brilliant Trinidadian thinker is remembered as an admirer of the US but he also warned of its dark political future
Harvey Neptune

Progress and modernity
The great wealth wave
The tide has turned – evidence shows ordinary citizens in the Western world are now richer and more equal than ever before
Daniel Waldenström

Neuroscience
The melting brain
It’s not just the planet and not just our health – the impact of a warming climate extends deep into our cortical fissures
Clayton Page Aldern

Falling for suburbia
Modernists and historians alike loathed the millions of new houses built in interwar Britain. But their owners loved them
Michael Gilson

Thinkers and theories
Rawls the redeemer
For John Rawls, liberalism was more than a political project: it is the best way to fashion a life that is worthy of happiness
Alexandre Lefebvre

Computing and artificial intelligence
Mere imitation
Generative AI has lately set off public euphoria: the machines have learned to think! But just how intelligent is AI?
- Featured Essay The Love of God An essay by Sam Storms Read Now
- Faithfulness of God
- Saving Grace
- Adoption by God
Most Popular
- Gender Identity
- Trusting God
- The Holiness of God
- See All Essays

- Best Commentaries
- Featured Essay Resurrection of Jesus An essay by Benjamin Shaw Read Now
- Death of Christ
- Resurrection of Jesus
- Church and State
- Sovereignty of God
- Faith and Works
- The Carson Center
- The Keller Center
- New City Catechism
- Publications
- Read the Bible
- TGC Pastors

U.S. Edition
- Arts & Culture
- Bible & Theology
- Christian Living
- Current Events
- Faith & Work
- As In Heaven
- Gospelbound
- Post-Christianity?
- The Carson Center Podcast
- TGC Podcast
- You're Not Crazy
- Churches Planting Churches
- Help Me Teach The Bible
- Word Of The Week
- Upcoming Events
- Past Conference Media
- Foundation Documents
- Regional Chapters
- Church Directory
- Global Resourcing
- Donate to TGC
To All The World
The world is a confusing place right now. We believe that faithful proclamation of the gospel is what our hostile and disoriented world needs. Do you believe that too? Help TGC bring biblical wisdom to the confusing issues across the world by making a gift to our international work.
Winner Announcement: TGC’s 2024 Essay Contest for Young Adults
More by staff.

Gen Z is a generation that faces the temptation to avoid hard things. With phones to hide behind, it’s easier than ever to get lost in a virtual world instead of facing the real world . Scripture tells us we shouldn’t be surprised when we face trials in this life as if something strange were happening to us, and that we can even rejoice in trials (1 Pet. 1:6–7; 4:12–13). Our young writers are learning this countercultural lesson. We have a God who cares more about our Christ-conformity than our comfort, and this is good news.
Over the past few months, we’ve had the privilege of reading the submissions to The Gospel Coalition’s 2024 Essay Contest for Young Adults . Nearly 200 young writers submitted original essays, and the editorial team reviewed them. These writers shared personal testimonies of their wrestling with God as they faced debilitating illness, societal pressure, and unfulfilled desires. We were impressed by their self-reflections on what they were pursuing more than God, whether it was acceptance into university, dream jobs, or the phones in their pockets.
Their writing displayed their desire to treasure Christ above all else.
Thoughtful Writers
The essays TGC received came from 183 young writers:
- They ranged in age from 16 to 22. Many were high school students; others were in college or just beginning their adult lives.
- As with last year’s contest , two-thirds of the writers were female.
- They’re members of local churches—Presbyterians, Baptists, and Anglicans predominated, with many nondenominational churches also represented.
- They submitted their essays from all over the U.S. and 14 other countries including Canada, South Africa, Malaysia, and the United Arab Emirates.
Many of these young writers poured out their hearts as they shared about times when God, in his love, withheld something from them. Others wrote of how they moved from clinging to their phones to clinging to Christ. Some shared how they see the need for men and women like themselves to give their lives to vocational ministry to reach the 3 billion people with no access to the gospel.
Our hearts were warmed as we read stories of Gen Z Christians refusing the lies their culture is feeding them. Instead, they’re inviting us to taste and see with them that the Lord is good (Ps. 34:8).
Personal Reflections
In TGC’s contest guidelines , we provided three prompts that allowed writers to reflect on their own lives as a means of speaking to their generation. Gen Zers are stereotypically called “screenagers” for spending a considerable amount of time on the internet. One prompt asked, “How has the gospel changed your relationship with your phone?” Many who chose this prompt were aware of their temptation to depend on their devices. They want to view their phones as tools, not as extra limbs.
Other writers shared why they’re considering full-time vocational ministry, knowing it’ll come at great cost. They’re willing to lay aside dream jobs with well-paying salaries for the sake of serving the Lord. Having to stand firm in the faith amid a deconstructing culture, they see themselves as equipped to reach their generation.
The most selected prompt was “When did the Lord love you by not giving you what you wanted?” By withholding something these young people wanted (though it was often a good thing), the Lord in his kindness revealed sin in their lives, drawing them closer to himself. What a beautiful picture of what our loving Father does for us, his children (Heb. 12:5–11).
We pray your hearts will be warmed and your souls edified as you read these essays (and TGC will be publishing more of them over the coming months).
Among the essays, three pieces stood out as well-crafted, thoughtful, and engaging. Our editorial team was clear about which winners to select, and we’re delighted to publish them on the site for you to read.
First Place: “ Who Was ‘i’ Without My iPhone? ” by Luke Simon
Luke opens his essay with these words: “Steve Jobs might’ve been a prophet. Or he at least predicted how his device would shape my future. After all, he placed the ‘i’ next to ‘Phone.’” Behind his screen, Luke Simon became luk3simon, forging a new identity and avoiding reality—and ultimately God. Eventually, he realized he needed a digital detox. Luke gives us practical ways to unhitch our identities from our phones, pointing us to the hope found in Jesus alone.
Second Place: “ How God’s ‘No’ to My Dream School Was a ‘Yes’ to the Local Church ” by Logan Watters
In her inspiring essay, Logan tells of how membership in a faithful, gospel-preaching church was a better pursuit than her dream school. And this made no sense to her friends. When we seek the Lord’s will and his plans above our own, the self-seeking world around us is left confused. Logan writes, “After a taste of [God’s] plans compared to mine, I don’t want anything else.”
Third Place: “ The Lord Loved Me by Giving Me a Broken Family ” by Karsten Harrison
In his essay, Karsten sees God’s love through unanswered prayer. Speaking to those who come from broken families, Karsten brings hope by pointing to the Lord’s steadfast love and the rich fellowship found with our church family. He writes, “God doesn’t simply give whatever we ask. Instead, we pray that his will would be accomplished, thus aligning our wills with his.” May we learn with him that God’s “No” always comes from his love for us and invites us to depend on him.
Take time today to read these essays and praise God for his faithfulness in his love toward us:
The steadfast love of the LORD never ceases; his mercies never come to an end; they are new every morning; great is your faithfulness. (Lam. 3:22–23)
Read more essays from young adults: 2022 and 2023 Contest Winners.
Now Trending
1 richard hays thinks god changed his mind about same-sex sex. is he right, 2 ‘rings of power’ season 2: getting better, still flawed, 3 honor your parents as you obey the great commission, 4 who was ‘i’ without my iphone, 5 god loved me by giving me a broken family.

The Curious Case of the Christian Reformed Church
The CRC traveled far down the road toward theological liberalism—and then hit the brakes. Here’s how a denomination found its way back to orthodoxy.
The 11 Beliefs You Should Know about Jehovah’s Witnesses When They Knock at the Door

As a Single Man, I Felt Little Pressure to Get Married. I Wish I Had.

Where the Political Parties Stand on Social Issues in 2024

Can a Man Feel Like He’s a Woman?

When Spiritual Disciplines Took Over My Life

Limiting My Phone Expanded My View of God

Latest Episodes
Trevin wax on reconstructing faith.

Who Is the Faithful and Wise Servant? (Matt. 24:45–25:46)

Examining the Current and Future State of the Global Church

Hoping Against Hope in American Democracy

Welcome and Witness: How to Reach Out in a Secular Age

Love in the Face of Adversity (Rom. 12:9–21)

Gaming Alone: Helping the Generation of Young Men Captivated and Isolated by Video Games

To Understand Salvation, Understand the Trinity

Faith & Work: How Do I Glorify God Even When My Work Seems Meaningless?

Let’s Talk Reunion: The Blessings of Bible Study with Friends

Getting Rid of Your Fear of the Book of Revelation

Looking for Love in All the Wrong Places: A Sermon from Julius Kim

Introducing The Acts 29 Podcast
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Edwidge Danticat's new collection of essays says 'We're Alone'

Ari Shapiro
Tinbete Ermyas

Jordan-Marie Smith
NPR's Ari Shapiro talks with author Edwidge Dandicat about her new essay collection, We're Alone .
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.

Vance Championed 2017 Report on Families From Architects of Project 2025
JD Vance, as he was dipping his toe into politics, praised the Heritage Foundation report — 29 essays opposing abortion and seeking to instruct Americans on how to raise children — as “admirable.”
In his introduction to the 2017 Heritage Foundation report, JD Vance argued that economic struggles were inextricable from what he saw as cultural decay. Credit... Jamie Kelter Davis for The New York Times
Supported by
- Share full article

By Lisa Lerer
- Sept. 3, 2024
Years before he became the Republican vice-presidential nominee, JD Vance endorsed a little-noticed 2017 report by the Heritage Foundation that proposed a sweeping conservative agenda to restrict sexual and reproductive freedoms and remake American families.
In a series of 29 separate essays, conservative commentators, policy experts, community leaders and Christian clergy members opposed the spread of in vitro fertilization and other fertility treatments, describing those treatments as harmful to women. They praised the rapidly expanding number of state laws restricting abortion rights and access, saying that the procedure should become “unthinkable” in America. And they cited hunger as a “great motivation” for Americans to find work.
Mr. Vance, then known as the author of a best-selling memoir, became a champion of the project. He wrote the introduction and praised the volume as “admirable,” and was the keynote speaker at the public release of the report at Heritage’s offices in Washington.
The report was released just months after Donald J. Trump became president, as social conservatives were laying the foundation for an aggressive agenda restricting sexual freedom and reproductive rights. Those policies became a hallmark of the Trump administration and Mr. Vance’s political career.
Taken together, the pieces in the report amount to an effort to instruct Americans on what their families should be, when to grow them and the best way to raise their children. Authors argued in the 2017 report that women should become pregnant at younger ages and that a two-parent, heterosexual household was the “ideal” environment for children.
“The ideal situation for any child is growing up with the mother and father who brought that child into the world,” wrote Katrina Trinko, a conservative journalist, in an essay detailing the “tragedy” of babies born to single mothers.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
Teachers' Day 2024: Ten Lines, Short and Long Essays For School Students
Published By : Suramya Sunilraj
Trending Desk
Last Updated: September 04, 2024, 09:00 IST
New Delhi, India

Students celebrate their teachers’ dedication and arduous work on this day by participating in exciting activities (Representative Image/ Shutterstock)
This special day encourages students to express their gratitude and admiration for their teachers, who have a significant impact on their lives and future
Teachers’ Day is an occasion set aside to celebrate and appreciate their hard work, dedication and contributions. Teachers’ Day is held every year on September 5 to commemorate the birth anniversary of Dr Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, a prominent scholar, teacher and India’s second president. This special day encourages students to express their gratitude and admiration for their teachers, who have a significant impact on their lives and future.
Students celebrate their teachers’ dedication and arduous work on this day by participating in exciting activities and events such as delivering speeches and writing essays, making cards and posters, reciting poetry and slogans, engaging in fun games, and singing and dancing. Here are some simple essays to write and share with your adored teachers.
10 Lines Essay on Teacher’s Day (Primary Level):
– Teachers play an important role in our lives.
– In India, people celebrate this day on September 5 of every year.
– The Teacher’s Day celebration was started in 1962.
– The day is commemorated to honour Dr S Radhakrishnan, the first vice president and second president of India, on his birthday.
– In addition to being a renowned scholar, diplomat and President of India, he was also acommitted teacher.
– He stated that people shouldcelebrate September 5 as Teacher’s Day rather than his birthday.
– The teaching community is respected on this day and is widely observed across the country.
– To show love and appreciation for teachers, students make greeting cards and give presents.
– Schools and other institutions host a variety of events and programmes on this day.
– A few exceptional teachers get awarded with National Awards from the Ministry of Education in recognition of their outstanding work.
Teacher’s Day 2024: Short Essays 150 words (Secondary Level)
Every year on the birth anniversary of Dr Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan, India observes Teachers’ Day. He was deeply committed to the teaching profession. Some kids reportedly approached him and asked whether he wanted to celebrate his birthday on September 5. He then suggested that they honour all teachers on this day to mark their outstanding efforts and accomplishments. Teachers are the genuine builders of the nation’s future, influencing the lives of students, who in turn shape the nation’s destiny.
Teachers have an essential role in nation-building. However, one hardly recognises the necessity of teachers in the community. Teachers’ Day has been honoured on September 5 each year since 1962. Our teachers not only teach us, but they also help us develop our personalities, confidence and abilities. They assist us in overcoming whatever hurdles we may encounter in life. Here’s a Happy Teachers’ Day to all the hardworking teachers across India!
Teachers’ Day 2024: Long Essays 250 words (Higher Secondary Level)
Every year on September 5, students observe Teacher Day. It honours the birth anniversary of Dr Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, India’s first Vice President and a dedicated teacher. He was a staunch promoter of education and was well-known for his work as a scholar, diplomat, educator and former President of India.
Teachers’ Day is a wonderful time to honour and cherish the relationship between teachers and students. Nowadays, students and instructors in schools, colleges, universities and other educational institutions exhibit their enthusiasm and excitement. Students often wish their teachers a long life. The relationship between teachers and students is something to be thankful for and treasure for a lifetime. These days, students and professors gladly participate in the celebrations at schools, colleges, universities and other educational institutions.
Students organise several events on Teachers’ Day to show respect for their teachers. These activities include cultural programmes, lectures, poems and small expressions of gratitude. Some students show their gratitude through heartfelt comments or notes. In some schools, senior students serve as instructors for the day, gaining experience with the problems and responsibilities of teaching.
We should recognise and cherish the teachers in our lives, and we should celebrate Teachers’ Day every year to express our gratitude for their work. Teachers, like our parents, help us develop our minds to thrive in life. And, it is our responsibility to honour them by adhering to all of their lessons and teachings. Happy Teachers’ Day to all!
- Dr Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
- teacher's day
- Teachers day celebrations

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some economics essay examples: Short Essay About Economics. The Role of Fiscal Policy in Economic Stimulus. Fiscal policy plays a crucial role in shaping economic conditions and promoting growth. During periods of economic downturn or recession, governments often resort to fiscal policy measures to stimulate the economy.
WRITING ASSIGNMENTS IN ECONOMICS 970 In Sophomore Tutorial (Economics 970), you will receive several writing assignments including a term paper, an empirical exercise, short essays, response papers, and possibly a rewrite. Below is a description of these types: • Term Paper (10-15pp.). In all tutorials, you will be required to write a
y to writing in any discipline. Part II, "Researching Economic Topics," tries to explain the scholarly and analytical a. proach behind economics papers. The third part, "Genres of Economics Writing," briefly surveys some of the kinds of pap. rs and essays economists write. It is in the fourth part, "Writing Economics," that the ...
3. Come up with a thesis statement. A thesis statement is the main argument you will make in your essay. It should be 1-2 sentences long and respond to the essential question that's being asked. The thesis will help you structure the body of your essay, and each point you make should relate back to the thesis. 4.
While the body of your essay will present both sides of the argument it is important to come down on one side. This demonstrates your ability to make an informed judgment. Justify why you have come down on this side of the argument. Identify the most important point which has shaped your judgment. Say what your conclusion depends on.
Essay Writing in Economics - Useful Advice This document is primarily aimed at students writing an essay. Much of the advice also applies to ... There should be a clear conclusion to your essay, even if it is very brief, where you summarise your main findings / conclusions. Conclusions may include (briefly) possible extensions and/or material ...
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation - primarily designed for A Level students. 1. Understand the question. Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
Step 3: Essay Introduction. In the introduction, include definitions of keywords in the question and spell out the economic framework you will employ for your answer as well as key definitions. Step 4: Body of Essay. In the body, there will be several paragraphs. The number of points/paragraphs depends on the question.
Short Essays (4-6 pages). Short essays may require you to analyze two articles and compare their policy implications, explain a model, criticize an argument, present a case study, extend a theory, evaluate an intellectual debate, and so on. Response Papers (1-2 pages). Response papers might involve summarizing the weekly
Structure the essay. Begin the essay with an introductory paragraph saying how you interpret the question. The ability to interpret a question in terms of models that you know is an important skill. Note that for many essay questions there are a number of ways in which the issues can be approached. The reader is interested in knowing at the ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement—instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.. Example: Returning to the thesis Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind ...
NOT GOOD: "Economic growth increased by 1 percentage point in 2017 to 2018". NOT GOOD: "GDP was $1.32403 trillion in 2017". GOOD: "The 2017 Budget's Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy — up 30% from 2016's $31 billion, and 20% higher than the inflation-adjusted long-term expenditure.".
Thesis - Justification - Support. This is the rhetoric used by Bray et al. Thesis - the main concept or idea that you are proposing. Justification - the reasons why your thesis is valid. Support - evidence that backs up your justification. Essay structure - your introduction, main body, and conclusion.
Economics essays often demand critical thinking, data analysis, and the ability to communicate complex economic ideas effectively. ... The conclusion of your economics essay serves as the final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers. A well-crafted conclusion should tie all the elements of your essay together and provide a ...
Conclusion; Your economics essay introduction should set the context and present your main argument. Here's how to structure it: Context Statement: Explain why the question is important. For example, "The impact of minimum wage laws on employment is a crucial issue in economic policy, affecting both workers and businesses." ...
Both essays use the same four-part structure: Part 1, the analysis - making assumptions, and using the correct diagram to show how a decision or policy will work to achieve an objective. Part 2, the evaluation begins with ' the bridge ' of the essay - assumptions are questioned and probably changed.
The IB Economics Paper 1 Essay Structure. In the new syllabus (May 2022 exams onward) and get to choose 1 out of 3 questions, chosen from any of the 4 units. Paper 1 is worth 20% of your final for HL students and 30% for SL students. You'll get get 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes).
The Conclusion sections of economics papers are the least standardized, and are an often neglected section. Conclusions may consist of a single paragraph restating the main points or main findings. Sometimes they suggest lines of future research. Your conclusion may do any or all of the following:
Essay writing. The idea of setting essays is to offer you the chance to make a longer, more complex argument. Nonetheless, in the model we recommend, the fundamentals remain the same. In each paragraph, a flow of main idea (thesis) — explanation / reasoning (justification) — evidence / example (support) is an excellent structure to use.
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
Economics Revision Essay Plans. This series of resources provides revision essay plans for a wide variety of essay topics, including synoptic questions. For the 2019 papers check out our collection of videos on building A* evaluation into your answers. Have you tried our series of more than 50 Quizlet revision activities?
Writing a college essay takes skill, but making a strong college essay conclusion is often the most important part. A great ending can make a big impact on your readers and bring your main ideas together. This guide will walk you through four strategies that will help you create impactful conclusions that resonate with your audience. 1. Writing a Memorable College Essay Conclusion The ...
Here is what I feel is a superbly clear and well-structured essay answer to a question on the economic and social effects of collusion within an oligopoly. Question. Evaluate the view that collusion between firms in an oligopoly always works against consumer and society's interests. Use game theory in your answer. KAA 1:
Writing a Band 6 HSC Economics essay can be difficult because the essay questions can vary from addressing a specific section of the syllabus to having a broad focus and therefore requiring synthesis of entire topics.. Furthermore, there are two HSC Economics essays in the HSC exam, which make up 40 marks of the whole exam! Section III - is a stimulus based economic essay response where you ...
Essays in Financial Economics. Fischer, Lukas Felix. This dissertation studies three topics related to different types of network effects in financial economics. The first chapter, "Of Coupons and Cargo - International Debt, Production, and Trade," quantifies the relationship between firms' supply chain networks and financing decisions.
Ancient and medieval political theorists, like Plato or Aquinas, often demand that people receive advanced spiritual and civic education as a prerequisite for participating in rule. This training is intricate. It takes time, and it can be expensive. Pre-industrial economic systems do not generate a very big surplus.
Gen Z is a generation that faces the temptation to avoid hard things. With phones to hide behind, it's easier than ever to get lost in a virtual world instead of facing the real world.Scripture tells us we shouldn't be surprised when we face trials in this life as if something strange were happening to us, and that we can even rejoice in trials (1 Pet. 1:6-7; 4:12-13).
NPR's Ari Shapiro talks with author Edwidge Dandicat about her new essay collection, We're Alone.
In a series of 29 separate essays, conservative commentators, policy experts, community leaders and Christian clergy members opposed the spread of in vitro fertilization and other fertility ...
Here are some simple essays to write and share with your adored teachers. 10 Lines Essay on Teacher's Day (Primary Level): - Teachers play an important role in our lives. - In India, people celebrate this day on September 5 of every year. - The Teacher's Day celebration was started in 1962.