My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

In this article:
Problem-Solution Outline
Problem-solution examples, criminal justice, environment, relationships, teen issues.
What to include in your problem-solution speech or essay?
Problem-solution papers employ a nonfiction text structure, and typically contain the following elements:
Introduction: Introduce the problem and explain why the audience should be concerned about it.
Cause/Effect : Inform the audience on what causes the problem. In some cases, you may also need to take time to dispel common misconceptions people have about the real cause.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Thesis Statement: The thesis typically lays out the problem and solution in the form of a question and answer. See examples below.
Solution : Explain the solution clearly and in detail, your problem-solving strategy, and reasons why your solution will work. In this section, be sure to answer common objections, such as “there is a better solution,” “your solution is too costly,” and “there are more important problems to solve.”
Call to Action: Summarize the problem and solution, and paint a picture of what will happen if your final solution is adopted. Also, let the reader know what steps they should take to help solve the problem.
These are the most used methods of developing and arranging:
Problem Solution Method Recommended if you have to argue that there is a social and current issue at stake and you have convince the listeners that you have the best solution. Introduce and provide background information to show what is wrong now.
List the best and ideal conditions and situations. Show the options. Analyze the proper criteria. And present your plan to solve the not wanted situation.
Problem Cause Solution Method Use this pattern for developing and identifying the source and its causes.
Analyze the causes and propose elucidations to the causes.
Problem Cause-Effect Method Use this method to outline the effects of the quandary and what causes it all. Prove the connection between financial, political, social causes and their effects.
Comparative Advantage Method Use this organizational public speaking pattern as recommendation in case everyone knows of the impasse and the different fixes and agrees that something has to be done.
Here are some examples of problems you could write about, with a couple of potential solutions for each one:
Marriage Problem: How do we reduce the divorce rate?
Solution 1: Change the laws to make it more difficult for couples to divorce.
Solution 2: Impose a mandatory waiting period on couples before they can get married.
Environmental Problem: What should we do to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Solution 1: Use renewable energy to fuel your home and vehicles.
Solution 2: Make recycling within local communities mandatory.
Technical Problem: How do we reduce Windows error reporting issues on PCs?
Solution 1: Learn to use dialogue boxes and other command prompt functions to keep your computer system clean.
Solution 2: Disable error reporting by making changes to the registry.
Some of the best problems to write about are those you have personal experience with. Think about your own world; the town you live in, schools you’ve attended, sports you’ve played, places you’ve worked, etc. You may find that you love problem-solution papers if you write them on a topic you identify with. To get your creativity flowing, feel free to browse our comprehensive list of problem-solution essay and paper topics and see if you can find one that interests you.
Problem-Solution Topics for Essays and Papers
- How do we reduce murder rates in the inner cities?
- How do we stop police brutality?
- How do we prevent those who are innocent from receiving the death penalty?
- How do we deal with the problem of gun violence?
- How do we stop people from driving while intoxicated?
- How do we prevent people from texting while driving?
- How do we stop the growing child trafficking problem?
- What is the best way to deal with domestic violence?
- What is the best way to rehabilitate ex-cons?
- How do we deal with the problem of overcrowded prisons?
- How do we reduce binge drinking on college campuses?
- How do we prevent sexual assaults on college campuses?
- How do we make college tuition affordable?
- What can students do to get better grades in college?
- What is the best way for students to effectively balance their classes, studies, work, and social life?
- What is the best way for college students to deal with a problem roommate?
- How can college students overcome the problem of being homesick?
- How can college students manage their finances more effectively?
- What is the best way for college students to decide on a major?
- What should be done about the problem of massive student loan debts?
- How do we solve the global debt crisis?
- How do we keep countries from employing child labor?
- How do we reduce long-term unemployment?
- How do we stop businesses from exploiting consumers?
- How do we reduce inflation and bring down the cost of living?
- How do we reduce the home foreclosure rate?
- What should we do to discourage consumer debt?
- What is the best way to stimulate economic growth?
- How do we lower the prime cost of manufacturing raw materials?
- How can book retailers deal with rising bookseller inventory costs and stay competitive with online sellers?
- How do we prevent kids from cheating on exams?
- How do we reduce the illiteracy rate?
- How do we successfully integrate English as a Second Language (ESL) students into public schools?
- How do we put an end to the problem of bullying in schools?
- How do we effectively teach students life management skills?
- How do we give everyone access to a quality education?
- How do we develop a system to increase pay for good teachers and get rid of bad ones?
- How do we teach kids to problem solve?
- How should schools deal with the problem of disruptive students?
- What can schools do to improve reading comprehension on standardized test scores?
- What is the best way to teach sex education in public schools?
- How do we teach students to recognize a noun clause?
- How do we teach students the difference between average speed and average velocity?
- How do we teach math students to use sign charts?
- How can we make public education more like the Webspiration Classroom?
- How do we stop pollution in major population centers?
- How do we reduce the negative effects of climate change?
- How do we encourage homeowners to lower their room temperature in the winter to reduce energy consumption?
- What is the best way to preserve our precious natural resources?
- How do we reduce our dependence on fossil fuels?
- What is the best way to preserve the endangered wildlife?
- What is the best way to ensure environmental justice?
- How can we reduce the use of plastic?
- How do we make alternative energy affordable?
- How do we develop a sustainable transportation system?
- How can we provide quality health care to all our citizens?
- How do we incentivize people to stop smoking?
- How do we address the growing doctor shortage?
- How do we curb the growing obesity epidemic?
- How do we reduce dependence on prescription drugs?
- How do we reduce consumption of harmful substances like phosphoric acid and acetic acid?
- How can we reduce the number of fatal hospital errors?
- How do we handle the health costs of people living longer?
- How can we encourage people to live healthier lifestyles?
- How do we educate consumers on the risk of laxatives like magnesium hydroxide?
- How do we end political corruption?
- How do we address the problem of election fraud?
- What is the best way to deal with rogue nations that threaten our survival?
- What can our leaders do to bring about world peace?
- How do we encourage students to become more active in the political process?
- What can be done to encourage bipartisanship?
- How can we prevent terrorism?
- How do we protect individual privacy while keeping the country safe?
- How can we encourage better candidates to run for office?
- How do we force politicians to live by the rules they impose on everyone else?
- What is the best way to get out of a bad relationship?
- How do we prevent cyberbullying?
- What is the best solution for depression?
- How do you find out where you stand in a relationship?
- What is the best way to help people who make bad life choices?
- How can we learn to relate to people of different races and cultures?
- How do we discourage humans from using robots as a substitute for relationships?
- What is the best way to deal with a long-distance relationship?
- How do we eliminate stereotypical thinking in relationships?
- How do you successfully navigate the situation of dating a co-worker?
- How do we deal with America’s growing drug problem?
- How do we reduce food waste in restaurants?
- How do we stop race and gender discrimination?
- How do we stop animal cruelty?
- How do we ensure that all citizens earn a livable wage?
- How do we end sexual harassment in the workplace?
- How do we deal with the water scarcity problem?
- How do we effectively control the world’s population?
- How can we put an end to homelessness?
- How do we solve the world hunger crisis?
- How do we address the shortage of parking spaces in downtown areas?
- How can our cities be made more bike- and pedestrian-friendly?
- How do we balance the right of free speech and the right not to be abused?
- How can we encourage people to use public transportation?
- How do we bring neighborhoods closer together?
- How can we eliminate steroid use in sports?
- How do we protect players from serious injuries?
- What is the best way to motivate young athletes?
- What can be done to drive interest in local sports?
- How do players successfully prepare for a big game or match?
- How should the revenue from professional sports be divided between owners and players?
- What can be done to improve local sports venues?
- What can be done to ensure parents and coaches are not pushing kids too hard in sports?
- How can student athletes maintain high academic standards while playing sports?
- What can athletes do to stay in shape during the off-season?
- How do we reduce teen pregnancy?
- How do we deal with the problem of teen suicide?
- How do we keep teens from dropping out of high school?
- How do we train teens to be safer drivers?
- How do we prevent teens from accessing pornography on the Internet?
- What is the best way to help teens with divorced parents?
- How do we discourage teens from playing violent video games?
- How should parents handle their teens’ cell phone and social media use?
- How do we prepare teens to be better workers?
- How do we provide a rational decision-making model for teens?
- How do we keep companies from mining our private data online and selling it for profit?
- How do we prevent artificial intelligence robots from taking over society?
- How do we make high-speed internet accessible in rural areas?
- How do we stop hackers from breaking into our systems and networks?
- How do we make digital payments more secure?
- How do we make self-driving vehicles safer?
- What is the best way to improve the battery life of mobile devices?
- How can we store energy gleaned from solar and wind power?
- What is the best way to deal with information overload?
- How do we stop computer makers from pre-installing Internet Explorer?
Compare and Contrast Speech [Topics and Examples]
Proposal Speech [Tips + 10 Examples]
1 thought on “Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]”
This is very greatfull Thank u I can start doing my essay
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Problem Solution Speech Topics, Outline & Examples

The problem solution speech is a type of informative speech that enumerates various problems and provides possible solutions to those problems.
If you have been asked to give such a speech, your goal should be to explain the problem and provide realistic and achievable suggestions to address it. In most cases, problem solution speeches are given with the hope that the audience will be inspired to do something about the problems that they are facing.
There are many pressing issues in society today that could be considered ripe material for a problem solution speech. For example, racism, sexism, homophobia, ableism, and ageism are all major social problems that need to be addressed.
Of course, you can’t just pick any old problem and start talking about it – you need to make sure that your topic is something that your audience will actually care about and be interested in hearing.
Problem-Solution Speech Outline
The key to delivering an effective problem-solution speech is to develop an outline and a step-by-step plan that will help focus on different parts of your speech.
Here is a basic outline that you can use for your problem-solution speech:
Introduction
Introduce yourself and give a brief overview of the problem that you will be discussing. This is also where you will need to state your thesis – that is, what solution you think is best for the problem.
Make sure that you are concise and to the point – you don’t want to give your audience too much information, as they will likely tune out if you do.
Thesis/Statement of the problem
Explain what the problem is that you will be discussing. This is where you will need to do your research and really dig into the details of the issue so it is interesting and your speech has gravity.
Also, make sure that your problem is something that can actually be solved – there is no point in discussing a problem if there is no possible solution.
Cause/Effect
Discuss the causes of the problem and the effects that it has on different people or groups. This is where you will really start to get into the nitty-gritty of your topic and show your audience that you understand the issue at hand.
Make sure to back up any claims that you make with research or data so that your speech is credible. Use attention getters to hook your audience and keep them interested.
Potential solutions
This is the meat of your problem-solution speech. Discuss different potential solutions to the problem and explain why you think they would be effective.
Again, make sure to back up your claims with research or data so that your audience knows that you have thoughtfully considered the issue and possible solutions. Keep it realistic – don’t propose a solution that is impossible to achieve.
Call to action
You have now armed your audience with the knowledge of the problem and potential solutions – now what? You will need to challenge your audience to actually do something about the issue.
This could be something as simple as signing a petition or donating to a cause, or it could be something more ambitious like starting a new organization or campaign. Whatever you choose, make sure it is achievable and that your audience knows how they can take action.
Use the outline above to tailor the specifics of your speech to fit your particular audience and situation and deliver an effective problem-solution speech.
Problem-Solution Presentation Techniques
Once you have your outline ready, it’s time to start working on your delivery. Here are some tips to keep in mind as you prepare your problem-solution speech:
- Be passionate : This is not the time for a dry, academic approach. You need to be enthusiastic about the issue at hand and really sell your audience on why they should care.
- Be clear : Make sure that your audience understands the problem and potential solutions. Use straightforward language and avoid jargon.
- Be concise : Remember, you only have a limited amount of time to make your case. Get to the point and don’t ramble.
- Use stories : A personal story or anecdote can be a powerful way to connect with your audience and make your speech more relatable.
- Use visuals : Visual aids can be a great way to engage your audience and break up your speech. Just make sure that they are clear and easy to understand.
- Practice, practice, practice : The only way to get comfortable with delivering a problem-solution speech is to practice it as much as you can. So get in front of a mirror, or even better, ask a friend or family member to listen to you and give feedback. The more you practice, the more confident you will be and overcome your fear of public speaking .
Problem-Solution Speech Topics
1. How can we make sure that all animals are treated humanely?
2. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to animal welfare?
3. How can we make sure that all animals have access to proper care and shelter?
4. Why should we care about animal rights?
5. Why is wildlife conservation important?
6. Why animal testing is cruel?
7. Why should the exotic pet trade be stopped?
9. What can we do about the food industry and mass animal killing?
1. How can we make sure that our technology is accessible to everyone?
2. What are the most important things to keep in mind when using social media?
3. How can we make sure that our online information is safe and secure?
4. What should we do about cyberbullying?
6. How can we make sure that our technology is sustainable?
7. What are the most important things to keep in mind when using new technology?
8. How can we make sure that our technology is user-friendly?
9. What should we do about outdated technology?
10. How can we make sure that our technology is accessible to people with disabilities?
11. What are the most important things to keep in mind when using technology in the classroom?
12. How can we make sure that our technology is used for good and not for evil?
13. What should we do about the digital divide?
14. How can we make sure that our technology is used responsibly?
15. What should we do about the growing problem of e-waste?
16. What are the most important things to keep in mind when using technology in the workplace?
17. What should we do about the increasing dependence on technology?
Relationships
1. How can we improve communication in relationships?
2. What are the biggest problems faced by long-distance relationships?
3. How can we make sure that our relationships are built on trust?
4. What causes jealousy in relationships and how can it be overcome?
5. When is it time to end a relationship?
6. How can we deal with infidelity in a relationship?
7. How can we make sure that our relationships are healthy and balanced?
8. What causes arguments in relationships and how can they be resolved?
9. What are the most important things to keep in mind when raising a family?
10. How can single parents make sure that their children are getting the attention they need?
11. What effect does social media have on relationships?
12. How can we make sure that our relationship with our parents is healthy and supportive?
13. What should we do when our friends or family get into a toxic relationship?
14. How can we deal with envy or jealousy within our friendships?
15. How can we deal with a friend or family member who is going through a tough break-up?
16. How can new relationships be started off on the right foot?
17. What are the most important things to keep in mind when moving in with a partner?
18. What should we do when our relationship starts to fizzle out?
19. How can we deal with the death of a loved one?
20. How can therapy help us improve our relationships?
Social Issues
1. How can we make sure that everyone has access to clean water?
2. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to food security?
3. How can we make sure that all children have access to education?
4. What are the most effective ways of helping people who are homeless?
5. How can we make sure that everyone has access to healthcare?
6. What are the most effective ways of combating climate change?
7. How can we make sure that our cities are sustainable?
8. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to transportation?
9. How can we make sure that our economy is fair and just?
10. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to social inequality?
11. How can we make sure that our government is effective and efficient?
12. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to voting?
13. How can we make sure that our media is responsible and ethical?
14. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to privacy?
15. How can we make sure that our technology is used responsibly?
16. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to security?
17. How can we make sure that our world is peaceful?
18. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to human rights?
19. How can we make sure that our world is sustainable?
20. What are the most important things to keep in mind when it comes to the environment?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
253 Easy Problem Solution Speech Topics for 2024
Well, here’s the good news: those pesky problem and solution essays can be way better. All you need is an easy topic.
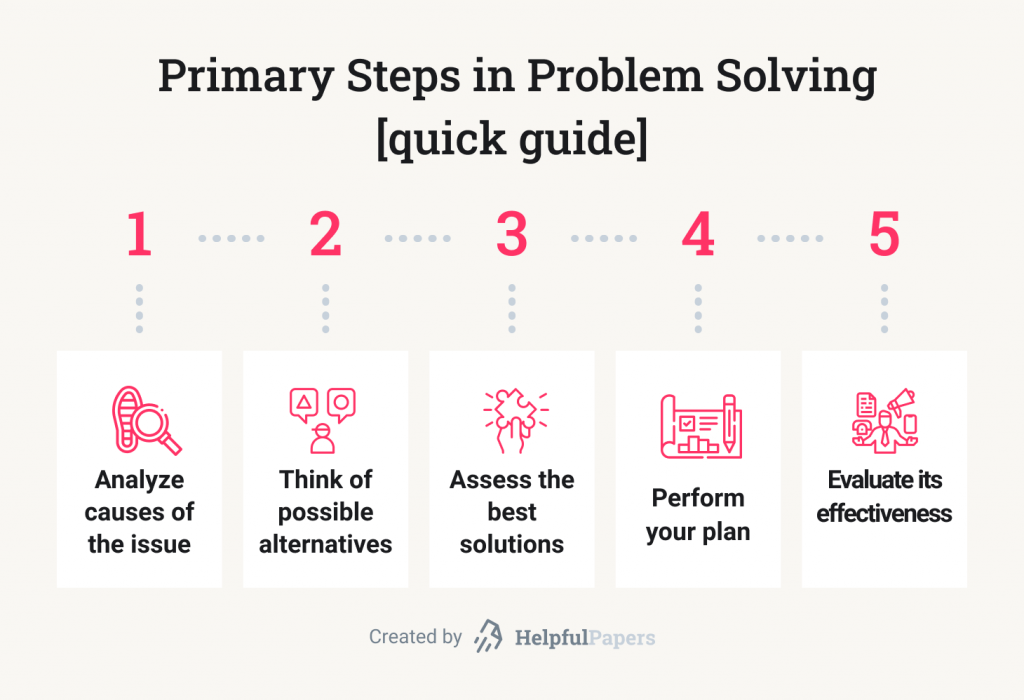
Here’s even better news: we’ve already compiled a list of 253 simple problem solution speech and essay topics for you.
- 🎓 Topics for College Students
- 🗣 Speech Topics
- 📝 Essay Topics
- 💊 Solutions
✅ Problem Solution Speech Examples
📍 problem-solution speech topics 2024.
- How to deal with school bullying?
- Air pollution: sources, effects, and prevention measures.
- What are the efficient ways of dealing with cyberbullying?
- Google’s corporate strategy, problems, and solutions.
- Better education for special needs children.
- What measures can be implemented to tame the problem of homelessness?
- How to incorporate healthy eating habits into your daily routine?
- How to improve teacher’s performance and development?
- Steps to improve healthcare organizations.
- Best methods to educate the public about the most common health issues.
- Ways to improve communication between schools and the community.
- How can child obesity in the United States be solved?
- How can lean project management improve developmental activities?
- Climate change: impact and possible solutions.
- How to reduce drunk driving incidents to a minimum.
🔧 Problem-Solution Speech. Manual
You might be wondering what a problem-solution is?
If you have never heard of such a term before, it should still be pretty straightforward that it deals with solving problems.
This article is created specifically for people who need a little extra inspiration and guidance in creating a problem solution speech or essay.
We will start with an overview of several vital aspects. 👇
Challenges of Problem Solution Speech Topics
What do we have to deal with when talking about problem solution topics in the first place?
- Problem-solution scenario appears to play an essential role in the modern world. It finds application in various areas of our lives, especially in business, education, and government-related fields.
- It is more than just sharing the view. The main aim of any problem-solution speech is to encourage the audience to take some action or support a particular idea.

- Defining the problem clearly. You should gather enough evidence to prove that the issue is quite severe and needs attendance immediately.
- Everyone should be able to understand the details. Your speech needs to be comprehensive, and its central idea – easy to grasp.
- Are people aware of your problem? Do they all realize its seriousness? There should be a short introduction if your target audience doesn’t understand the relevance of the topic.
- Research your listeners. Your main goal is to gain audience support – be aware of all the biases they are susceptible to. Find counterarguments to their opposing arguments.
- Creating convincing arguments. However, this issue should be discussed separately since every topic needs a personalized approach.
- Don’t forget to use a reasonable tone and respect your audience. Being polite and open to criticism is essential for your reputation as a serious author.
Strategies for Creative Problem Solving
You already picked a problem?
Here are helpful solution options you need to know.
The most important thing is to make the solution practical and effective.
- Suggest adding something to the existing problem . For example, many social and cultural issues would be resolved if they received additional funding or staff. The opposite approach might be as practical – removing the source of the problem. So, it’s not an issue anymore.
- Creating and enforcing specific rules or laws. It might be applied in various areas, especially in the governmental field of work and education.
- Educate and motivate people. Some of the main reasons for existing social and health problems are that people are not aware of what they should do or simply lack motivation. It appears to be the focus of campaigns against drugs, smoking, and alcohol.
- Offer to make some changes in the method . It sometimes happens that a specific instrument does not work for everyone, so it should be changed. Another example is implementing successful marketing campaigns for various products.
- Probably the current leadership and strategy do not work. In human resources, education, and any area that needs a problem solution, this strategy might be the most effective.
Problem and Solution Text Structure
The structure of any problem-solution speech or presentation is relatively universal. Even though there are two main types of outline used, the components tend to stay the same.
You should always introduce the situation , helping your listeners understand the problem’s background. Then, you should define the issue itself , explaining its urgency and significance. After that, it is time to present your solution . In the end, there is usually a quick overview of the speech and a call for action .

The methods for outlining your problem solution speech are known for those who have experience in writing essays:
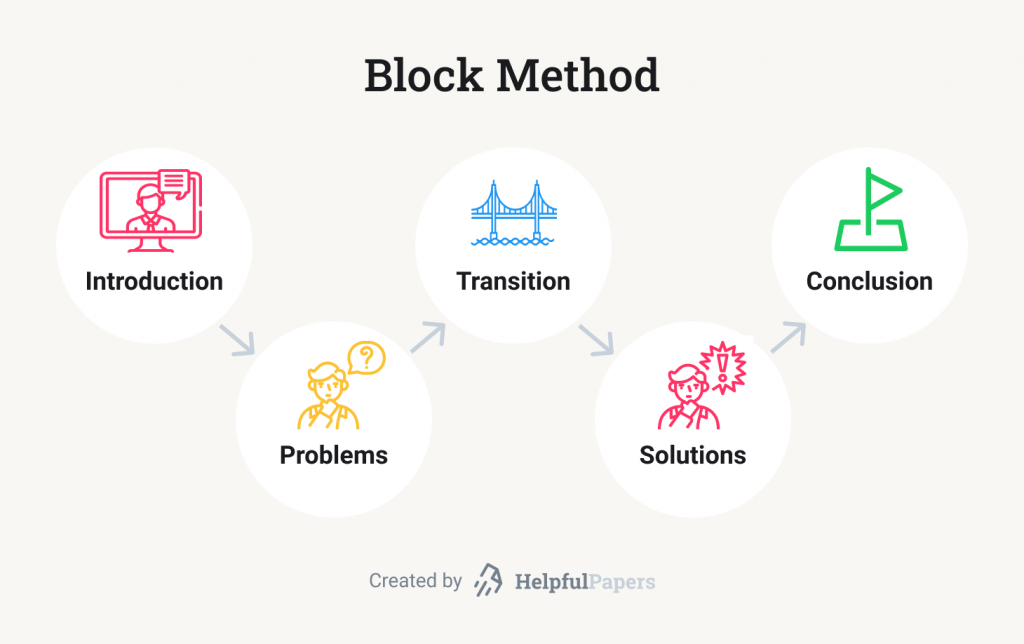
- The block method divides your speech into sections according to the categories. That is, first, you state all problems you have to address. Then make a short transition paragraph. Only then explain the solutions for the issues you discussed previously.
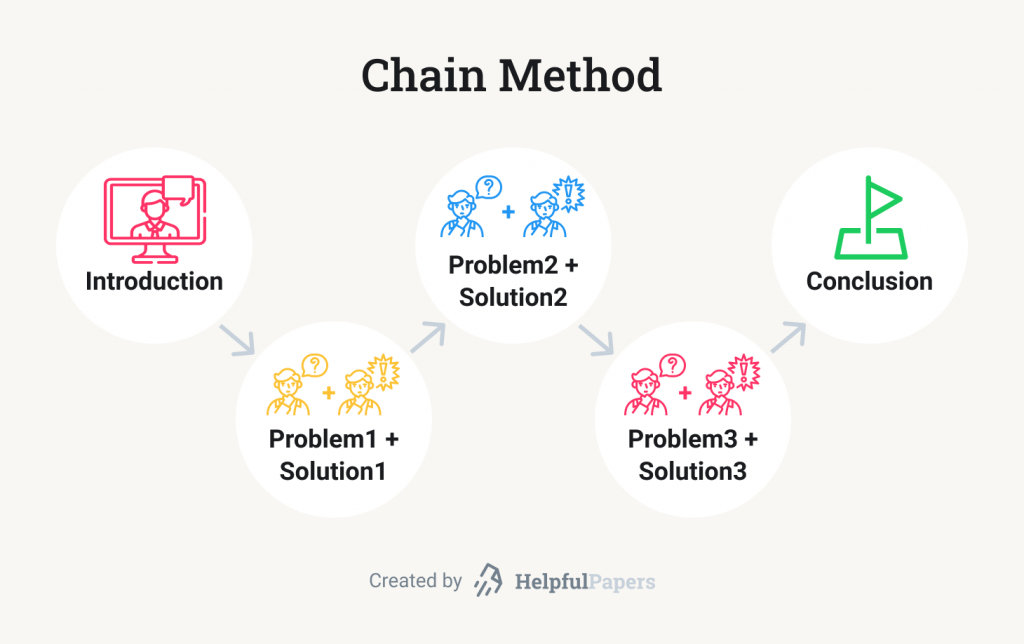
- The chain method has the same main components but is different in structure. Each time you talk about a problem, you need to discuss a solution. Therefore, if you want to address three issues, there should be three parts of the main body solving each problem at a time.
🎓 Problem Solution Speech Topics for College Students
Now, let’s get to the examples of the most relevant issues of today:
- How to prevent the increase in temperatures predicted to reach a dangerous point by the year 2100?
- How poverty causes crime, and is there a way to deal with it?
- What are the causes and possible solutions to India’s increasing death toll related to low air quality?
- How to take China out of the risk of losing the economy’s growth in the next several decades?
- How can the problem of posing education be solved?
- Total factor productivity: the issues with evaluating India’s output that shows productivity growth.
- Stagnating productivity as the cause of the unequal distribution of the world’s wealth. What are the solutions?
- Green Construction as an answer to environmental challenges.
- How to prevent the unemployment rates from increasing due to artificial intelligence development?
- How to achieve team cohesion?
- Technology as a threat to privacy and ways to deal with the problem?
- Best ways to address the health needs of an aging population.
- Webster University’s problems and solutions.
- How to protect societies from health issues related to overeating and low physical activity?
- The causes of air pollution and possible solutions.
- Practical solutions for the rising demand for talented employees in the STEM areas and lack of candidates.
- Is the driverless vehicle a solution to the high rates of death in the crushes on the roadways?
- Architecture and urbanism: how can more ecological and equitable cities be built with the latest technologies?
- How to improve your teamwork performance?
- What are the ways to reduce the cases of domestic violence in our society?
- Human genomes : how to avoid mistakes made while implementing any intelligence and lifespan enhancement tools?
- What are the most effective strategies suitable for diagnosing, treating, and preventing drug-resistant infections from becoming a threat?
- A step towards resolving financial issues facing U.S. higher education.
- Global development: how should the latest technologies in health, education, and nutrition be distributed among societies?
- Which strategies for dealing with epidemics and preparation methods can help prevent future global outbreaks?
- Technical urban planning : how should it be improved so that developing cities can find better solutions to increased global carbon emissions?
🎤 Easy Problem Solution Speech Topics
Someone may find these issues trifling, but try to solve them 😊
- How the lack of self-confidence affects your life and ways to deal with it.
- The problem of fast fashion and ways to deal with it.
- The problem of sexual assault and possible solutions.
- Mental health problems: how can an open discussion be encouraged in our society?
- The challenges of consumerism culture and ways to solve them.
- Why do so many people face an existential crisis , and are there any ways to deal with the issue?
- What are the right ways to resolve the ethical issue of advertising a harmful product?
- How has texting affected face-to-face communication, and what are the possible solutions to the problem?
- How can music prevent insomnia and improve your sleeping habits?
- How informal organization creates problems for managers, and how can these issues be redressed?
- Is including sex education in the program as a complete course can help to prevent early pregnancy?
- Can becoming a volunteer solve the self-confidence problem?
- Gender-specific bathrooms: what is a better way to prevent sexual assaults?
- Excluding all the personal information details from the CV to reduce job market discrimination.
- How does donating and recycling clothes help with the world poverty issue?
- Student parking problem and ways to deal with it.
- What are the best ways to reduce stress and anxiety?
- Open discussions and effective communication at the workplace as the ultimate problem-solving approach .
- Some universities are not as diverse as others. How can a college attract students from various backgrounds?
- Social fatigue: how can spending some time alone help fight it?
- Best ways to address various academic and learning challenges.
- Educating couples about proper budgeting as the way to prevent money-related conflicts.
- Reducing stress from social activity by planning daily routine.
- Legalizing medical marijuana : issues and solutions.
- The effect of social media on adolescents and possible interventions to limit the negative outcomes.
- Why is implementing a vegetarian diet one of the best ways to fight obesity?
- Psychological and physiological reasons why chewing gum helps with smoking addiction .
- Risks of medical tourism and some possible solutions .
- Consumption of a specific amount of red wine as a way to help with stomach ulcers.
- Contradictory but effective solution: taking selfies to boost self-confidence .
- How well does online video chatting help sustain an excellent long-distance relationship ?
- How can online fundraising campaigns help even more people in need?
- Do newspapers switching to online bases helps to reduce waste?
- Paper and reusable bags as an easy way to help reduce plastic waste.
- How strict should be water filtration rules to reduce water pollution?
- Planting trees as a way to deal with deforestation.
- Walking as the means of solving both pollution and health issues.
- How to better prepare students for adult life in the USA.
- How does setting up more drinking fountains help with reducing plastic pollution ?
- What are the ways to increase attendance at sports events?
🍭 Problem Solution Persuasive Speech Topics
The persuasive approach is mainly different from the other with the tone of your speech. It needs to be encouraging and trustworthy enough so that your audience accepts your idea. In case you wonder what are the best problem solution persuasive speech topics, here are some examples:
- How to get at least eight hours of sleep every day, and why is it an issue?
- The strategies to stop the increased consumption of sugar that leads to obesity.
- The problem of school counseling: why do Professional School Counselors Need to Pay Attention to Ethics?
- The ways to avoid the negative influence of hate towards religions on societies.
- How to introduce more gender-neutral concepts to the job market.
- Teaching gender and equal rights at schools to help decrease gender-related social issues .
- Paper recycling as a way to deal with environmental issues.
- Internships for all college students as the solution to high unemployment rates.
- More frequent evaluation of teachers as the way to fix educational issues.
- Social media regulated by university administration: putting an end to suicides .
- Resistance to change in organizations: problems and solutions.
- Introducing intercultural studies and foreign language classes at school to fight biases.
- New technologies: the ways to encourage people to start reading books .
- The problem of expensive education: why should community colleges be free?
- The necessity to implement cyber courts to help with the issue of cyberbullying.
- The ways that science and religion can co-exist to reduce worldwide conflicts.
- Allowing students to make jokes in class as a way to make education more engaging.
- Can going online improve the existing education system?
- Saving endangered species: can the government’s involvement help to solve the problem?
- Having a pet as a way to deal with emotional stress and anxiety for college students.
- How can cultural diversity benefit the business?
- How do we prevent job discrimination related to race and religion?
- Free professional help for divorced people as a means to prevent serious psychological issues .
- How can listening to sad songs help people release their emotions when they are upset?
- The difficulties of learning: how can music improve your academic performance?
- Radical solutions: legalizing marijuana as a way of preventing crimes related to drugs.
- Allowing people with tattoos to get any job helps increase tolerance and empathy.
- Psychology: the art of being happy as a mandatory class in colleges for increasing mental health.
- Learning a second language as a way toward self-improvement.
- Strict policy regarding dating at the workplace as the means to prevent conflicts.
- Practical strategies for fighting and elevating poverty around the globe.
✨ Problem Cause Solution Speech Topics
Problem-cause-solution speech is a very effective way to persuade your audience that you are a reliable expert. It requires you to analyze the causes of the issue in detail and come up with the best solution!
- The leading causes of binge drinking on college campuses and the ways to eliminate it.
- What are the decisive reasons for the high car accident rate, and how do we decrease it?
- Causes of global warming and possible ways of solving the problem .
- Why are so many prisons getting overcrowded , and what is the most humane solution?
- Inflation and high cost of living : how to find the solution to those problems?
- The evaluation system for teachers as the means of improving the quality of school education.
- The problem of school dropouts and possible interventions.
- What are the leading causes of sex education failure in school, and how to fix it?
- Why are we so dependent on fossil fuels, and how do we solve this issue?
- What causes truancy, and how to deal with it?
- Reducing the use of plastic as a way to solve some of the environmental problems.
- What is contributing to the current obesity epidemic , and how do we stop it?
- The reasons some people are dependent on prescription drugs and ways to solve them.
- Why did London’s new ambulance service fail, and how can the issue be resolved?
- Engage college students to become more politically active as a way to raise political consciousness.
- The problem of personal vs. private privacy and ways to solve it.
- The problem of toxic relationships and ways to solve it.
- What causes violence on social media, and what are the best ways to deal with it?
- Why are many long-distance relationships unsuccessful, and what are the ways to change that?
- Communities: why have we stopped getting along with neighbors, and what are the solutions?
- Kodak company’s strategic issue and solution.
- What causes so many teenagers to fall into depression, and how can family and teachers help to solve this issue?
- The leading causes of athletes using steroids in sports, and how can we stop it?
- What causes air pollution, and how to deal with it?
- Why do some teens keep dropping out of school , and how can it be prevented?
- How should we educate parents about controlling their child’s social media use, and why is that a problem at all?
- How do parents shape children’s understanding of relationships and ways to avoid bad influences and scenarios?
- Amazon Local Company’s failure: reasons and ways to fix it.
- Hackers can attack digital transactions. What are the ways to keep them safe?
- The main reasons for information overload and how should people avoid it?
📝 Problem Solution Essay Topics for Business
- Marketing ROI: the problem of ROI assessment and the potential solutions.
- How to avoid labor exploitation.
- What are the responsible management challenges and solutions for the B.P. company?
- The issue of youth unemployment and possible solutions.
- How should companies audit their policies to ensure they discourage, rather than encourage, discrimination among workers ?
- H.R. portfolio of evidence: project management and problem-solving techniques.
- How to effectively avoid social problems in a workplace.
- How do you deal with the problem of alcoholism at work?
- How to avoid sexual harassment in the workplace?
- Ways to deal with the company’s global communication problems.
- How to deal with the food prices increase?
- How can a company maintain a good conflict-resolution strategy?
- Ways to avoid bankruptcy.
- Classic Airlines marketing problems and possible solutions.
- The problem of monopolization in America : can a small business survive?
- Ways to improve employees’ satisfaction.
- How to incorporate problem-solving into marketing.
- How can Amazon Company’s ethical problems and challenges be resolved?
- Gender pay-gap issue in the U.S. and possible solutions.
- Ways to solve management problems in the tourism and hospitality industry
💭 Problem Solution Essay Topics 2024
Let’s see which 2024 problems are the most relevant so that you can use them as a problem solution essay topic:
- Is relying on COVID-19 vaccines the right strategy to fight the world pandemic?
- University education: problems and possible ways to improve?
- Accepting the new normal or fighting for the old normal: which is more effective for stopping the outbreak?
- Employing a diverse workforce: challenges and solutions.
- How do we help the most vulnerable communities during the COVID-19 outbreak?
- How to cultivate respect for other cultures?
- Learning issues in the public school system and ways to improve the condition.
- Climate change : is being prepared for the effects a better solution than trying to prevent it?
- What are the ways in which digital giants can improve to avoid information breaches and exposure?
- Innovative strategies to make big cities more equal and less divided for their citizens.
- How using renewable resources can help deal with climate change?
- How do migrants affect public health systems, and what should we do about it?
- How can we help small-scale farmers with adaptation to climate change?
- What are the best leadership styles that can contribute to the business’s success during COVID-19?
- The new ways to fact-check information online and prevent dangerous rumors.
- Restation of local economies by helping small businesses and encouraging young talents.
- Interdisciplinary studying: benefits, challenges, and solutions.
- Right and effective leadership as a way of achieving sustainable development goals.
- How can international collaboration for every country help to achieve carbon neutrality?
- Cloud services for businesses: issues, benefits, and possible solutions.
- What are the ways to reduce the number of tobacco consumption?
- The U.N. and multilateralism : how can we achieve more by working together as humanity?
- How can market analysis benefit the company?
- How can we help cultural cohesion and stop fragmentation by avoiding multiculturalism ?
- How are social issues such as violence and racism addressed in gangsta rap and rock music?
- Making cyberbullying a criminal offense as one of the most effective ways to fight it.
- Restore humanities: teaching children how to be humans as the way to solve the global crisis.
- Way to make an advertising campaign successful?
- Promoting values and cognitive behavioral therapy to fight mental health issues.
- How can promoting open debates on essential topics help fight herd mentality?
📚 Problem Solution Essay Topics for College Students
There is a variety of disciplines in this list, so any college student can find something suitable for them here:
- One random act of kindness as a way to create happier societies.
- Funding volunteering promotion as a way to boost people’s awareness.
- Social media and its effect on the younger generation: problems and solutions.
- Can everyone having personal solar panels help to save the environment?
- How do augmented reality glasses help people with disabilities see the world?
- Can strict gun control laws reduce the number of homicide cases committed in the USA?
- The problem with dolls: why should we promote the production of dolls of different shapes and colors for children ?
- What rules should be introduced to fight market monopolization and increase competition?
- What can society do to prevent people from getting an eating disorder?
- Can students’ active involvement in the learning process improve their academic results?
- Implementing A.I. and machine learning methods to help companies build a relationship with their customers.
- Promoting a specific level of individualism in a business setting to help problem-solving.
- How can total transparency boost the customer’s trust and increase sales?
- Time management problem and possible solutions.
- How can athletes prevent injuries that take them out of competitive sports?
- Setting some responsibilities and duties for children as the way to help them become more successful in life.
- Studying abroad and graduate employability: challenges and recommendations.
- Why does developing family traditions help the more substantial relationship and reduce conflicts?
- What is the main problem with current meal plans at schools, and what is the solution?
- Educating people about herbal remedies as a way to promote over-the-counter medicines .
- The challenges and solutions of introducing a new performance management system for a multicultural team.
- What policies should be implemented to eliminate the problem of child labor?
- Is raising the prices of tobacco an effective way to make humanity healthier?
- Switching to online learning platforms as the new approach to available and affordable education.
- Can the implementation of electric cars bring some positive environmental changes and a decrease in air pollution?
- Do kids prefer to read eBooks , and how can we use them to encourage book reading?
- Setting fair prices for streaming services as the way to fight online piracy .
- How can organizational goals help the company succeed?
- Should we all use adblocking software to avoid online fraud and malware?
- Creating more natural habitats such as national parks as a way to protect endangered species.
- How do you effectively manage organizational behavior?
- Small steps: how does local buying help reduce soil pollution from big companies?
- Kids and sports: how the lack of professional sports guides can be addressed?
- Should we pay more attention to cleaning trees from invasive vegetation?
- How to stop animal poaching by promoting the use of ethical materials?

🐻 Problem Solution Essay Topics for Middle School
Here are some great examples of topics that may interest or be discussed by middle school students:
- Can a college degree be one of the solutions for reducing the risks of divorce?
- Learning to smile through pain as the way to make you feel better.
- Online learning vs. face-to-face learning: problems and solutions.
- Small changes in life as a way to treat depression .
- Listening to audiobooks as a way to improve your literacy?
- Tourism industry: why should it be supported, what challenges does it faces, and what are the solutions?
- Switching chairs in classrooms to more comfortable ones as the way to improve attendance.
- If most of the world’s population turns vegetarians, will it help climate change?
- The issues with high school uniforms and possible solutions.
- The effectiveness of placing more speed bumps to reduce the rates of accidents.
- Implementing mandatory student exchange programs in colleges to fight cultural biases.
- The danger of popular diets and ways to deal with it.
- Fixing pollution issues as the only way to secure healthy nations in the Future.
- How does a fair division of house chores help prevent family conflicts?
- Homeschooling: issues and possible solutions.
- Owning and petting a cat regularly as the best way to reduce stress ?
- What are the best ways to prevent deaths due to drunk driving?
- How to keep a workplace safe, and why is it important?
- How does playing team sports help with communication skills in teenagers?
- How to deal with challenges at work as a team leader?
- Can people using eBooks contribute to solving environmental issues ?
- How do handwritten letters help share emotions within the family during the conflict?
- How can we use online communication to learn languages more effectively?
- Dealing with conflict: strategies for responses.
- How does the cultural trend of “going green” help with environmental changes?
- Should we focus on inventing more renewable energy sources to help pollution?
💊 Problem Solution Topics. Solutions
Here are some great examples of problem solution speech topics to get an idea of what it should look like:
- Limit the time kids spend on the internet.
- Make sure that kids use only appropriate for their age websites.
- Place the computer in an open common area to easily monitor kids’ activity.
- Educate teenagers on the unprecedented danger of using the internet.
- Parents should support their kids to make sure they can resist the influence of drug abuse.
- Schools should create programs that spread awareness of the consequence of drug use.
- The community should be more involved in drug prevention activities.
- The government should implement policies that address drug use among school-age youth.
- Enforce strong laws against child abusers.
- Spread awareness regarding the problem of child abuse.
- Take matters of child abuse seriously and lead comprehensive investigations.
- Implement behavior therapy that helps patients plan and deal with their strong food cravings.
- Use a cognitive approach that helps patients to channel and be in control of their negative thoughts.
- Expose patients to interpersonal psychotherapy, which focuses on “family-based” treatment.
- Parents should talk to their kids about their future career plans and encourage their developing interests and beginnings.
- Schools should facilitate tutoring, mentoring, and out-of-school programs.
- The government should provide more social and financial support to the students and their families.
- Avoid opening suspicious messages and e-mail attachments, especially from unknown users.
- Avoid Executing any Executable Programs in the attachments.
- Avoid downloading cracked software on websites.
- Block Scripts by Default in Internet Browsers.
- Install anti-virus software ad security patches.
- Disable Autorun for C.D.s, Flash Drives, and other Removable Media.
- Switch to biodegradable materials for packaging.
- Reduce the consumption of goods that use non-biodegradable plastic. Check out this link for more perspective solutions: 10 Measures that Must Be Taken to Prevent More Flooding in the Future
- Learn to identify barriers and problems.
- Build your own self-concept.
- Try to strengthen your emotional intelligence.
- Work on your self-disclosure and be open with your partner or family members.
- Learn to handle the conflicts.
- Parents should make sure that their kids feel loved and accepted.
- Praise children when they achieve their accomplishments, and don’t criticize them in front of their peers.
- Teach children to have positive self-statements and give them a chance to evaluate themselves. Let the children see how their good actions positively affect others.
By addressing real-world problems through our speeches, we can develop a sense of responsibility toward creating positive change. For your inspiration, we have prepared a short problem-solving speech example on obesity.
Obesity Problem Solution Speech
Good morning, everyone. It’s a pleasure to be here with you today! I want to direct your attention to an issue that has been steadily growing in significance and deserves our immediate concern – childhood obesity. Did you know that in 2021-2022, 17.0% of young people aged 10 to 17 had obesity? This rise in childhood obesity is a multifaceted issue with diverse causative factors, including sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, limited access to healthy foods, and societal influences. The consequences of childhood obesity are profound and alarming. It increases the risk of numerous health issues, such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, obese children often face social and emotional challenges, including stigmatization and low self-esteem, which can have long-lasting effects on their mental health and overall quality of life. So, what can we do to tackle childhood obesity effectively? The solution lies in a comprehensive and concerted effort involving various stakeholders, parents, educators, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the community. Firstly, promoting physical activity and reducing sedentary behaviors among children is paramount. This can be achieved by increasing access to sports facilities, integrating physical education into school curricula, and encouraging outdoor and recreational activities. Additionally, addressing dietary habits is crucial. Providing access to nutritious meals in schools, educating children and their parents about healthy eating practices, and limiting the availability of unhealthy food options can contribute to positive changes in children’s diets. In conclusion, combating childhood obesity requires a multifaceted approach encompassing education, environmental changes, and supportive policies. Thank you!
More Problem Solution Persuasive Speech Examples
Here are some bonus problem-solution speech examples given by TED Talk speakers.
- “The Simple Solution to Fast Fashion” — Josephine Philips In her TED Talk, Josephine Philips presents a simple solution to fast fashion. She advocates for a shift toward sustainable and ethical clothing consumption. By embracing timeless styles, supporting eco-friendly brands, and practicing mindful shopping, she believes individuals can significantly lessen the harmful effects of fast fashion on the environment.
- “A Close-to-Home Solution for Accessible Childcare” — Chris Bennett In his brilliant speech, Chris Bennett proposes a community-based approach to accessible childcare. He advocates for creating local co-op childcare centers where parents take turns supervising children. By leveraging existing resources and building a supportive network, he believes this model can provide affordable and reliable childcare for families in need.
- “The Real Solution to Global Warming” — Supratim Kundu In his TED Talk, Supratim Kundu argues that the real solution to global warming lies in harnessing the power of capitalism and private industry. He believes incentivizing the private sector to address environmental issues is more effective and efficient than relying solely on government intervention.
You got lucky when you found our list of problem solution speech topics! We will also direct you to other resources that will help you write a paper 😎
Start with this complete breakdown of how to write a problem solution essay , then create a problem solution speech structure , and—voila—you’re all set to conquer your text!
Check out more sources below in references.
And if you are still struggling with it, simply read some problem solution essay examples for both college and high school.
Have you grabbed a couple of problem solution essay topics from our list?
Good luck with solving them now🍀
🔗 References
- Transitions in Text; University of North Carolina
- Problem-Solution Essays: Definition and Examples
- Problem-Solving Skills: Definitions and Examples
- A Problem Solving Approach
- What Are Problem Solving Skills?
414 Proposal Essay Topics for Projects, Research, & Proposal Arguments
725 research proposal topics & title ideas in education, psychology, business, & more.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.2 Using Common Organizing Patterns
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the common speech organizational patterns: categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological.
- Understand how to choose the best organizational pattern, or combination of patterns, for a specific speech.

Twentyfour Students – Organization makes you flow – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this chapter we discussed how to make your main points flow logically. This section is going to provide you with a number of organization patterns to help you create a logically organized speech. The first organization pattern we’ll discuss is categorical/topical.
Categorical/Topical
By far the most common pattern for organizing a speech is by categories or topics. The categories function as a way to help the speaker organize the message in a consistent fashion. The goal of a categorical/topical speech pattern is to create categories (or chunks) of information that go together to help support your original specific purpose. Let’s look at an example.
| Specific Purpose | To persuade a group of high school juniors to apply to attend Generic University |
| Main Points | I. Life in the dorms |
| II. Life in the classroom | |
| III. Life on campus |
In this case, we have a speaker trying to persuade a group of high school juniors to apply to attend Generic University. To persuade this group, the speaker has divided the information into three basic categories: what it’s like to live in the dorms, what classes are like, and what life is like on campus. Almost anyone could take this basic speech and specifically tailor the speech to fit her or his own university or college. The main points in this example could be rearranged and the organizational pattern would still be effective because there is no inherent logic to the sequence of points. Let’s look at a second example.
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of college students about the uses and misuses of Internet dating |
| Main Points | I. Define and describe Internet dating. |
| II. Explain some strategies to enhance your Internet dating experience. | |
| III. List some warning signs to look for in potential online dates. |
In this speech, the speaker is talking about how to find others online and date them. Specifically, the speaker starts by explaining what Internet dating is; then the speaker talks about how to make Internet dating better for her or his audience members; and finally, the speaker ends by discussing some negative aspects of Internet dating. Again, notice that the information is chunked into three categories or topics and that the second and third could be reversed and still provide a logical structure for your speech
Comparison/Contrast
Another method for organizing main points is the comparison/contrast speech pattern . While this pattern clearly lends itself easily to two main points, you can also create a third point by giving basic information about what is being compared and what is being contrasted. Let’s look at two examples; the first one will be a two-point example and the second a three-point example.
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of physicians about Drug X, a newer drug with similar applications to Drug Y |
| Main Points | I. Show how Drug X and Drug Y are similar. |
| II. Show how Drug X and Drug Y differ. | |
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of physicians about Drug X, a newer drug with similar applications to Drug Y |
| Main Points | I. Explain the basic purpose and use of both Drug X and Drug Y. |
| II. Show how Drug X and Drug Y are similar. | |
| III. Show how Drug X and Drug Y differ. |
If you were using the comparison/contrast pattern for persuasive purposes, in the preceding examples, you’d want to make sure that when you show how Drug X and Drug Y differ, you clearly state why Drug X is clearly the better choice for physicians to adopt. In essence, you’d want to make sure that when you compare the two drugs, you show that Drug X has all the benefits of Drug Y, but when you contrast the two drugs, you show how Drug X is superior to Drug Y in some way.
The spatial speech pattern organizes information according to how things fit together in physical space. This pattern is best used when your main points are oriented to different locations that can exist independently. The basic reason to choose this format is to show that the main points have clear locations. We’ll look at two examples here, one involving physical geography and one involving a different spatial order.
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of history students about the states that seceded from the United States during the Civil War |
| Main Points | I. Locate and describe the Confederate states just below the Mason-Dixon Line (Virginia, North Carolina, and Tennessee). |
| II. Locate and describe the Confederate states in the deep South (South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida). | |
| III. Locate and describe the western Confederate states (Louisiana, Arkansas, and Texas). |
If you look at a basic map of the United States, you’ll notice that these groupings of states were created because of their geographic location to one another. In essence, the states create three spatial territories to explain.
Now let’s look at a spatial speech unrelated to geography.
| Specific Purpose | To explain to a group of college biology students how the urinary system works |
| Main Points | I. Locate and describe the kidneys and ureters. |
| II. Locate and describe the bladder. | |
| III. Locate and describe the sphincter and urethra. |
In this example, we still have three basic spatial areas. If you look at a model of the urinary system, the first step is the kidney, which then takes waste through the ureters to the bladder, which then relies on the sphincter muscle to excrete waste through the urethra. All we’ve done in this example is create a spatial speech order for discussing how waste is removed from the human body through the urinary system. It is spatial because the organization pattern is determined by the physical location of each body part in relation to the others discussed.
Chronological
The chronological speech pattern places the main idea in the time order in which items appear—whether backward or forward. Here’s a simple example.
| Specific Purpose | To inform my audience about the books written by Winston Churchill |
| Main Points | I. Examine the style and content of Winston Churchill’s writings prior to World War II. |
| II. Examine the style and content of Winston Churchill’s writings during World War II. | |
| III. Examine the style and content of Winston Churchill’s writings after World War II. |
In this example, we’re looking at the writings of Winston Churchill in relation to World War II (before, during, and after). By placing his writings into these three categories, we develop a system for understanding this material based on Churchill’s own life. Note that you could also use reverse chronological order and start with Churchill’s writings after World War II, progressing backward to his earliest writings.
Biographical
As you might guess, the biographical speech pattern is generally used when a speaker wants to describe a person’s life—either a speaker’s own life, the life of someone they know personally, or the life of a famous person. By the nature of this speech organizational pattern, these speeches tend to be informative or entertaining; they are usually not persuasive. Let’s look at an example.
| Specific Purpose | To inform my audience about the early life of Marilyn Manson |
| Main Points | I. Describe Brian Hugh Warner’s early life and the beginning of his feud with Christianity. |
| II. Describe Warner’s stint as a music journalist in Florida. | |
| III. Describe Warner’s decision to create Marilyn Manson and the Spooky Kids. |
In this example, we see how Brian Warner, through three major periods of his life, ultimately became the musician known as Marilyn Manson.
In this example, these three stages are presented in chronological order, but the biographical pattern does not have to be chronological. For example, it could compare and contrast different periods of the subject’s life, or it could focus topically on the subject’s different accomplishments.
The causal speech pattern is used to explain cause-and-effect relationships. When you use a causal speech pattern, your speech will have two basic main points: cause and effect. In the first main point, typically you will talk about the causes of a phenomenon, and in the second main point you will then show how the causes lead to either a specific effect or a small set of effects. Let’s look at an example.
| Specific Purpose | To inform my audience about the problems associated with drinking among members of Native American tribal groups |
| Main Points | I. Explain the history and prevalence of drinking alcohol among Native Americans. |
| II. Explain the effects that abuse of alcohol has on Native Americans and how this differs from the experience of other populations. |
In this case, the first main point is about the history and prevalence of drinking alcohol among Native Americans (the cause). The second point then examines the effects of Native American alcohol consumption and how it differs from other population groups.
However, a causal organizational pattern can also begin with an effect and then explore one or more causes. In the following example, the effect is the number of arrests for domestic violence.
| Specific Purpose | To inform local voters about the problem of domestic violence in our city |
| Main Points | I. Explain that there are significantly more arrests for domestic violence in our city than in cities of comparable size in our state. |
| II. List possible causes for the difference, which may be unrelated to the actual amount of domestic violence. |
In this example, the possible causes for the difference might include stricter law enforcement, greater likelihood of neighbors reporting an incident, and police training that emphasizes arrests as opposed to other outcomes. Examining these possible causes may suggest that despite the arrest statistic, the actual number of domestic violence incidents in your city may not be greater than in other cities of similar size.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing distinct main points in a clear manner is the problem-cause-solution speech pattern . In this format you describe a problem, identify what you believe is causing the problem, and then recommend a solution to correct the problem.
| Specific Purpose | To persuade a civic group to support a citywide curfew for individuals under the age of eighteen |
| Main Points | I. Demonstrate that vandalism and violence among youth is having a negative effect on our community. |
| II. Show how vandalism and violence among youth go up after 10:00 p.m. in our community. | |
| III. Explain how instituting a mandatory curfew at 10:00 p.m. would reduce vandalism and violence within our community. |
In this speech, the speaker wants to persuade people to pass a new curfew for people under eighteen. To help persuade the civic group members, the speaker first shows that vandalism and violence are problems in the community. Once the speaker has shown the problem, the speaker then explains to the audience that the cause of this problem is youth outside after 10:00 p.m. Lastly, the speaker provides the mandatory 10:00 p.m. curfew as a solution to the vandalism and violence problem within the community. The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution.
Psychological
A further way to organize your main ideas within a speech is through a psychological speech pattern in which “a” leads to “b” and “b” leads to “c.” This speech format is designed to follow a logical argument, so this format lends itself to persuasive speeches very easily. Let’s look at an example.
| Specific Purpose | To persuade a group of nurses to use humor in healing the person |
| Main Points | I. How laughing affects the body |
| II. How the bodily effects can help healing | |
| III. Strategies for using humor in healing |
In this speech, the speaker starts by discussing how humor affects the body. If a patient is exposed to humor (a), then the patient’s body actually physiologically responds in ways that help healing (b—e.g., reduces stress, decreases blood pressure, bolsters one’s immune system, etc.). Because of these benefits, nurses should engage in humor use that helps with healing (c).
Selecting an Organizational Pattern
Each of the preceding organizational patterns is potentially useful for organizing the main points of your speech. However, not all organizational patterns work for all speeches. For example, as we mentioned earlier, the biographical pattern is useful when you are telling the story of someone’s life. Some other patterns, particularly comparison/contrast, problem-cause-solution, and psychological, are well suited for persuasive speaking. Your challenge is to choose the best pattern for the particular speech you are giving.
You will want to be aware that it is also possible to combine two or more organizational patterns to meet the goals of a specific speech. For example, you might wish to discuss a problem and then compare/contrast several different possible solutions for the audience. Such a speech would thus be combining elements of the comparison/contrast and problem-cause-solution patterns. When considering which organizational pattern to use, you need to keep in mind your specific purpose as well as your audience and the actual speech material itself to decide which pattern you think will work best.
Key Takeaway
- Speakers can use a variety of different organizational patterns, including categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological. Ultimately, speakers must really think about which organizational pattern best suits a specific speech topic.
- Imagine that you are giving an informative speech about your favorite book. Which organizational pattern do you think would be most useful? Why? Would your answer be different if your speech goal were persuasive? Why or why not?
- Working on your own or with a partner, develop three main points for a speech designed to persuade college students to attend your university. Work through the preceding organizational patterns and see which ones would be possible choices for your speech. Which organizational pattern seems to be the best choice? Why?
- Use one of the common organizational patterns to create three main points for your next speech.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 10: Persuasive Speaking
Structure of a persuasive speech, learning objectives.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of an informative speech is to explain whereas the primary purpose of a persuasive speech is to advocate the audience adopt a point of view or take a course of action. A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence.
We can classify persuasive speeches into three broad categories:
- The widely used pesticide Atrazine is extremely harmful to amphibians.
- All house-cats should be kept indoors to protect the songbird population.
- Offshore tax havens, while legal, are immoral and unpatriotic .
The organizational pattern we select and the type of supporting material we use should support the overall argument we are making.
The informative speech organizational patterns we covered earlier can work for a persuasive speech as well. In addition, the following organization patterns are especially suited to persuasive speeches (these are covered in more detail in Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech):
- Causal : Also known as cause-effect, the causal pattern describes some cause and then identifies what effects resulted from the cause. This can be a useful pattern to use when you are speaking about the positive or negative consequences of taking a particular action.
- Problem-solution : With this organizational pattern, you provide two main points. The first main point focuses on a problem that exists and the second details your proposed solution to the problem. This is an especially good organization pattern for speeches arguing for policy changes.
- Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then explains the causes of the problem, and lastly proposes a solution to the problem.
- Comparative advantage : A speaker compares two or more things or ideas and explains why one of the things or ideas has more advantages or is better than the other.
- Monroe’s motivated sequence : An organizational pattern that is a more elaborate variation of the problem-cause-solution pattern. We’ll go into more depth on Monroe’s motivated sequence on the next page.
- Structure of a Persuasive Speech. Authored by : Mike Randolph with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


48 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, Problem-Solution, Comparative Advantages
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.
Organizing Persuasive Speeches

Previously in this text, we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Below are the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
| Steps | Audience Response |
|---|---|
| —Getting Attention | I want to listen to the speaker. |
| —Showing the Need, Describing the Problem | Something needs to be done about the problem. |
| —Satisfying the Need, Presenting the Solution | In order to satisfy the need or fix the problem this is what I need to do. |
| —Visualizing the Results | I can see myself enjoying the benefits of taking action. |
| —Requesting Audience Action or Approval | I will act in a specific way or approve a decision or behavior. |
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed, a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic. If this sounds familiar, it should! The attention step uses the same elements as an introduction for any speech: The attention getter, relevance, credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. This will be your first main point. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.

Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. This will be your second main point. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker responds to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. This will be your third main point. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break the action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
This step will be your conclusion. Again, it will have the same elements as a conclusion you would use for any speech.
Application
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Below is a checklist that contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
| Step in the Sequence | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
| Gained audience’s attention | □ | □ |
| Introduced the topic clearly | □ | □ |
| Showed the importance of the topic to the audience | □ | □ |
| Need is summarized in a clear statement | □ | □ |
| Need is adequately illustrated | □ | □ |
| Need has clear ramifications | □ | □ |
| Need clearly points the audience | □ | □ |
| Plan is clearly stated | □ | □ |
| Plan is plainly explained | □ | □ |
| Plan and solution are theoretically demonstrated | □ | □ |
| Plan has clear reference to practical experience | □ | □ |
| Plan can meet possible objections | □ | □ |
| Practicality of plan shown | □ | □ |
| Benefits of plan are tangible | □ | □ |
| Benefits of plan relate to the audience | □ | □ |
| Specific type of visualization chosen (positive method, negative method, method of contrast) | □ | □ |
| Call of specific action by the audience | □ | □ |
| Action is realistic for the audience | □ | □ |
| Concluding device is vivid | □ | □ |
The following video further details Monroe’s Motivated Sequence outlining each component and providing examples to provide an in-depth understanding of the organizational pattern.
For Future Reference | How to organize this in an outline |
Introduction: Attention Step
Main Point #1: Need Step
Main Point #2: Satisfaction Step
Main Point #3: Visualization Step
Conclusoin: Action Step
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
- Presentations
- Public Speaking
How to Make More Persuasive Speeches: Topics, Outlines, and Great Examples
A persuasive speech aims to inform, educate, and convince the audience on a topic or action. You want to convince the audience of your viewpoint. The best persuasive speeches are thought-provoking and clear.

When choosing a topic for your persuasive speech, choose one that you already have some knowledge of and an opinion on. You’ll need to be able to argue your topic and stand behind your points. Not only will you need to know your own opinion, but you'll be able to discuss the opposite viewpoint accurately.
This article will look at the different types of persuasive speech to help you choose the right one. We’ll also look at tips on what makes a good persuasive speech. Also, some persuasive speech topics that'll help you get started.
Different Types of Persuasive Speech
There are several different organizational structures for persuasive speeches. They include:
- Problem-solution
- Problem-cause-solution
- Comparison/contrast
Each type of speech has a different purpose and a unique structure. For example, a causal speech explains what happens as a result of a cause. (Source: bizfluent ). A comparative advantage speech examines two or more things and explains why some are better than others. (Source: Virtual Speech Coach )
Problem-solution speeches and problem-cause-solution speeches are related. In a problem-solution speech you present a problem followed by the solution to that problem. The problem-cause-solution speech is basically the same, except it examines the cause of the problem before presenting the solution. (Source: popsOpenText )
11 Tips on How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Writing a persuasive speech can be difficult. You want your persuasive speech to be successful in persuading the audience. Here are 11 tips to help you write a successful speech:
1. Choose the Right Topic

When looking at ideas for persuasive speech topics, it’s important to have a speech that's interesting to your audience and you. Also, consider whether your topic is appropriate for your audience. Choose a topic your audience would be interested in.
For example, if you're giving a speech to a dentist, then a persuasive speech on how brushing your teeth isn’t essential wouldn’t be appropriate. But an audience of dentists might be interested in the benefits of mouthwash.
2. Write How You Talk
Part of writing a persuasive speech is creating a persuasive speech outline and writing out your speech. As you're writing out your speech, consider writing how you talk. This means using short words and sentences.
Avoid any sentence that would cause you to stumble when speaking. A speech is meant to be spoken, not read off a sheet of paper. If you don’t have much experience in writing how you talk or aren’t confident, try reading the sentence aloud as you're writing. This will give you an idea of how easy your speech is to read, and it'll flow better.
3. Start Strong

Start your persuasive speech strong by letting your audience know what topic you're discussing, why your topic matters, and what you hope to convince them to do your speech. There are several ways to start strong.
- Grab their attention . This is a statement or visual that grabs your audience’s attention.
- Connect to the audience . This is where you show your connection to the audience, whether it’s a similar background or an emotional connection.
- Show evidence . This is where you show your knowledge or authority on the subject of your speech to your audience. Plus, you can highlight your research or professional experience.
- Share your goal . Explain what you hope the speech will accomplish for your audience.
4. Tell a Story
A good speech tells a story. A persuasive speech's story should tell the problem, cause, and solution. Having those essential elements makes your speech more persuasive than if it didn’t have them.
If you want to connect with your audience an excellent way to do that's to tell a relevant story about the topic you’re discussing. Sometimes a good story has more power than facts and statistics.
5. Structure

Figuring out your persuasive speech outline structure is challenging, but it's an important step. Sort your facts and points so they'll impact your audience. Your speech will be more persuasive if it's logical and clear.
A structured speech is your way of navigating your audience through your topic. Without structure, you could end up with a scattered, unprofessional speech that leaves the audience confused.
6. Be Concise
It can be harder to create a concise, persuasive speech than one that isn’t. Being concise is important. Giving your audience too much information makes it difficult for them to know what information is essential. Being concise makes managing your audience’s attention and focus easier.
7. Research Your Topic

When writing your persuasive speech, it’s essential to research your topic. Research shows your audience that you're creditable and did your research. This makes your speech more persuasive.
Remember, when finding persuasive speech topic sources, you must ensure that your sources are relevant. Some examples of relevant sources are:
- official documents
- online academic references
Using professional sources shows the audience that your points are creditable. Also, the main point of your persuasive speech topic should be able to be backed up by logical evidence that'll support your claims.
8. Discuss Counter-Arguments
When planning your persuasive speech topic, consider adding a counter-argument to your speech. Adding a counterargument will increase your creditability. Also, by discussing the counterargument, you'll have the chance to argue the point directly.
But, when debating the counterargument, make it a short discussion and free of bias and language that's angry, hostile, or passionate. If you present the counterargument with bias or angry language, the audience may think you aren't creditable and stop listening.
9. Authenticity

When considering your persuasive speech ideas , choosing a topic you believe in is best. Selecting an issue you believe in allows you to write your speech more easily. You’ll also easily convince the audience if you believe in your topic. If you want to connect to your audience, tell a story about why you believe in your persuasive speech topic.
10. Write it Well
When writing your speech, you must ensure that you do it well. Writing an excellent persuasive speech can be difficult, but it's rewarding to see the reaction to your speech. A good persuasive speech is thought-provoking, daring, and precise. Know and objectively state counterpoints.
11. Have a Call to Action

Use a call to action when creating your persuasive speech outline. Your audience can become committed to the action you’re calling them to and will become more persuaded.
20 Interesting Persuasive Speech Topics
One essential tip for creating a good persuasive speech is to have an interesting persuasive speech topic . When choosing your speech topic, you must have your audience in mind. Ask yourself:
- Would my audience be interested in this persuasive speech idea ?
- Is the topic appropriate for my audience?
- Would my audience benefit from the topic?
When you're considering what your speech topic should be, keep those questions in mind. Here are some topics to write a persuasive speech on :
- Is graffiti art?
- Which is better, paper books or e-books?
- Should interns be paid for work?
- Should the federal minimum wage be raised?
- Should cursive still be taught in schools
- Should college athletes be paid for being on a sports team?
- Should schools teach all children how to swim?
- Should schools teach high school students how to pay taxes?
- Do Robots help or hurt humanity?
- Should libraries be given unlimited access to e-books?
- Does technology isolate people?
- Should students get paid for having a high GPA?
- Should students who bully others be expelled and have a permanent mark on their permanent record?
- Are students wearing uniforms beneficial?
- Would it be beneficial for schools to require a foreign language?
- Should Black Fridays be banned?
- Should gym classes affect a student’s GPA?
- Are genetically modified foods harmful?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should Pluto be considered a planet?
Learn More About Making a Speech
Do you want to learn more about creating a speech? Here are some helpful articles:
.jpg)
The Best Source for Digital Assets for Persuasive Speeches
If you're using a presentation as a part of your speech, you'll most likely use digital creative assets. Examples of digital assets that could really help your persuasive presentation include:
- stock images
- PowerPoint presentation templates
All the digital elements are created by professionals, which means they're high quality.

Here's how you can have access to premium creative assets:
Envato Elements . It’s a subscription service with unlimited access to premium digital elements. If you pay a low monthly fee and subscribe , you'll have access to an Envato Elements subscription. It’s the best value for anyone who will need these digital elements.
Choose a Persuasive Speech Topic Today!
Now that you’ve read tips on making a good persuasive speech, use them when writing your next speech. If you're using a presentation when you’re giving your speech, try using a premium presentation template from Envato Elements. We’ve given you the tools to write a good speech. Now it’s up to you to use them. Good Luck!
Editorial Note: This content was originally published in June 2022. We're sharing it again because our editors have determined that this information is still accurate and relevant.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 3: Preparing for Your First Speech
Patterns of Organization: Persuasive Speeches
Cause/effect pattern.
If the specific purpose mentions words such as “causes,” “origins,” “roots of,” “foundations,” “basis,” “grounds,” or “source,” it is a causal order; if it mentions words such as “effects,” “results,” “outcomes,” “consequences,” or “products,” it is effect order. If it mentions both, it would of course be cause/effect order. This example shows a cause/effect pattern:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the causes and effects of schizophrenia.
I. Schizophrenia has genetic, social, and environmental causes.
II. Schizophrenia has educational, relational, and medical effects. It should be noted, however, that a specific purpose like this example is very broad and probably not practical for your class speeches; it would be better to focus on just causes or effects, or even just one type of cause
(such as genetic causes of schizophrenia) or one type of effect (relational or social). These two examples show a speech that deals with causes only and effects only, respectively.
Specific Purpose: To explain to my fellow Biology 1107 students the origin of the Ebola epidemic in Africa in 2014.
I. The outbreak began in March 2014 in Guinea with the death of one-year-old child who played in a tree with infected bats.
II. The virus next spread to Sierra Leone and Liberia.
III. In Fall of 2014 it spread to the U.S. and Europe by travelers from Liberia.
Specific Purpose: To describe to my classmates the effects of a diagnosis of autism on a child’s life.
I. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s educational plan.
II. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s social existence.
III. An autism diagnosis will affect the child’s family relationships.
Problem-Solution Pattern
The problem-solution pattern will be explored in more depth in the chapter on Persuasive Speaking because that is where it is used the most. Then, we will see that there are variations on it. The principle behind problem-solution pattern is that if you explain a problem to an audience, you should not leave them hanging without solutions. Problems are discussed for understanding and to do something about them.
Additionally, when you want to persuade someone to act, the first reason is usually that something is wrong! Even if you wanted your friends to go out to get some dinner, and they have recently eaten, you will probably be less successful because there is no problem for them—they are not hungry. Then you would have to come up with a new problem, such as you will miss their presence, which they may or may not see as a problem for them.
In another real-life example, let’s say you want the members of the school board to provide more funds for music at the three local high schools in your county. What is missing because music or arts are not funded? What is the problem ?
Specific Purpose: To persuade the members of the school board to take action to support the music program at the school.
I. There is a problem with eliminating extracurricular music pro- grams in high schools.
A. Students who do not have extracurricular music in their lives have lower SAT scores.
B. Schools that do not have extracurricular music programs have more gang violence and juvenile delinquency.
II. The solution is to provide $200,000 in the budget to sustain extra- curricular music in our high schools.
A. $120,000 would go to bands.
B. $80,000 would go to choral programs.
Of course, this is a simple outline and you would need to provide evidence to support the arguments, but it shows how problem-solution works.
Psychologically, it makes more sense to use problem-solution rather than solution-problem. The audience will be more motivated to listen if you address needs, deficiencies, or problems in their lives rather than giving them solutions first.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
A variation of the problem-solution pattern, and one that sometimes re- quires more in-depth exploration of an issue, is the “problem-cause-solution” pattern. If you were giving a speech on future extinction of certain animal species, it would be insufficient to just explain that numbers of species are about to become extinct. Your second point would logically have to explain the cause behind this happening. Is it due to climate change, some type of pollution, encroachment on habitats, disease, or some other rea- son? In many cases, you can’t really solve a problem without first identify- ing what caused the problem. This is similar to the organizational pattern called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence (German, Gronbeck, Ehninger & Monroe, 2012), which will be fully explained in Chapter 13. The Mon-
roe’s Motivated Sequence requires a discussion of cause to create a logical speech.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the age to obtain a driver’s license in the state of Georgia should be raised to 18.
I. There is a problem in this country with young drivers getting into serious automobile accidents leading to many preventable deaths.
II. One of the primary causes of this is younger drivers’ inability to remain focused and make good decisions due to incomplete brain development.
III. One solution that will help reduce the number of young drivers involved in accidents would be to raise the age for obtaining a driver’s license to 18.
Some Additional Principles of Organization
It is possible that you may use more than one of these organizational pat- terns within a single speech. For example, the main points of your speech could be one organizational pattern and the subpoints a different one. In the spatial example above about the Native American nations of Georgia, the subpoints might be chronological (emphasizing their development over time), or they could be topical (explaining aspects of their culture).
You should also note that in all of the examples to this point (which have been kept simple for the purpose of explanation), each main point is relatively equal in emphasis; therefore, the time spent on each should be equal as well. While you are not obliged to spend exactly the same amount of time on each main point, the time spent (and the importance of the main point) should be about the same. You would not want your first Main Point to be 30 seconds long, the second one to be 90 seconds, and the third 3 minutes. For example:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the rules of baseball.
I. Baseball has rules about equipment.
II. Baseball has rules about numbers of players.
III. Baseball has rules about play.
Main Point II is not really equal in importance to the other two. There is a great deal you could say about the equipment and even more about the rules of play, but the number of players would take you about ten seconds to say. If Main Point II were “Baseball has rules about the positions on the field,” that would make more sense and be closer in level of importance to the other two.
To give another example, let’s say you want to give a commemorative (or tribute) speech about a local veteran whom you admire.
I. James Owens is an admirable person because he earned the Silver Star in the Korean War.
II. James Owens is an admirable person because he served our com- munity as a councilman for 25 years.
III. James Owens is an admirable person because he rescued five pup- pies that were abandoned in his backyard.
Although Main Point III is a good thing to do, it’s really not equal to Main Points I and II in importance or in the amount of time you would need to spend on it.
Earlier in the chapter, we said that organizing a speech involves grouping, labeling, and ordering. Let’s address labeling here . You will also notice that in most of the examples so far, the main points are phrased using a similar sentence structure. For example, “The first chamber in the blood flow is…” “The second chamber in the blood flow is…” This simple repetition of sentence structure is called parallelism , a technique useful for speakers and helpful for the audience in remembering information. It is not absolutely necessary to use it and will not always be relevant, but par- allelism should be used when appropriate and effective.
In relation to the way each main point is written, notice that they are full grammatical sentences, although sometimes short and simple. For purposes of preparation, this is a good habit, and your instructor will probably require you to write your main points in full sentences. Your instructor may also expect you to write your subpoints in complete sentences as well, but he or she will discuss that with you.
Finally, in the way you phrase the main points, be sure they are adequate labeled and clearly explain your content. Students are often tempted to write main points as directions to themselves, “Talking about the health department” or “Mention the solution.” This is not helpful for you, nor will your instructor be able to tell what you mean by those phrases. “The health department provides many services for low-income residents” says something we can all understand.
We have included examples of outlines at the ends of chapters 12, 13, and We have tried to give examples of different kinds of formats, but individual instructors prefer specific format for outlines. Your instructor should give you examples of how they want the outline to be developed and for- matted, and you should follow their directions.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Thinking strategies and writing patterns, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Patterns for Presenting Information
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
According to conventional wisdom, you can summarize every story ever told in the following way: someone falls into a hole and must climb out. In other words, every story is about solving a problem. There are probably many exceptions to this observation; however, connecting the need to solve a real-life problem to your subject can draw your readers’ attention. The problem-cause-solution pattern can help you do this.

In a sense, this pattern is a variety of the specific-to-general pattern, as it often begins with specific details and moves to a somewhat generalized solution. However, rather than evoking a sense of mystery and suspense, the problem-cause-solution pattern focuses on concrete difficulties; and though a solution may appeal to abstract principles, the solution should have a practical application, enough to solve the real-life problem.
When to Use this Pattern
You may find the problem-cause-solution pattern useful in writing case studies, critiques, introductions, reports of scientific investigations, literary reviews, political and social discourse, white papers, proposals, many kinds of reports, and essay examinations.
How to Create this Pattern
The name of the problem-cause-solution pattern also describes the sequence in which to present your information.
Begin by describing the problem.
Proceed through diagnosing and analyzing the problem.
Then propose a solution.
The forms of analysis used to diagnose the problem may vary. You might, for example, use comparative analysis to evaluate for flaws in a process that may have led to the problem. You might use a combination of synthesis and cause and effect analysis to locate systemic conditions which caused the problem. However, in each instance—whether analyzing an entire process or analyzing a specific cause—the goal is to locate a cause or causes.
Example of this Pattern
There are two main kinds of ice that shape sea levels. The first is sea ice, which comes from ocean water that freezes solid. It makes up most of the ice at the North Pole. As it forms, it changes the saltiness of seawater and helps shape powerful ocean currents.
Melting sea ice doesn’t change the overall amount of water in the ocean, just as melting ice cubes don’t change the water level in a glass of water. But sea ice tends to reflect sunlight, while the darker ocean tends to soak up its heat. That speeds up warming and drives more ice melt in a worrying feedback loop. The warmer temperatures also contribute to the thermal expansion of water, which in turn can raise sea levels.
The second kind of ice is land ice, which builds up in sheets over thousands of years from compacted snow. In Antarctica, the ice sheet is 1.5 miles thick (2.4 km) on average, reaching up to 3 miles (5 km) in some areas. Greenland’s ice sheet averages a mile in thickness. When land ice starts to jut out over the ocean, it creates a floating ice shelf (Irfan, 2022, paras. 9-11).
Example Explained
Notice how the passage above begins with an implied problem: ice causing changes to sea levels. The passage proceeds to explain the causes of changing sea levels. These are the first two parts of our pattern. A few paragraphs later, the author shifts to discussing the beginnings of a solution.
Key Takeaways
- The problem-cause-solution approach will first describe the problem, then analyze the cause or responses to the problem, and then will lead to a solution.
- We practice this approach daily in our interactions with others, whether at work or home.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

17.3 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole.” German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods. Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138. We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table 17.1 "Monroe’s Motivated Sequence" lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table 17.1 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
| Steps | Audience Response |
|---|---|
| —Getting Attention | I want to listen to the speaker. |
| —Showing the Need, Describing the Problem | Something needs to be done about the problem. |
| —Satisfying the Need, Presenting the Solution | In order to satisfy the need or fix the problem this is what I need to do. |
| —Visualizing the Results | I can see myself enjoying the benefits of taking action. |
| —Requesting Audience Action or Approval | I will act in a specific way or approve a decision or behavior. |
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step First step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker attempts to get his or her audience’s attention. , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 "Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively" , a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step Second step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step Third step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step Fourth step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker asks his or her audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast. Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman. The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step Fifth step in Monroe’s motivated sequence where a speaker asks for an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table 17.2 "Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist" also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table 17.2 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
| Step in the Sequence | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
| Gained audience’s attention | □ | □ |
| Introduced the topic clearly | □ | □ |
| Showed the importance of the topic to the audience | □ | □ |
| Need is summarized in a clear statement | □ | □ |
| Need is adequately illustrated | □ | □ |
| Need has clear ramifications | □ | □ |
| Need clearly points the audience | □ | □ |
| Plan is clearly stated | □ | □ |
| Plan is plainly explained | □ | □ |
| Plan and solution are theoretically demonstrated | □ | □ |
| Plan has clear reference to practical experience | □ | □ |
| Plan can meet possible objections | □ | □ |
| Practicality of plan shown | □ | □ |
| Benefits of plan are tangible | □ | □ |
| Benefits of plan relate to the audience | □ | □ |
| Specific type of visualization chosen (positive method, negative method, method of contrast) | □ | □ |
| Call of specific action by the audience | □ | □ |
| Action is realistic for the audience | □ | □ |
| Concluding device is vivid | □ | □ |
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.
Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
- Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.

COMMENTS
Thesis Statement: The thesis typically lays out the problem and solution in the form of a question and answer. See examples below. Solution: Explain the solution clearly and in detail, your problem-solving strategy, and reasons why your solution will work.In this section, be sure to answer common objections, such as "there is a better solution," "your solution is too costly," and ...
Here are some tips to keep in mind as you prepare your problem-solution speech: Be passionate: This is not the time for a dry, academic approach. You need to be enthusiastic about the issue at hand and really sell your audience on why they should care. Be clear: Make sure that your audience understands the problem and potential solutions.
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
Our experts have been working with problem solution topics for more than five years. That is why we asked them to compose a list of good topics examples. We divided them into seven most frequently used categories so that you will find the necessary one. 1. Economics and finances.
Problem Cause Solution Speech Topics. Problem-cause-solution speech is a very effective way to persuade your audience that you are a reliable expert. It requires you to analyze the causes of the issue in detail and come up with the best solution! The leading causes of binge drinking on college campuses and the ways to eliminate it.
Examples and Breakdown: Detailed examples of how to develop a problem-solution speech, including how to identify the problem, ... The list of problem-cause solution persuasive speech topics provided below will help you come up with interesting research ideas for your speech. Take a look at the numerous options for social issues and other ...
Problem-Cause-Solution Speech Outline. Sally Star. Financial Illiteracy Among College Students. To persuade. To persuade myclassmates that all college students should be required to. take a financial literacy course before graduating. aduate without basic financial literacy, andthis is because o.
Below are thirty problem solution persuasive speech topics to help you get started. 1. The problems with plastic surgery and how to fix them. 2. The rise of eating disorders and what can be done about it. 3. Why there needs to be more education on mental health and how to prevent suicide. 4.
The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution. Psychological A further way to organize your main ideas within a speech is through a psychological speech pattern in which "a" leads to "b" and "b" leads to ...
A. Cardiovascular disease, the nation's leading cause of death, is caused by inactivity. 1. Clogged arteries and veins are a result of inactivity. (example) 2. Excess fat also caused by inactivity leads to a higher incidence of heart disease. (Statistically, then, you will die at an earlier age if you do not exercise.)
A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence. ... Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then ...
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.
Persuasive Speech Outline: Problem-Cause-Solution Format I. Introduction: A. Attention Getter: B. Audience Relevance: C. Credibility: D. Thesis and Preview:
Problem-solution; Problem-cause-solution; Comparison/contrast; Each type of speech has a different purpose and a unique structure. For example, a causal speech explains what happens as a result of a cause. (Source: bizfluent). A comparative advantage speech examines two or more things and explains why some are better than others.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern. A variation of the problem-solution pattern, and one that sometimes re- quires more in-depth exploration of an issue, is the "problem-cause-solution" pattern. If you were giving a speech on future extinction of certain animal species, it would be insufficient to just explain that numbers of species are about ...
The problem-cause-solution approach will first describe the problem, then analyze the cause or responses to the problem, and then will lead to a solution. We practice this approach daily in our interactions with others, whether at work or home. Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783.
The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution. While these two patterns are recognized as persuasive speech patterns, you can use any organizational pattern to structure your argument.
Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker's persuasive proposal. The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem.